You searched for: 证券理财系统快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建证券理财系统快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建5yYpppS8SW
<< Previous | Displaying results 151-200 of 214 for "证券理财系统快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建证券理财系统快速搭建【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建5yYpppS8SW" | Next >>
-
Erzsebet Markovics Katz
ID CardErzsebet was born to Jewish parents living in a town on the Bodrog River in northeastern Hungary. Sarospatak was a picturesque town with a ruined medieval fortress, the Windischgratz castle, and many wineries, flour mills, and brickworks. Erzsebet's father was a locksmith and sheet-metal worker. 1933-39: Erzsebet has married Jozsef Katz. It was a lovely, formal wedding. Jozsef comes from a large Jewish family. He's a joiner by trade and was working in Sarospatak when they met. Now they have moved here to…

-
Itzik Rosenblat
ID CardItzik, also known as Izak, was one of three sons born to Yiddish-speaking Jewish parents. When Itzik was a young child his family moved to the city of Radom. Itzik left school when he was 11 to apprentice as a women's tailor. After he apprenticed with several tailors in Radom and Warsaw, he went back to school and earned a tailor's license. 1933-39: In 1938 Itzik married Taube Fishman, the daughter of his first employer, after a 13-year courtship much opposed by her family. They lived in Radom, where…

-
Atrocities against Burma's Rohingya Population
ArticleThe Burmese military has targeted the Rohingya people because of their ethnic and religious identity. The military’s actions constitute genocide and crimes against humanity. Learn more

-
Dismissal letter from the Berlin transit authority
DocumentA letter written by the Berlin transit authority (Berliner Verkehrs Aktiengesellschaft) to Viktor Stern, informing him of his dismissal from his post with their agency as of September 20, 1933. This action was taken to comply with provisions of the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service. On April 7, the German government issued the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service (Gesetz zur Wiederherstellung des Berufsbeamtentums), which excluded Jews and political opponents…

-
Sandor (Shony) Alex Braun describes how music gave him the strength to survive while imprisoned in concentration camps
Oral HistoryShony was born to religious Jewish parents in a small Transylvanian city. He began to learn the violin at age 5. His town was occupied by Hungary in 1940 and by Germany in 1944. In May 1944, he was deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland. He was transferred to the Natzweiler camp system in France and then to Dachau, where he was liberated by US troops in April 1945. In 1950, he immigrated to the United States, and became a composer and a professional violinist.

-
Leopold Page describes meeting German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

-
Sally Pitluk describes her removal from forced labor at Budy
Oral HistorySally Pitluk was born to Jewish parents in Płońsk, Poland in 1922. A few days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, Płońsk was occupied. Sally and her family lived in a ghetto from 1940-1942. In October of 1942, Sally was transported to Auschwitz, where she was tattooed and moved into the subcamp Budy for forced labor. She stayed in the Auschwitz camp complex until the beginning of 1945 when she and other prisoners were death marched to several different camps. She was liberated in 1945 and…

-

-
The Holocaust and World War II: Key Dates
ArticleRead a detailed timeline of the Holocaust and World War II. Learn about key dates and events from 1933-45 as Nazi antisemitic policies became more radical.

-
Nazi Camps
ArticleNazi Germany and its allies established over 44,000 concentration camps and incarceration sites during the Holocaust. Read about the Nazi camp system.

-
Kovno
ArticleKovno had a rich and varied Jewish culture. Learn about the Soviet and German occupations of Kovno, ghettoization, secret archives, and resistance in Kovno during WWII and the Holocaust.

-
Law, Justice, and the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the role of the legal profession as the Nazi leadership gradually moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship.

-
Glossary of Terms and Individuals in the Nazi Judicial System
ArticleLearn more about the Holocaust Encyclopedia’s key terms and individuals in the Nazi judicial system.
-
Hidden Children: Hardships
ArticleParents, children, and rescuers faced daunting challenges once the decision was made for a child to go into hiding during the Holocaust.

-
1944: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1944 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Hermann Göring: Key Dates
ArticleHermann Göring held many positions of power and leadership within the Nazi state. Learn about key dates in the life of Hermann Göring.

-
Buchenwald
ArticleThe Nazi regime established the Buchenwald camp in 1937. Learn about the camp’s prisoners, conditions there, forced labor, subcamps, medical experiments, and liberation.

-
Children's Aid Society (Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants)
ArticleDuring WWII, the Children’s Aid Society (OSE) operated 14 children's homes throughout France to save Jewish children from internment and deportation to killing centers.

-
Les Milles Camp
ArticleUnder the Vichy regime, the Les Milles camp held foreign Jews before emigration or, in most cases, deportation to German concentration camps and killing centers.

-
Berlin-Marzahn (camp for Roma)
ArticleThe Berlin-Marzahn camp was established a few miles from Berlin's city center, for the detention of Roma, on the eve of the 1936 summer Olympics.

-
Nazi Party Platform
ArticleThe Nazi Party Platform was a 25-point program for the creation of a Nazi state and society. Hitler presented it at the Hofbräuhaus Beerhall in Munich in February 1920.

-
Gleichschaltung: Coordinating the Nazi State
ArticleGleichschaltung is the German term applied to the Nazification of all aspects of German society following the Nazi rise to power in 1933.

-
Earl G. Harrison: Biography
ArticleEarl G. Harrison, Commissioner for Immigration and Naturalization under FDR, is known for a report harshly criticizing the US and British treatment of Jewish DPs.

-
Grafeneck T4 Facility
ArticleThe Grafeneck T4 Center was the first centralized killing center to be established by German authorities within the context of the Nazi “euthanasia,” or T4, program.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #9, The Einsatzgruppen Case
ArticleThe Einsatzgruppen Case was Case #9 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
Polish hostages arrested during the "pacification" of Bydgoszcz
PhotoPolish hostages in the Old Market Square. Bydgoszcz, Poland, September 9–10, 1939. Just after the German invasion of Poland, armed groups of ethnic Germans in the city of Bydgoszcz staged an uprising against the local Polish garrison. This was put down by the next day, one day prior to the entrance of German troops in the city on September 5. A local command structure was quickly put into place by Major General Walter Braemer, and in response to continued attacks upon German personnel in the city,…

-
Law Limits Jews in Public Schools
Timeline EventApril 25, 1933. On this date, the German government issued the Law against Overcrowding in Schools and Universities, limiting the amount of Jewish students.

-
Death Penalty for Aiding Jews
Timeline EventSeptember 5, 1942. On this date, Germans issued this poster announcing the death penalty for anyone found aiding Jews who fled the Warsaw ghetto.

-
Nuremberg Race Laws
ArticleLearn more about the Reich Citizenship Law and the Law for the Protection of German Blood and German Honor, collectively known as the Nuremberg Race Laws.
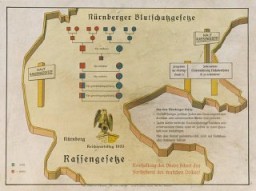
-
Alfred Dreyfus and the "Dreyfus Affair"
ArticleJewish military officer Alfred Dreyfus was wrongfully convicted of treason against France in 1894. The trial and ensuing events are known as the “Dreyfus Affair.” Learn more.

-
Nesse Galperin Godin describes a roundup in the Siauliai ghetto
Oral HistoryNesse's family had a dairy business. The Germans occupied Lithuania in 1941 and established a ghetto in Siauliai. Nesse lived in the ghetto until 1943 when she was old enough to work. In 1944 Nesse, her mother, and a brother were deported to the Stutthof camp near Danzig. Nesse worked in several Stutthof subcamps until January 1945, when the inmates were put on a death march. She was liberated by the Soviets in March. Nesse, her mother, and two brothers survived, and she arrived in the United States in…

-
President Obama's Remarks at Buchenwald
ArticlePresident Barack Obama visited Buchenwald concentration camp in Germany on June 5, 2009. In a speech at the site, he repudiated Holocaust denial. Browse transcript.

-
United States Immigration and Refugee Law, 1921–1980
ArticleUS immigration and refugee laws and policies evolved in response to World War I, the 1918 influenza pandemic, and World War II and the Holocaust. Learn more.

-
Agate (Agi) Rubin describes events following the German occupation of Hungary
Oral HistoryIn April 1944, after the German occupation of Hungary, Agi, her mother, six-year-old brother, and aunt were forced into the Munkacs ghetto. Before deportation to Auschwitz, Agi was forced to work in the ghetto's brick factory. At Auschwitz, Agi, then 14 years old, was chosen as part of a Sonderkommando. This forced-labor detachment had to sort the clothing and possessions of inmates and victims at Auschwitz. In January 1945, Agi and other prisoners were forced on a death march from Auschwitz. She was…

-
Felix Horn describes antisemitism in Lvov and conditions in the Janowska camp
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Sandor (Shony) Alex Braun describes playing the violin for SS guards in Dachau. after two prisoners before him had been killed
Oral HistoryShony was born to religious Jewish parents in a small Transylvanian city. He began to learn the violin at age 5. His town was occupied by Hungary in 1940 and by Germany in 1944. In May 1944, he was deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland. He was transferred to the Natzweiler camp system in France and then to Dachau, where he was liberated by US troops in April 1945. In 1950, he immigrated to the United States, and became a composer and a professional violinist.

-
Sandor (Shony) Alex Braun describes the death of his father in Kochendorf, a subcamp of Natzweiler
Oral HistoryShony was born to religious Jewish parents in a small Transylvanian city. He began to learn the violin at age 5. His town was occupied by Hungary in 1940 and by Germany in 1944. In May 1944, he was deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland. He was transferred to the Natzweiler camp system in France and then to Dachau, where he was liberated by US troops in April 1945. In 1950, he immigrated to the United States, and became a composer and a professional violinist.

-
Mir
ArticleThe Mir ghetto was established in Mir, Poland in 1941. Learn more about life and resistance in the ghetto.

-
Flight and Rescue
ArticleExplore the story of over 2,000 Polish Jewish refugees who fled east to escape war-torn Europe. They sought safety in such distant places as China and Japan.

-
Freiberg
ArticleLearn about the Freiburg subcamp of Flossenbürg, including its establishment, prisoner population, and conditions there.
-
München-Schwabing
ArticleLearn about the establishment and history of the Dachau subcamp München-Schwabing, and the role of Eleonore Baur (also known as Schwester Pia or Sister Pia).
-
First Letter to All Judges
ArticleLearn how the "First Letter to all Judges" increased the pressure on German judges to give verdicts and sentences according to Nazi principles and ideology.

-
Art and Survival: György Beifeld's Visual Memoir from the Russian Front, 1942–1943
ArticleGyörgy Beifeld, a Jewish conscript in the Hungarian army, created a visual memoir of his experiences on the eastern front in 1942–1943 as a member of a forced-labor battalion .

-
The Holocaust in Macedonia: Deportation of Monastir Jewry
ArticleIn March 1943, Bulgarian authorities transported the entire Jewish community of Monastir to a transit camp from which they were deported to Treblinka.

-
Halle
ArticleHalle an der Saale was a satellite camp of Buchenwald concentration camp. It was established by the Nazis in Saxony, Germany in 1941.
-
The Nazi Kripo (Criminal Police)
ArticleThe Nazi Kripo, or Criminal Police, was the detective force of Nazi Germany. During the Nazi regime and WWII, it became a key enforcer of policies based in Nazi ideology.

-
Sobibor
ArticleTo carry out the mass murder of Europe's Jews, the Nazis established killing centers that used assembly-line methods of murder. Sobibor was among these facilities.

-
Oranienburg
ArticleThe Oranienburg concentration camp was established as one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany on March 21, 1933. Learn more

-
Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B
ArticleIn 1939, the Nazis established the Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B camp in Germany. Learn more about the camp’s history, prisoners, and liberation.
-
Japanese American Relocation
ArticleLearn more about the forcible relocation of some 120,000 people of Japanese descent living in the US to “relocation centers.”

