You searched for: 海外基金理财源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建海外基金理财源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建6kKoTke9kg
<< Previous | Displaying results 126-150 of 267 for "海外基金理财源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建海外基金理财源码快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建6kKoTke9kg" | Next >>
-
Halle
ArticleHalle an der Saale was a satellite camp of Buchenwald concentration camp. It was established by the Nazis in Saxony, Germany in 1941.
-
Berga-Elster ("Schwalbe V")
ArticleAt the Berga-Elster subcamp of Buchenwald, prisoners were forced to do dangerous and brutal work in tunnels to support fuel production for the German war effort.

-
Mirjana Babunovic Dimitrijevic
ID CardMirjana was the second of three children born to well-to-do Serbian parents in the capital of Bosnia, in central Yugoslavia. Her father was a successful businessman and prominent Serbian nationalist. Like her parents, Mirjana was baptized in the Serbian Orthodox faith. Mirjana attended elementary school in the multi-ethnic city of Sarajevo. 1933-39: While in secondary school, Mirjana studied foreign languages and toured western Europe. In 1938 she graduated. That fall she enrolled as a student of English…

-
Cedomir Milan Sorak
ID CardCedomir was the oldest of five children born to Serbian Orthodox parents. The Soraks lived in the multi-ethnic city of Sarajevo, the capital of the region of Bosnia. Cedomir's father, Milan, was an engineer employed by the Yugoslav state railways, and his Hungarian-born mother, Andjelija, was a housewife. 1933-39: The Sorak family moved to Zagreb after Cedomir's father was promoted to the position of assistant director of the rail system in the region of Croatia. He graduated from secondary school in 1938…

-
Wladyslaw Piotrowski
ID CardWladyslaw was born to Catholic parents in Russian-occupied Poland. He grew up in Plock, a town located in a rural area north of Warsaw. Wladyslaw married in 1918 and he and his wife, Marie, raised four children. 1933-39: Wladyslaw worked as a bookkeeper, and then as an accountant for a local farmers' cooperative. In 1931 he was sent to the town of Wyszogrod to close a failing branch of the farmers cooperative. A year later, he organized a new, successful cooperative in Wyszogrod with local farmers and…

-
Germans search Jews for weapons
PhotoGerman personnel on Grzybowska Street arrest and search Jewish men who supposedly hid weapons prior to the German occupation of Warsaw. Warsaw, Poland, October-December 1939. This is one of a series of photos taken by Arthur Grimm, an SS propaganda company photographer, documenting the investigative work of the Sicherheitsdienst (SD) in occupied Warsaw for the Berliner Illustrierte Zeitung. Although only some of the photos were published, it is likely that the incidents depicted in the BIZ were staged…

-
Krakow Ghetto: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during the history of the Krakow ghetto in German-occupied Poland.

-
Bergen-Belsen: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of the history of the Bergen-Belsen camp in the Nazi camp system. Initially a POW camp, it became a concentration camp in 1943.

-
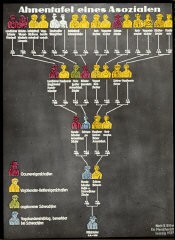
Decree against Public Enemies
ArticleThe Decree against Public Enemies was a key step in the process by which the Nazi leadership moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship.
-

-
Return to Europe of the St. Louis
ArticleIn May 1939, the St. Louis set sail from Germany to Cuba. Most of the passengers, fleeing Nazi Germany, were denied entry. Learn more about their fates.

-
Hungary before the German Occupation
ArticleTowards the end of 1940, Hungary joined the Axis powers and invaded Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union. Learn more about Hungary before the German occupation.
-
Polish Victims
ArticleIn September 1939, the Germans launched a campaign of terror intended to destroy the Polish nation and culture. Learn more about the German occupation of Poland.

-
History of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
ArticleThe United States Holocaust Memorial Museum opened in April 1993. Explore the history of the nation's memorial to the millions murdered during the Holocaust.

-
The Evian Conference
ArticleAt the July 1938 Evian Conference, delegates from nations and organizations discussed the issue of Jewish refugees fleeing persecution in Nazi Germany. Learn more

-
Locating the Victims
ArticleThe Germans and their collaborators used paper records and local knowledge to identify Jews to be rounded up or killed during the Holocaust.

-
Killing Center Revolts
ArticleUnder the most adverse conditions, prisoners initiated revolts in killing centers. Learn more about prisoner uprisings in Treblinka, Sobibor, and Auschwitz.

-
Prisoners of the Camps
ArticleJews were the main targets of Nazi genocide. Learn about other individuals from a broad range of backgrounds who were imprisoned in the Nazi camp system.

-
1938: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of Nazi Germany during 1938.

-
Althammer
ArticleThe Germans established the Althammer camp in September 1944. It was a subcamp of Auschwitz. Read more about the camp's history and conditions there.
-
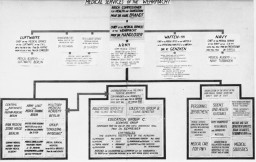
The Nuremberg Code
ArticleLeading German physicians and administrators were put on trial for their role during the Holocaust. The resulting Nuremberg Code was a landmark document on medical ethics. Learn more
-
Reich Security Main Office (RSHA)
ArticleThe Reich Security Main Office (RSHA), created by Heinrich Himmler, brutally coordinated and perpetrated many aspects of the Holocaust.

-
Evidence from the Holocaust at the First Nuremberg Trial
ArticleProsecutors before the IMT based the case against 22 leading Nazi officials primarily on thousands of documents written by the Germans themselves. Learn more.

-
The Rwanda Genocide
ArticleFrom April to July 1994, extremist leaders of Rwanda’s Hutu majority directed a genocide against the country’s Tutsi minority. Learn more

-
Chaim Yelin
ArticleYiddish writer Chaim Yelin was a leader of the Kovno ghetto underground resistance movement again the Germans.

