You searched for: 抖音点赞系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建抖音点赞系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建3mlAWU9cIS
<< Previous | Displaying results 51-75 of 274 for "抖音点赞系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建抖音点赞系统源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建3mlAWU9cIS" | Next >>
-
Prisoners of the Camps
ArticleJews were the main targets of Nazi genocide. Learn about other individuals from a broad range of backgrounds who were imprisoned in the Nazi camp system.

-
1938: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of Nazi Germany during 1938.

-
1939: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1939 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Mohamed Helmy
ArticleDr. Mohamed Helmy and Frieda Szturmann helped save a Jewish family in the heart of Nazi Germany. Helmy was the first Arab recognized as Righteous Among the Nations.

-
Jewish Population of Europe in 1933: Population Data by Country - Photographs
Media EssayApproximately 9.5 million Jews lived in Europe in 1933, the year Hitler came to power. This number represented 1.7% of Europe's total population and more than 60 percent of the world's Jewish population. By 1945, most European Jews—2 out of every...
-
Moses Rechnitz: Maps
Media EssayMoses Rechnitz was born to Jewish parents in the Polish town of Bedzin on June 3, 1923. Moses was 16 years old when German troops invaded Poland in September 1939. By 1941, he was a slave laborer on a German railroad construction project outside o...
-
Boycott of Jewish Businesses - Photograph
Media EssayOn April 1, 1933—less than 3 months after rising to power—the Nazis staged a nationwide boycott of Jewish businesses. The boycott signaled the start of the Nazi movement to exclude Jews from all aspects of German society.
-
The Boycott of Jewish Businesses - Photograph
Media EssayOn April 1, 1933—less than 3 months after rising to power—the Nazis staged a nationwide boycott of Jewish businesses. The boycott signaled the start of the Nazi movement to exclude Jews from all aspects of German so...
-
Jewish Population of Europe
Media EssayApproximately 9.5 million Jews lived in Europe in 1933, the year Hitler came to power. This number represented 1.7% of Europe's total population and more than 60 percent of the world's Jewish population. By 1945, most European Jews—2 out of every 3—...
-
Portrait of David Kamchi and his wife Sara
PhotoPortrait of David Kamchi, son of Masliach Kamchi, and his wife Sara. They lived at Gostivarska 3 in Bitola. This photograph was one of the individual and family portraits of members of the Jewish community of Bitola, Macedonia, used by Bulgarian occupation authorities to register the Jewish population prior to its deportation in March 1943.

-
Police search a messenger for a Social Democratic newspaper
PhotoPolice search a messenger at the entrance to the building where Vorwaerts, a Social-Democratic Party newspaper, was published. The building was subsequently occupied during the suppression of the political left wing in Germany that was carried out in response to the Reichstag Fire. Berlin, Germany, March 3–4, 1933.

-
German troops marching into the Sudetenland stop at a former Czech frontier post
PhotoGerman troops marching into the Sudetenland stop at a former Czech frontier post. Nazi officials and Sudeten Germans salute the troops. The sign between the swastikas reads: "One People, One Reich, One Führer." Grottau, Czechoslovakia, October 2 or 3, 1938.

-
German soldiers guard Jews during deportation from the Zychlin ghetto
PhotoYoung German soldiers assist in the deportation of Jews from the Zychlin ghetto to the Chelmno killing center. The Nazis planned this deportation to fall on the Jewish holiday of Purim. Poland, March 3, 1942.

-
Erich Mühsam
PhotoIdentification picture of Erich Mühsam taken in the Oranienburg concentration camp. Mühsam, an anarchist and a pacifist, worked as an editor and writer; he was imprisoned during World War I for opposing the war. Arrested during the massive roundup of Nazi political opponents following the Reichstag fire (February 27, 1933), Mühsam was tortured to death in Oranienburg on July 11, 1934. Oranienburg, Germany, February 3, 1934.

-
Wedding portrait of former Bielski partisan, Berl Kagan
PhotoWedding portrait of former Bielski partisan, Berl Kagan. Emden, Germany, April 3, 1948. Pictured from left to right are Ita Rubin (the bride), her mother, Sarah Rubin, and Berl Kagan. All three were passengers on the Exodus 1947.

-
Soviet prisoners of war wait for rations
PhotoSoviet prisoners of war wait for food in Stalag (prison camp) 8C. More than 3 million Soviet soldiers died in German custody, mostly from malnutrition and exposure. Zagan, Poland, February 1942. Second only to the Jews, Soviet prisoners of war were the largest group of victims of Nazi racial policy.

-
The Netherlands
ArticleLearn more about the Netherlands during the Holocaust and the fate of Dutch Jews after the 1940 German invasion.

-
Fire Oaths
Article“Fire Oaths” were statements that declared why the works of certain authors were thrown into the flames during the 1933 burning of books under the Nazi regime.

-
The 103rd Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 103rd Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating a subcamp of Kaufering in 1945.
-
Mass grave for individuals murdered by the NKVD in Lvov prisons
PhotoA mass grave dug by Jewish forced laborers for the bodies of individuals murdered by the NKVD in Lvov prisons. The NKVD (Soviet secret police) murdered thousands of Ukrainian nationalists, as well as some Jews and Poles, before retreating from the Nazi invasion. The Germans and their Ukrainian collaborators then used the massacre as a pretext for anti-Jewish pogroms, claiming that the Jews had helped the secret police. Lvov, Poland, July 3, 1941.

-
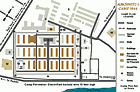
Auschwitz I camp, 1944
MapSelected Features 1. Camp Commandant's House 2. Main Guard House 3. Camp Administrative Office 4. Gestapo 5. Reception Building/Prisoner Registration 6. Kitchen 7. Gas Chamber and Crematorium 8. Storage Buildings and Workshops 9. Storage of Confiscated Belongings 10. Gravel Pit: Execution Site 11. Camp Orchestra Site 12. "Black Wall" Execution Site 13. Block 11: Punishment Bunker 14. Block 10: Medical Experiments 15. Gallows 16. Block Commander's Barracks 17. SS Hospital
-
The Destruction of the German Garrison in Lenin
ArticleAfter the German occupation of Lenin, there was a garrison established. Learn about the partisan attack and subsequent destruction.

-
Gurs
ArticleIn 1939, the French government established the Gurs camp. Learn more about the history of the camp before and after the German invasion of France.

-
German Administration of Poland
ArticleGermany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Learn about the administrative units that Germany established after annexing and occupying parts of prewar Poland.

-
Danzig
ArticleHitler was determined to overturn the military and territorial provisions of the Versailles treaty, among it was much resented loss of the city of Danzig after WWI.

