
Women in the Third Reich
German women played a vital role in the Nazi movement, one which far exceeded the Nazi Party’s propaganda that a woman’s place was strictly in the home as mothers and child-bearers. Of the estimated forty million German women in the Reich, some thirteen million were active in Nazi Party organizations that furthered the regime’s goals of racial purity, imperial conquest, and global war.
Key Facts
-
1
They served as welfare workers, teachers, secretaries, nurses, auxiliaries in the armed forces and police, and in many other occupations including as guards in concentration camps.
-
2
A minority of German women who resisted the regime’s policies or were branded biologically inferior were persecuted. Hundreds of thousands were forcibly sterilized and tens of thousands were incarcerated in the camp system.
-
3
A few of the most active resisters, such as anti-war protestor Sophie Scholl who co-led the White Rose movement, were executed.
Population Policy

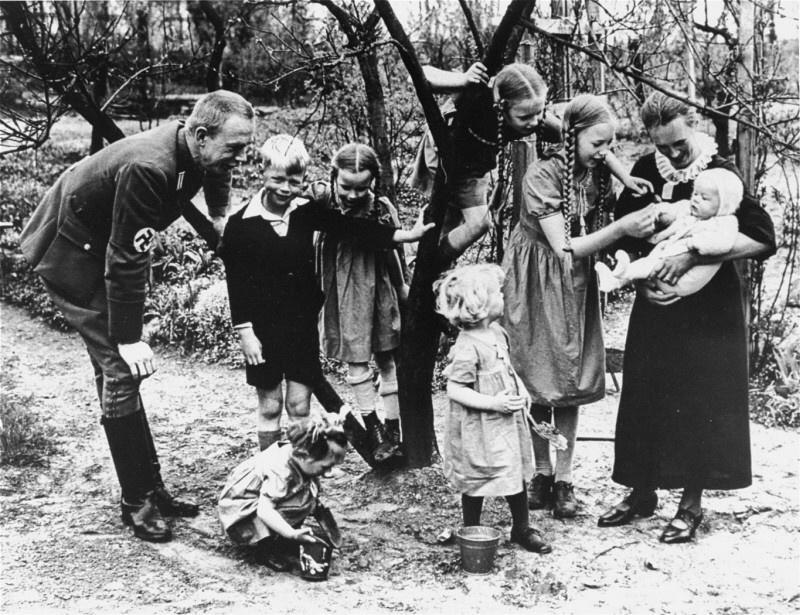
Women were central to Adolf Hitler’s plan to create an ideal “Aryan” community (Volksgemeinschaft). Praising German women as “our most loyal, fanatical fellow-combatants,” Hitler valued women for both their activism in the Nazi movement and their biological power as generators of the race. In Nazi thinking, a larger, racially purer population would enhance Germany’s military strength and provide settlers to colonize conquered territory in eastern Europe. The Third Reich’s aggressive population policy encouraged “racially pure” women to bear as many children as possible.
Nazi population policy took a radical turn in 1936 when SS leaders created the state-directed program known as Lebensborn (Fount of Life). In an extension of the SS Marriage Order of 1932, the 1936 Lebensborn ordinance prescribed that every SS member should father four children, in or out of wedlock. Lebensborn homes sheltered single mothers with their children, provided birth documents and financial support, and recruited adoptive parents for the children.
In the end, however, the Lebensborn program was never promoted aggressively. Instead, Nazi population policy concentrated on the family and marriage. The state encouraged matrimony through marriage loans, dispensed family income supplements for each new child, publicly honored "child-rich" families, bestowed the Cross of Honor of the German Mother on women bearing four or more babies, and increased punishments for abortion.
Wives, Mothers, and Workers
The National Socialist Women's Union and German Women's Agency used Nazi propaganda to encourage women to focus on their roles as wives and mothers. Besides increasing the population, the regime also sought to enhance its "racial purity" through "species upgrading," notably by promulgating laws prohibiting marriage between "Aryans" and "non-Aryans" while preventing those with handicaps and certain diseases from marrying at all.

Girls were taught to embrace the role of mother and obedient wife in school and through compulsory membership in the Nazi League of German Girls (Bund Deutscher Mädel; BDM), which started at the age of ten years old. However, rearmament followed by total war obliged the Nazis to abandon the domestic ideal for women. The need for labor prompted the state to prod women into the workforce (for example, through the Duty Year, the compulsory-service plan for all women) and even into the military itself (the number of female auxiliaries in the German armed forces approached 500,000 by 1945).
Women in the War
Gearing up for the war and waging it obliged Nazi leaders to mobilize female workers. Young women provided free labor in annual summer camps, and in 1939 all single women had to report for compulsory labor service in war-related industries. By war’s end, the number of female auxiliaries in the German armed forces approached 500,000, including some 3,700 women who served as guards in the Nazi camp system.
Equally numerous to the female auxiliaries were the many women who were secretaries in the Nazi machinery of destruction, supportive wives of SS officers, and nurses in the Euthanasia Program.

An incalculable but significant number of women were accomplices and perpetrators of the Holocaust as plunderers, organizers of the deportations and the mass shootings. Some went so far as to commit murder. After the war, the majority remained silent about the crimes that they committed and witnessed.
Opponents of the Reich
Aside from the many women who aided in implementing Nazi policies and driving the war effort were those who actively opposed the regime or were persecuted by the party for being outside the boundaries of what was socially acceptable. Included were women considered to be political opponents for their association with communism who were then sent to camps in the early period of the political purges and the women who led active resistance efforts, such as Sophie Scholl of die Weiße Rose (the White Rose).
Also sent to the camps were women considered “asocials” for behavior deemed inappropriate to a woman’s role or those who were murdered in the T-4 (“Euthanasia”) program. Others persecuted by the Reich included thousands of women who were punished for attempting an abortion.
Critical Thinking Questions
- What pressures and motivations may have affected decisions by women to participate in crimes, to collaborate, or to be indifferent to those actions?
- How might women specifically be targeted or recruited for participation in national programs that persecute minorities?

