You searched for: 余额宝理财系统搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建余额宝理财系统搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建1tVO4utgRM
<< Previous | Displaying results 251-300 of 652 for "余额宝理财系统搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建余额宝理财系统搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建1tVO4utgRM" | Next >>
-
The judges at the Doctors Trial
PhotoAmerican judges (top row, seated) during the Doctors Trial, case #1 of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings. Presiding Judge Walter B. Beals is seated second from the left. Nuremberg, Germany, December 9, 1946–August 20, 1947.

-
View of a criminal wing in the prison at Nuremberg
PhotoView of a criminal wing in the prison at Nuremberg, housing war crimes trials defendants. Baltic guards under the supervision of American authorities patrol the wing and keep constant watch over the prisoners. The upper floors are screened off with heavy chicken wire to discourage suicide attempts. Nuremberg, Germany, between November 20, 1945, and October 1, 1946.

-
Newspaper headlines about the sentences given at the International Military Tribunal
PhotoAn American correspondent reads a special edition of the Nürnberger newspaper reporting the sentences handed down by the International Military Tribunal. Nuremberg, Germany, October 1, 1946.

-
Defendant Fritz Sauckel
PhotoFritz Sauckel follows the proceedings of the International Military Tribunal trial of war criminals at Nuremberg. He was found guilty of war crimes and crimes against humanity and was sentenced to death. Photograph taken in Nuremberg, Germany, between November 20, 1945, and October 1, 1946.

-
Boycott of Jewish-owned businesses
PhotoMembers of the Storm Troopers (SA), with boycott signs, block the entrance to a Jewish-owned shop. One of the signs exhorts: "Germans! Defend yourselves! Don't buy from Jews!" Berlin, Germany, April 1, 1933.

-
Insignia of the 1st Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 1st Infantry Division. The 1st Infantry Division's nickname, the "Big Red One," originated from the division's insignia, a large red number "1" on a khaki field. This nickname was adopted during World War I, when the 1st was the first American division to arrive in France.

-
Ion Antonescu before his execution
PhotoFormer Romanian prime minister Ion Antonescu (center) before his execution as a war criminal. Fort Jivava, near Bucharest, Romania, June 1, 1946.

-
Aliyah Bet ("illegal" immigration) ship Tiger Hill
PhotoAliyah Bet ("illegal" immigration) ship Tiger Hill, carrying Jewish refugees from Europe, lands in Tel Aviv, Palestine. Jewish residents of Palestine greet the ship. September 1, 1939.

-
Signing of the Tripartite Pact
PhotoBulgarian leader Bogdan Filov (standing) and German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop (seated, center) during the signing of the Tripartite Pact. This treaty formally aligned Bulgaria with the Axis powers. Vienna, Austria, March 1, 1941.

-
Liberated inmates of Dora-Mittelbau
PhotoLiberated inmates of the Dora-Mittelbau concentration camp, located near Nordhausen, view an area where camouflaged V-1 and V-2 rocket parts were stored. Germany, after April 11, 1945.

-
US delegation views an underground factory at Dora-Mittelbau
PhotoMembers of a US congressional committee investigating German atrocities view a V-2 rocket on the assembly line of an underground factory at the Dora-Mittelbau concentration camp, near Nordhausen. Germany, May 1, 1945.

-
Aftermath of pogrom in Iasi
PhotoRoma (Gypsies) remove bodies from the Iasi-Calarasi death train during its stop in Tirgu-Frumos. Two trains left Iasi on June 30, 1941, bearing survivors of the pogrom that took place in Iasi on June 28-29. Hundreds of Jews died on the transports aboard crowded, unventilated freight cars in the heat of summer. Romania, July 1, 1941.

-
Excerpts from the President's Commission Report
ArticleIn 1978, the President's Commission on the Holocaust was charged with submitting a report on the creation of a Holocaust memorial in the US. Read excerpts.

-
Law against the Founding of New Parties
ArticleThe Law against the Founding of New Parties proclaimed the Nazi Party as the only political party in Germany, which became a one-party dictatorship led by the Nazis.

-
Roma (Gypsies) in Prewar Europe
ArticleFor centuries, Roma (labeled “Gypsies”) were scorned across Europe. Read more about Romani peoples, including the Sinti, and their lives in Europe.

-
Ona Simaite, Joop Westerweel, Irena Sendler
ArticleLearn about the rescue activities and the fates of Ona Simaite in Lithuania, Joop Westerweel in the Netherlands, and Irena Sendler in Poland.

-
Fire Oaths
Article“Fire Oaths” were statements that declared why the works of certain authors were thrown into the flames during the 1933 burning of books under the Nazi regime.

-
Bad Reichenhall Displaced Persons Camp
ArticleAfter WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Bad Reichenhall DP camp.

-
Nazi officials and Catholic bishops listen to a speech by Wilhelm Frick
PhotoNazi officials and Catholic bishops listen to a speech by Wilhelm Frick, Reich Minister of the Interior, at an official ceremony in the Saarbrucken city hall marking the reincorporation of the Saarland into the German Reich. March 1, 1935. Among those pictured is Joseph Goebbels (seated at the far right), Franz Rudolf Bornewasser (Bishop of Trier) and Ludwig Sebastian (Bishop of Speyer).

-
The 800-meter race at the 1936 Olympic Games
PhotoRunners competing in the 800-meter race at the Olympic games in Berlin. In this photograph, American John Woodruff is just visible in the outside lane. He came from behind to win the race in 1:52.9 minutes. Source record ID: 95/73/12A.

-
Britain and France Declare War
Timeline EventSeptember 3, 1939. On this date, Great Britain and France declared war on Germany after the German invasion of Poland.

-
Adolf Hitler passes through the Brandenburg Gate on his way to the opening ceremonies of the Olympic Games
PhotoAdolf Hitler passes through the Brandenburg Gate on the way to the opening ceremonies of the Olympic Games. Berlin, Germany, August 1, 1936.

-
Albert Speer standing in the defendants' dock at Nuremberg
PhotoThe defendants and their lawyers at the International Military Tribunal trial of war criminals at Nuremberg. Defendant Albert Speer (standing at right) delivers a statement in the dock. Nuremberg, Germany, November 20, 1945-October 1, 1946.

-
Destruction in Warsaw
PhotoFollowing the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Warsaw suffered heavy air attacks and artillery bombardment. German troops entered the city on September 29, shortly after its surrender. This photograph was taken by Julien Bryan, an American documentary filmmaker who captured the German bombardment and its impact on the Polish citizenry. Warsaw, Poland, ca. 1939.

-
Portrait of writer Sigrid Undset
PhotoPortrait of writer Sigrid Undset, who won the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1928. Often with feminist themes, her novels were banned and burned in part because of her public criticism of the Nazi regime. Photo taken by Anders Beer Wilse on July 1, 1923.

-
Gisha Galina Bursztyn: Maps
Media EssayBorn to Jewish parents in Poland, Gisha Galina Bursztyn moved to the city of Warsaw after she married. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Warsaw fell four weeks later, and a ghetto was set up in November 1940. During a massive roundup i...
-

-
Chiune Sugihara
Media EssayChiune (Sempo) Sugihara (January 1, 1900-1986) was the first Japanese diplomat posted to Lithu...

-
Hoess affidavit
ArtifactAffidavit signed by Rudolf Hoess attesting to the gassing of Jews while he was the commandant of the Auschwitz killing center. The German text reads: "I declare herewith under oath that in the years 1941 to 1943 during my tenure in office as commandant of Auschwitz Concentration Camp 2 million Jews were put to death by gassing and a 1/2 million by other means. Rudolf Hoess. May 14, 1946." The confession is also signed by Josef Maier of the US Chief of Counsel's office. A photoreproduction of the original…

-
Lodz ghetto model
ArtifactLeon Jakubowicz, a shoemaker by training and a native of Lodz, began constructing this model of the Lodz ghetto soon after his arrival there from a prisoner-of-war camp in April 1940. The case holds a scale (1:5000) model of the ghetto, including streets, painted houses, bridges, churches, synagogue ruins, factories, cemeteries, and barbed wire around the ghetto edges. The model pieces are made from scrap wood. The case cover interior is lined with a collection of official seals, a ration card, and paper…

-
Model of the Lodz ghetto
ArtifactLeon Jakubowicz, a shoemaker by training and a native of Lodz, began constructing this model of the Lodz ghetto soon after his arrival there from a prisoner-of-war camp in April 1940. The case holds a scale (1:5000) model of the ghetto, including streets, painted houses, bridges, churches, synagogue ruins, factories, cemeteries, and barbed wire around the ghetto edges. The model pieces are made from scrap wood. The case cover interior is lined with a collection of official seals, a ration card, and paper…

-
Diagram of the “Gypsy camp” in Hodonín u Kunštátu
DocumentDiagram of the Hodonín u Kunštátu (Hodonin bei Kunstadt) camp in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (Czech Republic). Before it was converted into a Zigeunerlager (“Gypsy camp”) in 1942, it served as a penal labor camp. Translation of key: Scale 1:500 Sleeping quarters Sleeping quarters Mess-hall Infirmary Offices, prison Living quarters for guard staff Economic/Agricultural Building Latrine Well Mess-hall for guard staff Pens for guard dogs
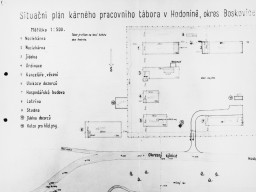
-
Scene during the opening of the 11th Summer Olympic Games
PhotoOn August 1, 1936, Hitler opened the 11th Summer Olympic Games. Inaugurating a new Olympic ritual, a lone runner arrived bearing a torch carried by relay from the site of the ancient Games in Olympia, Greece. This photograph shows an Olympic torch bearer running through Berlin, passing by the Brandenburg Gate, shortly before the opening ceremony. Berlin, Germany, July-August 1936.

-
SA members post anti-Jewish boycott signs
PhotoAn SA member instructs others where to post anti-Jewish boycott signs on a commercial street in Germany. A German civilian wearing a Nazi armband holds a sheaf of anti-Jewish boycott signs, while SA members paste them on a Jewish-owned business. Most of the signs read, "Germans defend yourselves against Jewish atrocity propaganda/Buy only at German stores." Germany, ca. April 1, 1933.

-
Auschwitz I camp, 1944
MapSelected Features 1. Camp Commandant's House 2. Main Guard House 3. Camp Administrative Office 4. Gestapo 5. Reception Building/Prisoner Registration 6. Kitchen 7. Gas Chamber and Crematorium 8. Storage Buildings and Workshops 9. Storage of Confiscated Belongings 10. Gravel Pit: Execution Site 11. Camp Orchestra Site 12. "Black Wall" Execution Site 13. Block 11: Punishment Bunker 14. Block 10: Medical Experiments 15. Gallows 16. Block Commander's Barracks 17. SS Hospital
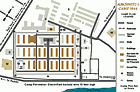
-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936: Inauguration of the Olympic Torch Relay
ArticleThe 1936 Olympics were the first to employ the torch relay. Learn more about this new ritual, Nazi propaganda, and the Olympic Games in Berlin, Germany.

-
Siege (1940)
ArticleJulien Bryan’s ten-minute film Siege, first non-Nazi produced footage of the start of WWII, records horror and chaos in Warsaw following the German invasion.

-
German Administration of Poland
ArticleGermany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Learn about the administrative units that Germany established after annexing and occupying parts of prewar Poland.

-
Danzig
ArticleHitler was determined to overturn the military and territorial provisions of the Versailles treaty, among it was much resented loss of the city of Danzig after WWI.

-
Encircling the Ruhr
ArticleEncircling the Ruhr region was a key Allied military goal. Learn about the military campaign to capture the industrial center of western Germany in the last months of WWII.

-
The Doctors Trial: The Medical Case of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings
ArticleThe Medical Case, or Doctors Trial, was Case #1 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Ben Hecht
ArticleAmerican-Jewish journalist and author Ben Hecht co-wrote the We Will Never Die pageant and advocated for the rescue of Jewish victims from Nazism. Learn more.
-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings
ArticleAmerican military tribunals presided over 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Anna Seghers
ArticleAnna Seghers was an influential, antifascist author. Her novel, in which she spoke out against social injustice, was burned in Nazi Germany in 1933. Learn more.
-

-
Prewar photo of the extended Kracowski family
PhotoThe Kracowski family was living in Bialystok when German Order Police Battalion 309 killed 2,000-3,000 Jews on June 27, 1941. Dr. Samuel Kracowski was among the hundreds of Jews locked in the Great Synagogue and burned alive. After the Germans ordered the establishment of a ghetto in Bialystok, Samuel's wife, Esther, and children, Ewa and Julek, were given a room in the ghetto clinic. Photo dated September 1, 1935. Samuel and Esther are seated in the center, with Julek seated in the front row on the…
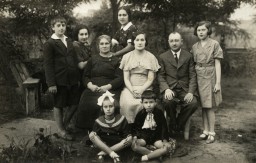
-
The 1st Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 1st Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating two subcamps of Flossenbürg in 1945.
-
The 99th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 99th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating subcamps of the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.
-
Axis Powers in World War II
ArticleThe three principal partners in the Axis alliance were Germany, Italy, and Japan. Learn more about the Axis powers in WW2.

-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936
ArticleThe 1936 Olympics in Berlin under Adolf Hitler's Nazi dictatorship were more than just a worldwide sporting event, they were also a show of Nazi propaganda.

