Lithuania
Lithuania is the southernmost of the Baltic states. During the Holocaust, the Germans murdered about 90 percent of Lithuanian Jews, one of the highest victim rates in Europe.
Key Facts
-
1
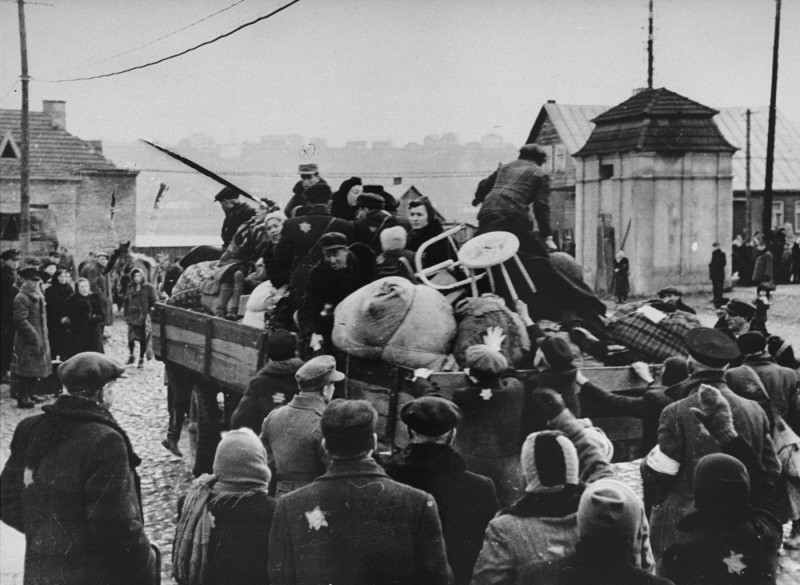
Lithuanians carried out violent riots against the Jews both shortly before and immediately after the arrival of German forces.
-
2
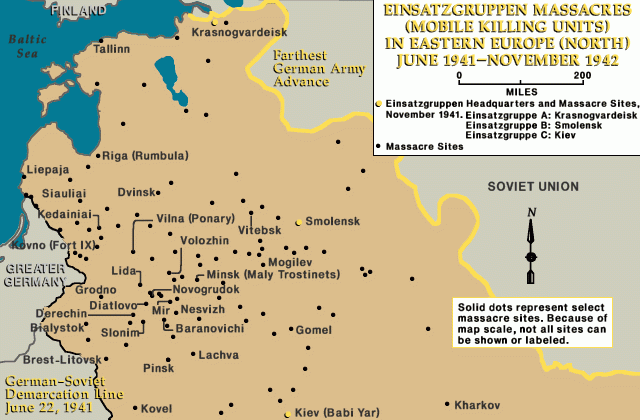
In June and July 1941, detachments of German Einsatzgrupen together with Lithuanian auxiliaries, began murdering the Jews of Lithuania.
-
3
By the end of August 1941, most Jews in rural Lithuania had been shot. By November 1941, the Germans had also massacred most of the Jews who had been concentrated in ghettos in the larger cities.
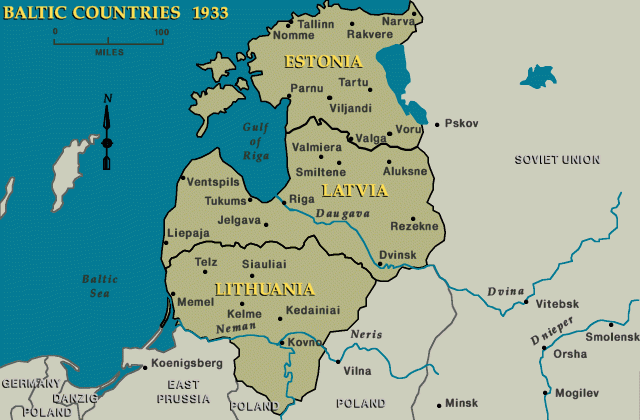
Lithuania is the southernmost of the Baltic states.

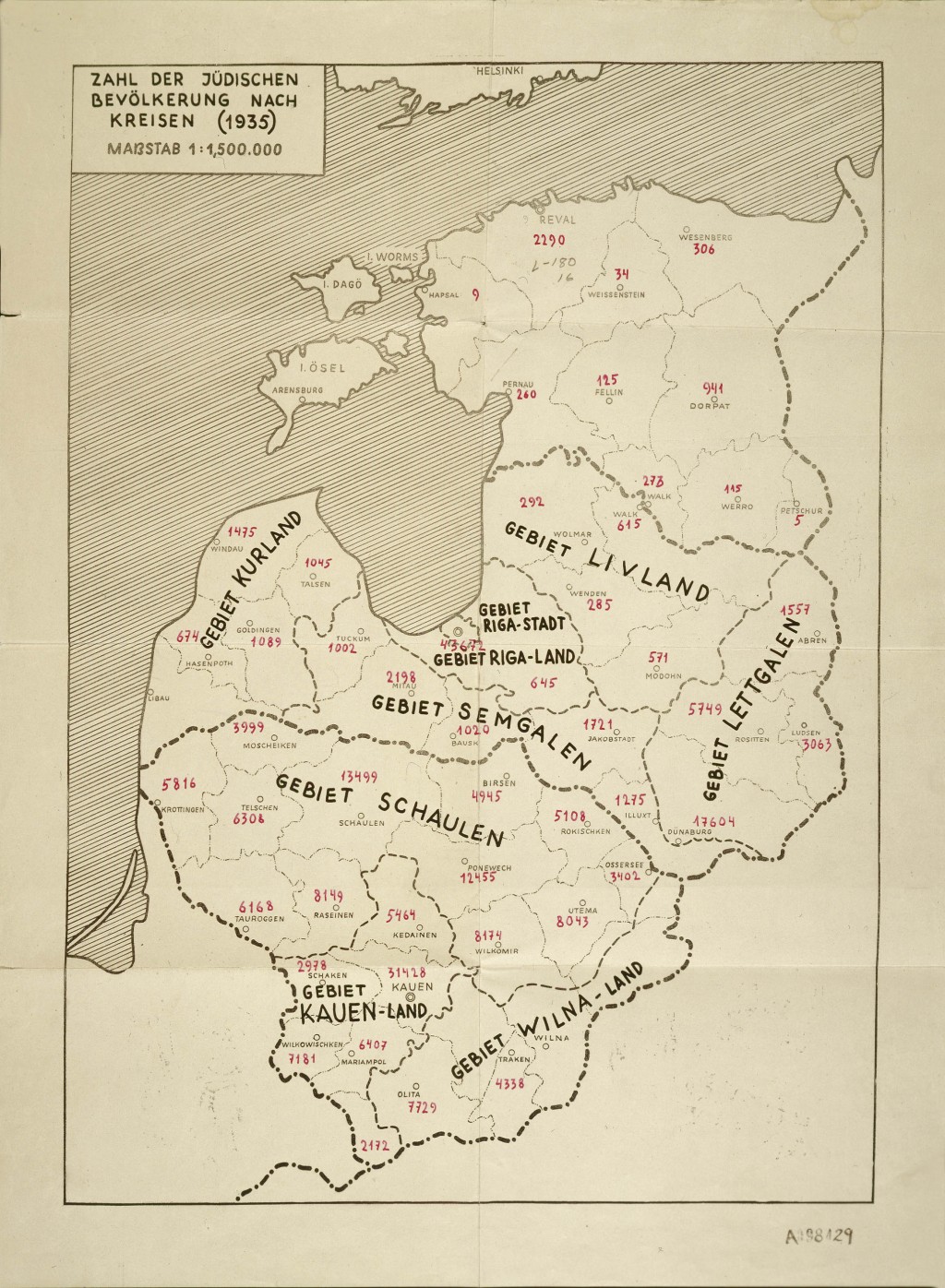
The Jews of Lithuania had their own distinct and highly developed Jewish culture, including a special dialect of the Yiddish language. Lithuanian Jewry played a profound role in many Jewish ideologies, including the Jewish workers' movement, Zionism, and rational religious thought. Before World War II, the Lithuanian Jewish population was some 160,000, about 7 percent of the total population.
Lithuania was an independent country from the end of World War I until 1940. In March 1939, Nazi Germany delivered an ultimatum to Lithuania to cede the territory of Memel (Klaipeda), a region with an ethnic German majority, to the Reich. On March 21, the Lithuanian government agreed to the German terms. The following day the German and Lithuanian foreign ministers signed a treaty that returned the Memel territory back to Germany and included a non-aggression pact between the two parties. The Soviet Union occupied Lithuania in June 1940 and annexed the country in August 1940. By 1941, the Jewish population of Lithuania swelled by an influx of refugees from German-occupied Poland to reach about 250,000, or 10 percent of the population.
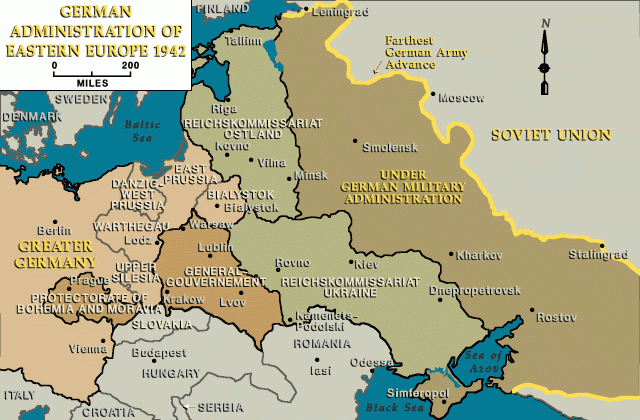
In June and July 1941, following the German invasion of the Soviet Union, the Germans occupied Lithuania. During the German occupation, Lithuania was incorporated into the Reich Commissariat Ostland (Reichskommissariat Ostland), a German civilian administration covering the Baltic states and western Belorussia.
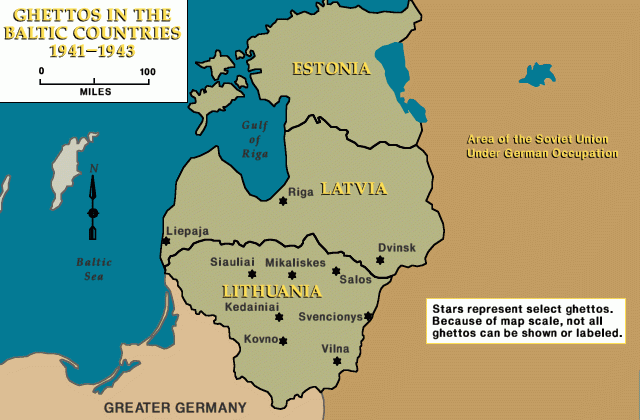
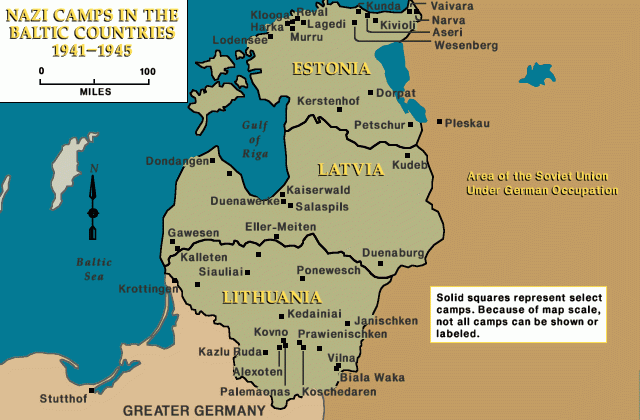
The Lithuanians carried out violent riots against the Jews both shortly before and immediately after the arrival of German forces. In June and July 1941, detachments of German Einsatzgruppen together with Lithuanian auxiliaries, began murdering the Jews of Lithuania. By the end of August 1941, most Jews in rural Lithuania had been shot. By November 1941, the Germans also massacred most of the Jews who had been concentrated in ghettos in the larger cities. The surviving 40,000 Jews were concentrated in the Vilna, Kovno, Siauliai, and Svencionys ghettos, and in various labor camps in Lithuania. Living conditions were miserable, with severe food shortages, outbreaks of disease, and overcrowding
In 1943, the Germans destroyed the Vilna and Svencionys ghettos, and converted the Kovno and Siauliai ghettos into concentration camps. Some 15,000 Lithuanian Jews were deported to labor camps in Latvia and Estonia. About 5,000 Jews were deported to killing centers in German-occupied Poland, where they were murdered. In summer 1944, the Germans dissolved the Kauen (Kovno or Kaunas) concentration camp and its subcamps (including Schaulen or Šiauliai) and deported the Jewish prisoners to other camps.
Soviet troops reoccupied Lithuania in the summer and fall of 1944. In the previous three years, the Germans and their collaborators had murdered the overwhelming majority of Lithuanian Jews, one of the highest victim rates in Europe. Most were murdered in the first six months of the German occupation.
Critical Thinking Questions
What factors might serve as precursors to mass atrocity and genocide?
Explore the motives and pressures that led individuals to abandon their fellow human beings—or to make the choice to help. What questions are raised about the roles of professionals during this history?
Learn more about the history of the Jewish community in Lithuania.
Are the events of the Holocaust commemorated in Lithuania?
How and why might anniversaries of historical events encourage reflection about the warning signs that led to the Holocaust?