You searched for: 共享汽车系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建共享汽车系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建8hg3iTUBS4
<< Previous | Displaying results 51-100 of 250 for "共享汽车系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建共享汽车系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建8hg3iTUBS4" | Next >>
-
Defendant Paul Blobel pleads not guilty at the Einsatzgruppen Trial
PhotoOn September 15, 1947, defendant Paul Blobel pleads not guilty during his arraignment at the Einsatzgruppen Trial. Blobel was the commander of the unit responsible for the massacre at Babi Yar (near Kiev). He was convicted by the military tribunal at Nuremberg and sentenced to death. Blobel was hanged at the Landsberg prison on June 8, 1951.

-
Staff from the Hadamar euthanasia killing center
PhotoStaff from the Hadamar euthanasia center, including senior physician Adolf Wahlmann (front, left), during their trial. Wiesbaden, Germany, October 8-15, 1945.

-
Nazi leaders at the opening of an antisemitic exhibition
PhotoNazi district leader of Franconia Julius Streicher (right), propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels (second from right), and other Nazi officials attend the opening of the exhibition Der ewige Jude (The Eternal Jew). Munich, Germany, November 8, 1937.

-
Africa Corps commander Erwin Rommel
PhotoErwin Rommel (center), German commander of the Africa Corps, at an airfield in Libya during an Axis offensive into neighboring Egypt. British troops decisively defeated Rommel's forces at El Alamein. Libya, September 8, 1942.

-
World War II in Eastern Europe, 1942–1945
ArticleBefore 1942, Nazi Germany had expanded across much of Europe. Learn more about major Allied victories in eastern Europe that led to the German surrender.

-
Luxembourg
ArticleBefore WWII, over 3,500 Jews lived in Luxembourg. Under the German occupation, this community was almost completely destroyed. Learn more.

-
Fire Oaths
Article“Fire Oaths” were statements that declared why the works of certain authors were thrown into the flames during the 1933 burning of books under the Nazi regime.

-

-
Josef Stalin
ArticleJosef Stalin was the General Secretary of the Soviet Communist Party and the head of the Soviet state. His works were burned in Nazi Germany in 1933. Learn more.

-
German Order Police Battalion 101
PhotoA member of the German Order Police Battalion 101 stands next to a sign marking the entrance to the Lodz ghetto in German-occupied Poland, 1940–1941. The German text of the sign reads: "Announcement: In accordance with a police order of February 8, 1940, all Germans and Poles are forbidden entry into the ghetto area."

-
The "Final Solution"
SeriesThe Nazi “Final Solution to the Jewish Question” was the deliberate, planned mass murder of European Jews. Learn more about how the Nazis implemented the "Final Solution."
-
The Nazi Olympics Berlin 1936: African American Voices and "Jim Crow" America - Photos and Videos
Media Essay18 African Americans (16 men and 2 women) competed in the 1936 Olympic Games in Berlin. This was three times the number who had competed in the 1932 Los Angeles Games. The African American athletes on the 1936 US Olympic team brought home 14...

-
Fall of Warsaw
FilmGerman troops reached parts of Warsaw on September 8 and 9, 1939. During the German siege of Warsaw, the city sustained heavy damage from air attacks and artillery shelling. Warsaw surrendered on September 28. Here, German troops occupy Warsaw. This footage comes from "Tale of a City," a film made by a Polish underground film unit.

-
Sisters Eva and Liane Münzer
PhotoSisters Eva and Liane Münzer. They were placed in hiding with a devout Catholic couple. In 1944, Eva and Liane were reported to the police as a result of a fight between their rescuers. The husband denounced his wife and the two Jewish girls. The three were immediately arrested and sent to the Westerbork camp. On February 8, 1944, eight- and six-year-old Eva and Liane were deported to Auschwitz, where they were murdered. Photograph taken in The Hague, the Netherlands, 1940.

-
Auschwitz I camp, 1944
MapSelected Features 1. Camp Commandant's House 2. Main Guard House 3. Camp Administrative Office 4. Gestapo 5. Reception Building/Prisoner Registration 6. Kitchen 7. Gas Chamber and Crematorium 8. Storage Buildings and Workshops 9. Storage of Confiscated Belongings 10. Gravel Pit: Execution Site 11. Camp Orchestra Site 12. "Black Wall" Execution Site 13. Block 11: Punishment Bunker 14. Block 10: Medical Experiments 15. Gallows 16. Block Commander's Barracks 17. SS Hospital
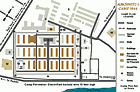
-
Portrait of Aron's family on his mother's side
PhotoPortrait of Aron's family on his mother's side, taken when Aron's cousin moved to Israel in 1933-1934. Aron is seated second from left, bottom row. His mother, Miriam, is in the center row, second from right. Aron's father is behind her and to her right. Aron himself was 8 or 9 years old when this picture was taken in either May or June. At the time, Aron recalled, "I was thinking about going to summer camp." Slonim, Poland, 1933-1934.

-
Third Reich: An Overview
ArticleThe Third Reich began with the Nazi rise to power in 1933 and ended with the German surrender in 1945. Learn more about Nazi Germany during World War II.

-
Norway
ArticleGermany invaded Norway on April 9, 1940. Read more about this invasion, the collaborator Vidkun Quisling, and the tragic fate of Norway’s Jews.

-
Sephardi Jews during the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the fate of Sephardi Jewish communities during the Holocaust. On the eve of WWII, Europe's Sephardi Jews lived mostly in the Balkan countries.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #6, The IG Farben Case
ArticleThe IG Farben Case was Case #6 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #7, The Hostage Case
ArticleThe Hostage Case was Case #7 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #10: The Krupp Case
ArticleThe Krupp Case was Case #10 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-

-
The 1st Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 1st Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating two subcamps of Flossenbürg in 1945.
-
The 89th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 89th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Ohrdruf subcamp of Buchenwald in 1945.

-
World War II: In Depth
ArticleGermany started World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, by invading Poland. War would continue until 1945. Learn more about key events in the history of WWII.

-
1941: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1941 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Boleslaw Brodecki
ID CardRaised by religious Jewish parents, Boleslaw and his older sister grew up in an apartment complex in a Jewish section of Warsaw. His father worked as an accountant. When Boleslaw was 8 years old, his mother died, and an aunt moved in to help raise him and his sister. Boleslaw loved electronics. When he was 10 years old, he succeeded in building a portable radio. 1933-39: The Germans attacked Warsaw on September 8, 1939. The bombing was relentless. Boleslaw's father wouldn't leave his ill relatives but…

-
Third Reich
ArticleThe “Third Reich” is another name for Nazi Germany between 1933-1945. Learn more about life under Nazi rule before and during World War II.

-
Fürstengrube
ArticleLearn about Fürstengrube subcamp of Auschwitz, including its establishment, administration, prisoner population, and forced labor and conditions in the camp.
-
Theresienstadt: Concentration/Transit Camp for German and Austrian Jews
ArticleLearn about the role of Theresienstadt in the deportation of German and Austrian Jews to killing sites and killing centers in the east.

-
Hitler Comes to Power
ArticleHitler rose to power during a time of economic and political instability in Germany. Learn more about how and when Hitler came to power.

-
German passport Issued to Erna "Sara" Schlesinger (inside)
DocumentGerman police authorities issued this passport to Erna "Sara" Schlesinger on July 8, 1939, in Berlin. This first page of the passport illustrates the German laws that facilitated the identification of Jews in Germany. From 1938, German regulations required that Jewish women with a first name of "non-Jewish" origin use the middle name "Sara" on all official documents. Jewish men had to add the name "Israel". The letter "J" (standing for "Jude," that is, the word "Jew" in German) was stamped in red on the…

-
100-meter race at the Olympic Games in Berlin, 1936
Film[This video is silent] Olympic athlete Jesse Owens won four medals at the 1936 Olympic Games in Berlin, Germany: 100-meter dash, gold200-meter dash, goldBroad (long) jump, gold4x100-meter relay, gold This footage shows Owens winning the 100-meter dash in a time of 10.3 seconds. Owens was one of the 18 African Americans (16 men and 2 women) who competed in the 1936 Olympic Games in Berlin. These athletes brought home 14 medals: 8 gold; 4 silver; and 2 bronze.

-
The Hadamar Trial
ArticleThe Hadamar Trial of October 1945 was the first mass atrocity trial held in the US occupation zone of Germany following World War II.

-
Karolina Dresler
ArticleChildren's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking experiences of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Karolina Dresler.

-
Trawniki: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Trawniki in German-occupied Poland.

-
World War II in the Pacific
ArticleThe United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941, following the attack on Pearl Harbor. Learn more about World War II in the Pacific.

-
Budapest
ArticleNazi Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944. Learn about the experiences and fate of Jews in Budapest, Hungary's capital, before and after the occupation.

-
Einsatzgruppen and other SS and Police Units in the Soviet Union
ArticleLearn more about how and why Nazi German SS and police units, including the Einsatzgruppen, perpetrated mass killings of Jews in the occupied-Soviet Union.

-
Lend-Lease
ArticleLearn more about the Lend-Lease Act, which was the American policy that extended material aid to the WWII Allied powers from 1941-1945.

-
Battle of the Bulge
ArticleThe Battle of the Bulge was a failed German counter-offensive against the Allied armies. Learn more about the Battle of the Bulge and its impact on WWII.

-
The Wannsee Conference and the "Final Solution"
ArticleThe Wannsee Conference was a high-level meeting of Nazi Party and German State officials to coordinate “the Final Solution of the Jewish Question.” Learn more.

-
At the Killing Centers
ArticleThe Nazis established killing centers in German-occupied Europe to mass murder Jews. Learn more about what happened to Jewish people at these killing centers.

-
Liberation: An Overview
ArticleLearn more about the end of Nazi tyranny in Europe and the liberation of camps and other sites of Nazi crimes. This article includes dates of liberation of some of the camps.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #11: The Ministries Case
ArticleThe Ministries Case was Case #11 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Bosnia
ArticleIn July 1995, Bosnian Serb forces killed as many as 8,000 Bosniaks from Srebrenica. It was the largest massacre in Europe since the Holocaust.

-
Charles Bedzow
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Charles Bedzow.

-
German Surrender
Timeline EventMay 7, 1945. On this date, German armed forces surrendered unconditionally to Allied forces in the west.

-
Beer Hall Putsch
Timeline EventNovember 9, 1923. On this date, Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party attempted to overthrow the Weimar Republic.

