You searched for: ���������������qee9.com������������������������6������S2O
<< Previous | Displaying results 151-175 of 267 for "���������������qee9.com������������������������6������S2O" | Next >>
-
Janusz Korczak
ArticleJanusz Korczak ran a Jewish orphanage in Warsaw. He and his staff stayed with the children even as German authorities deported them to their deaths at Treblinka in 1942.

-
Helena Husserlova with her daughter, Zdenka
PhotoIn this portrait, Helena Husserlova, wearing a Jewish badge, poses with her daughter Zdenka who is holding a teddy bear. The photograph was taken shortly before they were deported to Theresienstadt. Zdenka was born in Prague on February 6, 1939. On October 10, 1941, when Zdenka was just two and a half years old, her father was deported to the Lodz ghetto. He died there almost a year later, on September 23, 1942. Following his deportation, Helena and Zdenka returned to Helena's hometown to live with…
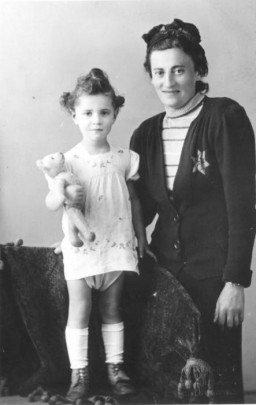
-
Portrait of Margot (Miriam) and Gerhard (Gad) Beck
PhotoGerhard and Margot's mother came from a Protestant family. She met her future husband when she went to work in the telephone exchange at his company. She converted to Judaism in 1920. The couple married in 1920, and in 1923 had their twins Gerhard and Margot. Both Gerhard and Margot would become active in Jewish youth movements, and took on Hebrew names (Gad and Miriam). On February 17, 1943, Gad was ordered to report to the temporary internment camp established at a former Jewish community building on…

-
St. Louis Sets Sail
Timeline EventMay 13, 1939. On this date, the German transatlantic liner St. Louis left Hamburg, Germany for Havana, Cuba.

-
The 84th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 84th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating two Neuengamme subcamps, Hannover-Ahlem and Salzwedel, in 1945.
-
Axis Powers in World War II
ArticleThe three principal partners in the Axis alliance were Germany, Italy, and Japan. Learn more about the Axis powers in WW2.

-
Axis Invasion of Yugoslavia
ArticleThe Axis powers invaded Yugoslavia on April 6, 1941. Learn about the Axis invasion and partition, collaboration, and the fate of Jewish people living in Yugoslavia.

-
Stefania (Fusia) Podgorska
ID CardStefania was born to a Catholic family in a village near Przemysl. They lived on a large farm and cultivated several different crops. While her father worked with the farmhands in the fields, Stefania's mother, a trained midwife, managed the house and cared for her eight children. 1933-39: Stefania's father died in 1938 after an illness. With her mother's approval, she joined her sister in Przemysl in 1939. At 14 she worked in a grocery store owned by the Diamants, a Jewish family. They treated her like…
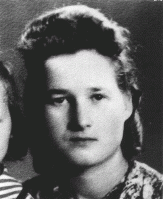
-
Yitzhak (Irving) Balsam
ID CardYitzhak was the second of four children born to religious Jewish parents. The family lived on the Polish-German border in Praszka, a small town where Yitzhak's father worked as a tailor. His work was not steady, and the family struggled to make ends meet. Yitzhak attended Polish public school in the mornings and Hebrew school in the afternoons. 1933-39: At 4 a.m. on September 1, 1939, the Balsams were awakened by an explosion. The Polish army had blown up the bridge over the Prosna River to impede the…

-
Aaron Lejzerowicz
ID CardAaron was one of four children born to a Jewish family in the northeastern Polish town of Zdzieciol. His father was a shoemaker and, along with a business partner, he also ran a shoe store in the town. Aaron attended a private Jewish school, where he studied the Polish language and history as well as Jewish history and Hebrew. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Three weeks later, Poland was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union [under the German-Soviet Pact]. Aaron and his…

-
Feige Schwarzfink
ID CardFeige was born to a religious Jewish family in the small village of Szydlowiec [in Poland]. She lived with her parents, six brothers and sisters, and elderly grandparents in a small house which, like many homes in the village, had no running water, indoor plumbing, or electricity. Feige's father was a shoemaker. 1933-39: In the afternoons after public school Feige studied at a Jewish religious school. Although her parents didn't know it, she attended meetings of the Bund, the Jewish Socialist party. Feige…

-
Meyer (Max) Rodriguez Garcia
ID CardMax was born to a Jewish family in Amsterdam. He lived in a working-class district occupied by many diamond polishers, of which his father was one. In the 1920s and 30s Amsterdam was a cosmopolitan city with a diverse population. Though his father hoped Max would follow him in the diamond trade, Max dreamed of becoming an architect. 1933-39: Max's happiest years were with close friends in school. His father encouraged him to learn by bringing home newspapers to help his English. After 1933 German Jews…

-
Aron Tabrys
ID CardAron was the second of six children born to Jewish parents in Vilna, a city known as a center of Jewish cultural life. He was called Arke by his friends and family. Aron's father supported his large family on the meager income of a chimney sweep. 1933-39: As a child Aron attended a Jewish day school, and then went on to attend a public secondary school. When he was 14 his father had an accident which rendered him blind, and Aron had to start working full-time to support the family. Aron belonged to an…

-
Julius (Julo) Levin
ID CardJulo was born to a Jewish family in the city of Stettin in northeastern Germany. From an early age Julo showed an interest in art; at 6 he had collected more than 3,000 pictures. His family hoped he would become a businessman, but his interest in painting absorbed all his energy. In 1926 he graduated from art school and by 1931 he secured his first commission in Duesseldorf. 1933-39: Until the Nazis came to power in 1933, Julo was a highly regarded artist. The Nazis' strict interpretation of art, however,…

-
Francis Ofner
ID CardFrancis grew up in a city with a Jewish community of 5,000. The Ofners belonged to a synagogue that sponsored many social activities, from sports to care for the elderly. In 1931 Francis began law school at the University of Zagreb. While a student, he organized a service that posted on university bulletin boards the translations of speeches by Nazi leaders broadcast on the radio. 1933-39: By the time Hitler became chancellor of Germany, Francis was heavily involved in trying to unify the university's…

-
Nikola Mrvos
ID CardThe oldest of five children, Nikola was born in a small village in the Croatian part of Yugoslavia. Like his parents, Nikola was baptized in the Serbian Orthodox faith. After receiving his medical degree from Prague University, he married, and in 1912 moved with his wife to Serbia. During World War I he served in the Serbian army, and then settled in Novi Sad where he co-owned a medical clinic. 1933-39: Nikola and his wife raised three children in Novi Sad. Then difficult times brought on by the 1930s…

-
Milica Popovic Kuhn
ID CardMilica was the fourth of nine children born to Serbian Orthodox landowners in the Croatian part of Yugoslavia. In 1922 Milica married Milan Kuhn, a Catholic Serb, in a Serbian Orthodox ceremony, and the couple moved to the Macedonian part of Yugoslavia, where Milan was working on hydroelectric projects. In 1932 the couple returned with their young daughter to live in northern Yugoslavia. 1933-39: The Kuhns lived in the city of Zrenjanin in the Vojvodina region where Milan worked as a hydroengineer…

-
Janusz Piotrowski
ID CardJanusz was the eldest of four children born to Catholic parents in Plock, a town located in a rural area north of Warsaw. His father was an accountant. Janusz attended local schools, and became active in scouting. 1933-39: Janusz went to Warsaw to study civil engineering. On September 1, 1939, the Germans began bombing Warsaw. One week later, all able-bodied men who had not been mobilized were directed to retreat east. On September 17, Janusz was 90 miles from the Romanian border. That night, the Soviets…

-
Lore Heumann
ID CardThe younger of two girls, Lore was born to Jewish parents in a village close to the Belgian border. The Heumanns lived above their general store. Across the street lived Lore's grandfather, who kept horses and cows in his large barn. When Lore was a year old, her family moved to the city of Lippstadt. The Lippe River flowed beyond the large garden in back of their house. 1933-39: When Lore was 6, her family moved to the nearby city of Bielefeld, where she entered public school. A year later, she and her…

-
Vladan Popovic
ID CardVladan was the oldest of five children born to well-to-do Serbian Orthodox parents in the village of Gnjilane in the Serbian part of Yugoslavia. Vladan went to Montpelier, France, where he earned a law degree from the university. When Vladan returned to Yugoslavia, he worked as an attorney in Belgrade. He married and had one daughter. 1933-39: Vladan's wife died in 1933, and his 4-year-old daughter went to live with her maternal great-aunt. Meanwhile, Vladan had expanded his law practice and was…

-
Miso Vogel
ID CardMiso came from a religious family in a small village in Slovakia, where his father was a cattle dealer. He was the eldest of five children. When Miso was 6 his family moved to Topol'cany, where the children could attend a Jewish school. Antisemitism was prevalent in Topol'cany. When Miso played soccer, it was always the Catholics versus the Jews. 1933-39: In 1936 Miso had his bar mitzvah and was considered a man. His grandparents traveled 50 miles for it; he was so happy they were all together. In March…

-
Freya Karoline Lang
ID CardAn only child, Freya was born to Jewish parents who lived in a small German town in the Rhine River valley. The Langs owned a successful dry goods business. At this time ready-made clothes were still rare in the countryside. Townspeople and local farmers would purchase fabric at the Lang's store and then take it to their tailor or seamstress to be sewn into a garment. 1933-39: When Freya was growing up, the Nazi party was in power. Many Jews left Germany--Grandmother Lang and one of Freya's uncles sailed…

-
Zofia Rapaport
ID CardZofia was born to a Jewish family in Warsaw. Zofia's father, a self-made man who had put himself through university, was a successful banker. The Rapaports lived on a street of single-family homes with gardens. Zofia's room was decorated with yellow lacquered furniture. 1933-39: As a young child, Zofia loved to play with her dog, Chapek. Sometimes she got to go shopping with her mother downtown. Each year during the Jewish holiday of Passover her family visited Zofia's grandparents in Lvov. In late August…
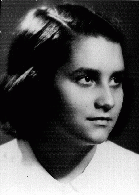
-
David J. Selznik
ID CardThe village in Lithuania where David grew up was located near the Latvian border. His father was a peddler. At age 6, David was sent to Ukmerge, a town known to Jews by its Russian name, Vilkomir, to study traditional Jewish texts at the rabbinical academy there. Six years later, David was called to return home to head the Selznik family because his father had died. 1933-39: David lost his job in 1933, so he left Lithuania and went to the United States and then Portugal. But in 1936 the Baltic states were…

-
Yosel Coller
ID CardOne of six children, Yosel was raised in a religious Jewish family in Lodz, an industrial city in western Poland. His father was a businessman. At the age of 6, Yosel began attending a Jewish day school. His two older sisters attended public school in the morning and religious school in the afternoon. Yosel spent much of his free time playing soccer with his brothers. 1933-39: Yosel's family lived in a modest house in the northern section of Lodz. He went to a Jewish day school and had many friends there.…

