You searched for: 数字货币游戏,加密货币游戏,数字币游戏,used博彩游戏,【www.2266.com,复制打开网址】,ust泰达币博彩网站,区块链游戏排名,区块链游戏nft,区块链游戏平台,nft游戏有哪些,nft是什么游戏,以太坊游戏,区块链游戏赚钱网站,币圈游戏,区块链博彩平台,网址kaefhfkccdckbghcd
<< Previous | Displaying results 1-50 of 1781 for "数字货币游戏,加密货币游戏,数字币游戏,used博彩游戏,【www.2266.com,复制打开网址】,ust泰达币博彩网站,区块链游戏排名,区块链游戏nft,区块链游戏平台,nft游戏有哪些,nft是什么游戏,以太坊游戏,区块链游戏赚钱网站,币圈游戏,区块链博彩平台,网址kaefhfkccdckbghcd" | Next >>
-
US Army Trials in Postwar Germany
ArticleFrom 1945 to 1947, the US Army tried a variety of officials, camp personnel, and German civilians accused of war crimes and mass atrocities against Allied civilians and prisoners of war.

-
Recognition of US Liberating Army Units
ArticleLearn about US Army Divisions that have been recognized as liberating units by the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum and the US Army's Center of Military History.

-
US troops in Nuremberg
PhotoThe inhabitants of Nuremberg watch a parade of US troops through their city. Nuremberg, Germany, 1946.

-
US troops at the Wöbbelin camp
PhotoOn May 2, 1945, the 8th Infantry Division and the 82nd Airborne Division encountered the Wöbbelin concentration camp. This photograph shows US troops in the Wöbbelin camp. Germany, May 4–6, 1945.

-
US troops at Gardelegen
PhotoUS troops with the 102nd Infantry Division at a barn outside Gardelegen, where over 1,000 prisoners were burned alive by the SS. Germany, April 14, 1945.

-

-
US troops enter Buchenwald
PhotoUS soldiers enter the Buchenwald concentration camp following the liberation of the camp. Buchenwald, Germany, after April 11, 1945.

-
US soldiers inspect Hadamar
FilmIn Nazi usage, "euthanasia" referred to the killing of those whom the Nazis deemed "unworthy of life." In 1941 the Hadamar psychiatric clinic served as one of the euthanasia killing centers in Germany. Patients selected by German doctors for euthanasia were transferred to Hadamar or one of the other facilities and were killed in gas chambers. Over 10,000 people were gassed at Hadamar before the Euthanasia Program officially ended in August 1941. Although the program had officially ended, killings continued…

-
Treatment of US POWs
FilmA former US prisoner of war (POW), United States Navy Lieutenant Jack Taylor, testifies to the treatment he and other American POWs received in the Mauthausen concentration camp in Austria.

-
US Army unit at Camp Ritchie
PhotoOtto Perl poses with his US Army unit at Camp Ritchie, Maryland, circa 1945. Born in Austria, Perl served in the Austrian Army until March 1938, when he was dismissed because he was Jewish. With the help of a friend, Perl was able to obtain a US visa. He reached New York in 1940. Several thousand of the soldiers who trained at Camp Ritchie were Jewish refugees who had immigrated to the United States to escape Nazi persecution.

-
US soldiers care for Dachau survivors
FilmThe Dachau concentration camp, northwest of Munich, Germany, was the first regular concentration camp the Nazis established in 1933. About twelve years later, on April 29, 1945, US armed forces liberated the camp. There were some 30,000 starving prisoners in the camp at that time. In this footage, soldiers of the US Seventh Army feed and disinfect survivors of the camp.

-
US army officer with survivors of Ohrdruf
PhotoA US army officer (far right) poses with survivors of the Ohrdruf camp, a subcamp in the Buchenwald camp system. Photograph taken after the liberation of the camp. Ohrdruf, Germany, April 1945.

-
US Army Signal Corps photographers
PhotoUS Army Signal Corps photographers from Combat Unit 123 photograph ruins in the city of Naumburg, Germany. Photograph taken by J Malan Heslop. April 10, 1945.

-
Meeting of US and Soviet forces at Torgau
PhotoAn African American soldier is among those members of the Soviet and US armed forces posing here upon the historic meeting of the two armies on the Elbe River. Torgau, Germany, April 26, 1945.

-

-
US supply ships in the Philippines
PhotoSupply ships reinforce US forces on the Philippine island of Leyte during the US invasion of the Philippines. 1944.

-
Synagogue used as a warehouse
PhotoA synagogue used as a warehouse for the belongings of deported Jews. Szeged ghetto, Hungary, 1944.

-
US Ratifies Genocide Convention
Timeline EventNovember 5, 1988. On this date, the US ratified the UN Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide.

-
Scales used by refugees
ArtifactScale used by refugees Masza Swislocki and George Lieberfreund to weigh jars of artificial honey, which they manufactured and sold in the restricted area of Shanghai. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Members of the US Olympic team
PhotoMembers of the US Olympic team—runners Helen Stephens and Jesse Owens—at the Berlin Olympic Games. Germany, August 1936.

-
US Marines on Peleliu Island
PhotoUS Marines during the final stage of the fight for Peleliu Island in the Pacific theater of war. September 14, 1944.

-
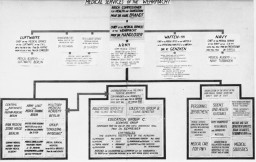
Chart used in the Doctors' Trial
PhotoChart used by the prosecution in the Doctors' Trial illustrates the organization of the Medical Services of the Wehrmacht (German armed forces). Nuremberg, Germany, December 9, 1946-August 20, 1947.
-
US troops land on Guadalcanal
PhotoUS troops land on Guadalcanal, in the Solomon Islands group. Guadalcanal was the focus of crucial battles in 1942–43. American victory in the Solomons halted the Japanese advance in the South Pacific. Guadalcanal, August 1942.

-
US troops landing on Guadalcanal
PhotoUS troops land on Guadalcanal, in the Solomon Islands groups. Guadalcanal was the focus of crucial battles in 1942–43. American victory in the Solomons halted the Japanese advance in the South Pacific. Guadalcanal, date uncertain.

-
US Forces Liberate Flossenbürg
Timeline EventApril 23, 1945. On this date, US forces liberated the Flossenbürg camp in Germany.

-
Identity Card Used in Hiding
Timeline EventAugust 3, 1943. On this date, Kurt I. Lewin was issued a forged ID card for "Roman-Paul Mytka." He used that identity to survive the war.

-
US Forces Liberate Buchenwald
Timeline EventApril 11, 1945. On this date, Buchenwald prisoners stormed the watchtower and seized control of the camp. US forces liberated the camp the same day.

-
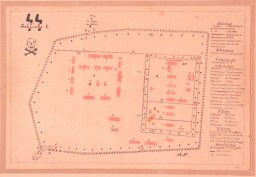
Map used as trial evidence
ArtifactThis map of the Treblinka I forced-labor camp was drawn by Holocaust survivor Manfred Kort in 1946. In 1990 Kort donated the map to the United States Holocaust Memorial Musem. In March 1997, at the request of the Office of Special Investigations, the Museum sent the original drawing to Chicago to be used as evidence at the trial of one Bronislaw Hajda. At the conclusion of Hajda's trial on April 10, 1997, the U.S. Department of Justice announced that "a federal judge in Chicago has revoked the naturalized…
-
US Prosecutor Jackson
FilmIn the summer of 1945, representatives of the victorious Allied nations—the United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union—met in London to discuss the formation of an International Military Tribunal. The questions on the table were daunting: how and where such a court would convene, what the criminal charges would be, and which perpetrators would be put on trial. US President Harry S. Truman issued an executive order designating Supreme Court Justice Robert H. Jackson to be the US…

-
US soldiers view the bodies of prisoners in Ohrdruf
PhotoUS soldiers view the bodies of prisoners found in the newly liberated Ohrdruf concentration camp. Ohrdruf, Germany, April 6, 1945.

-
Two US soldiers cross the Rhine River
PhotoTwo American soldiers cross the Rhine River into Germany on March 29, 1945. In the foreground is Jack Caminer, who emigrated from Germany to the United States in 1938. After he was drafted into the US Army, Caminer was sent to Camp Ritchie to prepare for intelligence work. Caminer participated in the liberation of Ohrdruf.

-
US troops view bodies of Wöbbelin victims
PhotoTroops of the American 82nd Airborne Division view bodies of inmates at Wöbbelin, a subcamp of the Neuengamme concentration camp. Germany, May 6, 1945.

-
US generals view corpses of victims at Ohrdruf
PhotoGenerals Eisenhower, Patton, and Bradley view corpses of inmates at Ohrdruf, a subcamp of Buchenwald. Germany, April 12, 1945.

-
Resistance group in Buchenwald meets with US troops
PhotoMembers of a resistance organization in the camp meet with American soldiers in front of the entrance to the Buchenwald concentration camp. Buchenwald, Germany, after April 11, 1945. In early April 1945, as US forces approached the camp, the Germans began to evacuate some 28,000 prisoners from the main camp and an additional several thousand prisoners from the subcamps of Buchenwald. About a third of these prisoners died from exhaustion en route or shortly after arrival, or were shot by the SS. The…

-
US condemnation of Kristallnacht
FilmOn November 9, 1938, the Nazis led a nationwide pogrom against Jews. During the pogrom, known as "Kristallnacht" (the "Night of Broken Glass"), bands of Storm Troopers (SA) destroyed thousands of Jewish-owned businesses and hundreds of synagogues. Almost 100 Jews were killed in the process. This footage shows scenes from a protest rally in New York City. Rabbi Stephen S. Wise voiced the outrage of the American Jewish community. As part of an official protest by the United States government against the…

-
US soldiers during World War I
PhotoSurrounded by destruction, US soldiers of the 23rd Infantry fire a gun during World War I, 1918.

-
Flag graphic for US 103rd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 103rd Infantry Division flag. The US 103rd Infantry Division (the "Cactus" division) was established in 1942. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Innsbruck. The division also uncovered a Nazi subcamp attached to Kaufering camp complex. The 103rd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the US Army's Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum…

-
Flag graphic for US 20th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 20th Armored Division's flag. The US 20th Armored Division was occasionally known as the "Armoraiders" during World War II. They participared in the liberation of the Dachau concentration camp. The 20th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 4th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 4th Armored Division's flag. The US 4th Armored Division is also known as the "Breakthrough" division. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and overran Ohrdruf, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 4th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 63rd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 63rd Infantry Division's flag. The US 63rd Infantry Division (the "Blood and Fire" division) was established in 1943. During World War II, they took the town of Heidelberg and liberated several Kaufering subcamps. The 63rd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 2000 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 6th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 6th Armored Division's flag. The US 6th Armored Division is also known as the "Super Sixth." During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and overran the Buchenwald concentration camp. The 6th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for the US 101st Airborne Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 101st Airborne Division's flag. The US 101st Airborne Division (the "Screaming Eagles" division) was established in 1942. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day and the Battle of the Bulge. The division also captured the city of Eindhoven and uncovered the Kaufering IV camp. The 101st Airborne Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum…

-
Flag graphic for US 26th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 26th Infantry Division's flag. The US 26th Infantry Division (the "Yankee" division) was formed in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Linz. The division also overran the Gusen concentration camp. The 26th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 2002 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum…

-
Flag graphic for US 36th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 36th Infantry Division's flag. The US 36th Infantry Division (the "Texas" or "Lone Star" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Allied invasions of North Africa and the Battle of the Bulge. The division also overran some of the Kaufering subcamps of the Dachau concentration camp. The 36th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1995 by the United States Army Center of…

-
Flag graphic for US 42nd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 42nd Infantry Division's flag. The US 42nd Infantry Division (the "Rainbow" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they captured the cities of Würzburg, Schweinfurt, and Fürth. The division also entered the Dachau concentration camp. The 42nd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum…

-
Flag graphic for US 45th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 45th Infantry Division's flag. The US 45th Infantry Division (the "Thunderbird" division) was established in 1924. During World War II, they were involved in the Allied invasions of North Africa and Italy, as well as the capture of the city of Nuremberg. The division also liberated the Dachau concentration camp. The 45th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States…

-
Flag graphic for US 71st Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 71st Infantry Division's flag. The US 71st Infantry Division (the "Red Circle" division) was established in 1943. During World War II, they were involved in taking the cities of Coburg, Bayreuth, and Regensburg. The division also liberated Gunskirchen, a subcamp of Mauthausen. The 71st Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 82nd Airborne Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 82nd Airborne Division's flag. The US 82nd Airborne Division (the "All American" division) was established in 1918 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day and Battle of the Bulge. The division also overran Wöbbelin, a subcamp of Neuengamme. The 82nd Airborne Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1991 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 84th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 84th Infantry Division's flag. The US 84th Infantry Division (the "Railsplitter" division) was established in 1917. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Hannover. The division also uncovered Hannover-Ahlem and Salzwedel, two satellite camps of the Neuengamme concentration camp. The 84th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and…

-
Flag graphic for US 89th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 89th Infantry Division's flag. The US 89th Infantry Division (the "Rolling W" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they captured the town of Eisenach and the city of Zwickau. The division overran Ohrdruf, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 89th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

