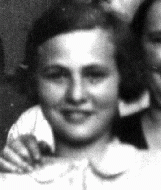You searched for: 公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建1wW6pnGvVO
<< Previous | Displaying results 401-450 of 652 for "公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建1wW6pnGvVO" | Next >>
-
History of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
ArticleThe United States Holocaust Memorial Museum opened in April 1993. Explore the history of the nation's memorial to the millions murdered during the Holocaust.

-
Corrie ten Boom
ArticleCorrie ten Boom was recognized as a Righteous Among the Nations for her efforts to shelter Jews during the German occupation of the Netherlands

-
Prisoners of the Camps
ArticleJews were the main targets of Nazi genocide. Learn about other individuals from a broad range of backgrounds who were imprisoned in the Nazi camp system.

-
1938: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of Nazi Germany during 1938.

-
Flossenbürg: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Flossenbürg camp in the Nazi camp system from its establishment in 1938 until liberation in 1945.

-
Foehrenwald Displaced Persons Camp
ArticleAfter WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Foehrenwald DP camp.

-
Wilhelm Keitel: Biography
ArticleField Marshal Wilhelm Keitel was commander of all German armed forces during World War II. Learn about his military career and postwar trial.

-
The Nuremberg Code
ArticleLeading German physicians and administrators were put on trial for their role during the Holocaust. The resulting Nuremberg Code was a landmark document on medical ethics. Learn more
-
Nazi Propaganda and Censorship
ArticleNazi efforts to control forms of communication through censorship and propaganda included control of publications, art, theater, music, movies, and radio.

-
Emanuel Ringelblum and the Creation of the Oneg Shabbat Archive
ArticleEmanuel Ringelblum was a Warsaw-based historian and social welfare worker before WWII. Learn about the secret archive he would establish in the Warsaw ghetto.

-
Vittel
ArticleGerman authorities established the Vittel internment camp in occupied France in 1941. It belonged to the complex of POW camps designated Frontstalag 194.

-
Warsaw Polish Uprising
Timeline EventAugust 1, 1944. On this date, the Warsaw uprising began with the Polish Home Army rising against the Nazis in an attempt to liberate Warsaw.

-
Liberation of Ravensbrück
Timeline EventApril 30, 1945. On this date, Soviet forces arrived at Ravensbrück concentration camp in Germany.

-
Battle of the Somme
Timeline EventJuly 1, 1916. On this date, the most causalities in a single day during World War I occurred at the Battle of Somme.

-
Law on Alteration of Family and Personal Names
Timeline EventAugust 17, 1938. On this date, the German government issued the Executive Order on the Law on the Alteration of Family and Personal Names.

-
German Jews' Passports Declared Invalid
Timeline EventOctober 5, 1938. On this date, the Reich Ministry of the Interior invalidated all German Jews' passports and required them to have a "J" stamped on them.

-
Revision of Paragraph 175
Timeline EventJune 28, 1935. On this date, the German government revised Paragraphs 175 and 175a, facilitating the persecution of gay men and men accused of homosexuality.

-
Adolf Eichmann Found Guilty
Timeline EventDecember 15, 1961. On this date, Adolf Eichmann was found guilty of crimes against the Jewish people and sentenced to death.

-
The 42nd Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 42nd Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.
-
Collections Highlight: Auschwitz Through the Lens of the SS
ArticleKarl Höcker created a personal album of photographs chronicling SS officers’ activities at Auschwitz. Learn about this chilling collection.

-
Auschwitz Through the Lens of the SS: The Album
ArticleLearn about photographs contained in Karl Höcker’s album depicting official visits, ceremonies, and the social activities of the Auschwitz camp staff.

-
Katzenberger Case, March 13, 1942
ArticleThe Nuremberg Special Court ruled on the Katzenberger Race Defilement Case in 1942. Learn more about the outcome and impact of the case.
-
Herzogenbusch Main Camp (Vught)
ArticleThe Herzogenbusch concentration camp in the Netherlands began functioning in January 1943. Learn about its establishment, administration, prisoners, and conditions there.

-
What does war make possible?
Discussion QuestionPersecution of Jews and other targeted groups was already government policy in Germany once the Nazis were in power in 1933. But following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, war provided the opportunity and motivation for more ext...

-
The Farhud
ArticleThe Farhud (pogrom), an outbreak of mob violence against Baghdad Jewry in June 1941, was a turning point in the history of Jews in Iraq. Learn more
-
World War II: In Depth
ArticleGermany started World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, by invading Poland. War would continue until 1945. Learn more about key events in the history of WWII.

-
Deceiving the Public
ArticleThe Nazis frequently used propaganda to disguise their political aims and deceive the German and international public. Learn more.

-
Gusen
ArticleIn 1940, the Nazis established Gusen concentration camp. Learn more about camp conditions, forced labor, and liberation.

-
World War I and its Aftermath: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of World War I and its aftermath. Learn about the conflict and its divisive peace.

-
International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg
ArticleThe International Military Tribunal (IMT) opened in Nuremberg within months of Germany’s surrender. Learn about the judges, defendants, charges, and legacies.

-
Danuta Justyna
ID CardDanuta was born to Roman Catholic parents in the small industrial town of Piotrkow Trybunalski in central Poland. Her father and mother were school teachers. She and her younger sister, Maria, became friends with two Jewish girls, Sabina and Helena Szwarc. Although their houses were more than a mile apart, the girls often played together. 1933-39: Danuta was planning on attending college in September 1939, but on September 1 Germany invaded Poland. Four days later, German soldiers streamed into Danuta's…
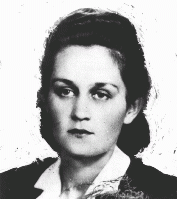
-
Kazimiera Banach Justynowa
ID CardKazimiera was born to Roman Catholic parents in the town of Mierzen. After graduating from a teacher's college in Staniatki, she married Wincenty Justyna, a secondary school teacher. The couple settled in the small industrial city of Piotrkow Trybunalski and raised three children, Jerzy (a boy), Danuta and Maria. Kazimiera worked as a school teacher. 1933-39: With their combined incomes the Justynas were able to buy a plot of land and build a house. The Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, and…

-
Maria Justyna
ID CardMaria was born to Roman Catholic parents in the industrial town of Piotrkow Trybunalski in central Poland. Her father and mother were school teachers. Maria attended grade school and secondary school in Piotrkow. She and her older sister, Danuta, became friends with two Jewish girls, Sabina and Helena Szwarc. Although their houses were more than a mile apart, the girls often played together. 1933-39: The Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, and occupied Piotrkow four days later. Most schooling for…

-
Yitzhak (Irving) Balsam
ID CardYitzhak was the second of four children born to religious Jewish parents. The family lived on the Polish-German border in Praszka, a small town where Yitzhak's father worked as a tailor. His work was not steady, and the family struggled to make ends meet. Yitzhak attended Polish public school in the mornings and Hebrew school in the afternoons. 1933-39: At 4 a.m. on September 1, 1939, the Balsams were awakened by an explosion. The Polish army had blown up the bridge over the Prosna River to impede the…

-
Hinda Chilewicz
ID CardHinda was the eldest of three children in a comfortable middle class Jewish family. Her father owned a textile business in Sosnowiec and her mother attended to the home. Sosnowiec in southwestern Poland had a growing Jewish community of almost 30,000 people. There was a Jewish hospital as well as religious schools. 1933–39: Hinda was just 13 years old when German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Three days later, they occupied Sosnowiec and terrorized the Jewish community, killing over a…

-
Moniek Rozen
ID CardOne of 12 children, Moniek grew up in Dabrowa Gornicza, an industrial town in western Poland. His father, Jacob, owned a general store, which he was forced to close in 1938 as the result of a boycott by local antisemites. Moniek attended both public and Jewish schools, and his father hoped that one day he would become a rabbi. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, Moniek was awakened by the sounds of airplanes flying overhead as German forces invaded Poland. As the war drew closer, Moniek fled eastward, but…

-
Tania Marcus
ID CardTania grew up in Smorgonie, a Polish town where Jews constituted more than half of the population. Her father was a successful businessman who sold farming equipment and purchased flax for export. Her grandfather, an affluent merchant, traveled frequently and brought the first truck to Smorgonie. The Marcuses took part in the town's vibrant Jewish culture, attended the theater, and hosted discussions about art in their home. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, German troops invaded Poland, triggering World…

-
Regina Gutman
ID CardRegina was born in Radom, a city that had 120,000 inhabitants. Her father worked as a leather cutter for a large shoe manufacturer and her mother took care of their six children. The Gutmans were very religious and Regina attended Hebrew school in the afternoons. Radom had a vibrant Jewish community of some 30,000 people, several Yiddish daily newspapers, and beautiful synagogues. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, the German army invaded Poland, and seven days later, Radom was occupied. Soon afterward, the…

-
Sam Spiegel
ID CardSam was the eldest of five children born to Jewish parents in Kozienice, a town in east central Poland. His father owned a shoe factory and his mother cared for the children and the home. Kozienice had a thriving Jewish community that made up about half of the town's population. 1933–39: On September 1, 1939, German troops invaded Poland. That morning the Spiegels heard an air raid siren blaring and quickly left their house. Fifteen minutes later a bomb struck the building. Sam was just 17 years old.…

-
Elzbieta Lusthaus
ID CardElzbieta grew up in Iwonicz, a resort town in southwestern Poland noted for its mineral water. Her father, Edmund, was a respected physician and Helena, her mother, had studied pharmacology. At home, they spoke Polish and were among the few Jewish families who lived in Iwonicz. 1933–39: When German troops invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Elzbieta's father was drafted into the Polish army. Seventeen days later, the Soviet army drove in from the east and Edmund was captured. He was transported to a…

-
Lisa Nussbaum
ID CardLisa was born to a Jewish family who lived in a town about three miles from the German border. Her family had lived there for generations. Lisa's father exported geese to Germany, and her mother owned a fabric store. The family lived with Lisa's grandmother in a large, single-level, gray stucco house. Lisa attended a small Hebrew school in Raczki. 1933-39: In 1937 Lisa transferred to a public school. One day, in fifth grade during recess, some boys grabbed her long blonde hair. Others joined in and pinned…

-
Urszula Kaczmarek
ID CardUrszula was one of four children born to Franciszek and Jadwiga Kaczmarek, who lived in the industrial city of Poznan in western Poland. The family lived at 11 Smolnej Street. Like their parents, the Kaczmarek children were baptized in the Roman Catholic faith. 1933-39: As one of the older children in the family, Urszula helped her mother with the housework. She was 10 years old when the Germans invaded Poland on Friday, September 1, 1939. German planes bombed Poznan that same day, and German troops…

-
Aaron Lejzerowicz
ID CardAaron was one of four children born to a Jewish family in the northeastern Polish town of Zdzieciol. His father was a shoemaker and, along with a business partner, he also ran a shoe store in the town. Aaron attended a private Jewish school, where he studied the Polish language and history as well as Jewish history and Hebrew. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Three weeks later, Poland was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union [under the German-Soviet Pact]. Aaron and his…

-
Paula Wajcman
ID CardPaula was raised in a religious Jewish family in Kielce, a city in the southeast of Poland. Her family lived in a modern two-story apartment complex. Paula's father owned the only trucking company in the district. Her older brother, Herman, attended religious school, while Paula attended public kindergarten in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. 1933-39: Paula's school uniform was a navy blazer with a white blouse and pleated skirt. At age 9, she did the "Krakowiak" dance at school. Boys…
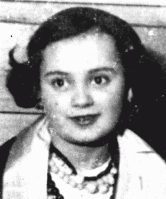
-
Jakob Frenkiel
ID CardJakob was one of seven boys in a religious Jewish family. They lived in a town 50 miles west of Warsaw called Gabin, where Jakob's father worked as a cap maker. Gabin had one of Poland's oldest synagogues, built of wood in 1710. Like most of Gabin's Jews, Jakob's family lived close to the synagogue. The family of nine occupied a one-room apartment on the top floor of a three-story building. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, just a few months before Jakob turned 10, the Germans started a war with Poland.…

-
Peter Somogyi
ID CardPeter and his twin brother, Thomas, were the youngest of three children born to an observant Jewish family. They lived in Pecs, an industrial center where goods such as bricks and ceramics were produced. Peter's father owned a prosperous business selling accessories and parts for cars, motorcycles and bicycles. He was also a regional sales representative for Ford automobiles. 1933-39: A German nanny took care of Peter, Thomas, and their older sister. She taught them German and they became quite fluent.…

-
Rachel Lejzerowicz Rechnitz
ID CardRachel, or Ruchla as she was called, was raised by Jewish parents in the small southwestern Polish town of Bedzin. In 1930 she moved with her husband, Bernard, to the nearby city of Katowice, where Bernard had a wholesale leather business. The couple lived with their two children, Moses and Genia, in a three-bedroom, upper-floor apartment on Jordana Street. 1933-39: Ruchla was active in Hadassah, a women's Zionist organization, and in 1939 she and her husband prepared to immigrate to Palestine [Aliyah…
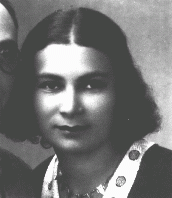
-
Feige Schwarzfink
ID CardFeige was born to a religious Jewish family in the small village of Szydlowiec [in Poland]. She lived with her parents, six brothers and sisters, and elderly grandparents in a small house which, like many homes in the village, had no running water, indoor plumbing, or electricity. Feige's father was a shoemaker. 1933-39: In the afternoons after public school Feige studied at a Jewish religious school. Although her parents didn't know it, she attended meetings of the Bund, the Jewish Socialist party. Feige…

-
Helena Manaster
ID CardHelena was the eighth of 10 children born to a Jewish family in the town of Lesko. Her father was a landowner. When Helena was a young girl the family moved to nearby Orelec, where they had a summer home. As there were no schools in Orelec, Helena and her siblings continued attending school in Lesko. Later, Helena traveled three hours by train daily to attend the nearest high school, which was in Przemysl. 1933-39: The German army invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. By the beginning of October the…
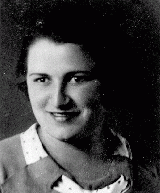
-
Celia Petranker
ID CardCelia was the youngest of three daughters born to Jewish parents living in Stanislav [Stanislawow], Poland. Her father was an ardent Zionist, and dreamed of moving his family to Palestine to help build a Jewish homeland. Celia and her sisters attended private Hebrew primary and secondary schools to help prepare them for their eventual immigration to Palestine. 1933-39: Celia's oldest sister, Pepka, left for Palestine one week after the Germans invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Pepka's departure was…