The Vélodrome d'Hiver (Vél d'Hiv) Roundup
The Vélodrome d'Hiver (or "Vél d'Hiv") roundup was the largest French deportation of Jews during the Holocaust. It took place in Paris on July 16–17, 1942.
Key Facts
-
1
To preserve the fiction of a French police force independent of the German occupiers, French policemen carried out the mass arrest of some 13,000 Jewish men, women, and children.
-
2
In order to avoid a public outcry on Bastille Day, a French national holiday, the roundup was moved from July 13–15 to July 16–17.
-
3
The majority of those arrested were deported to Auschwitz.
Background
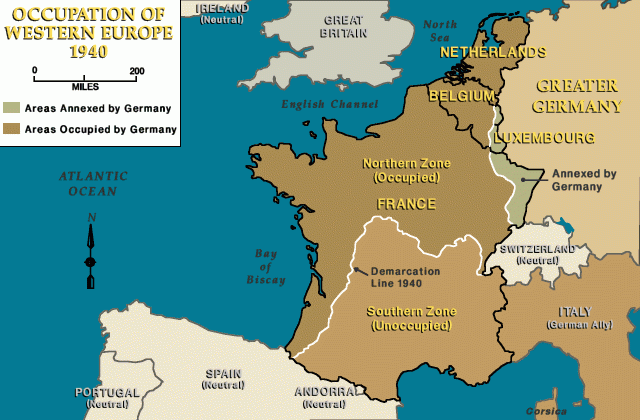
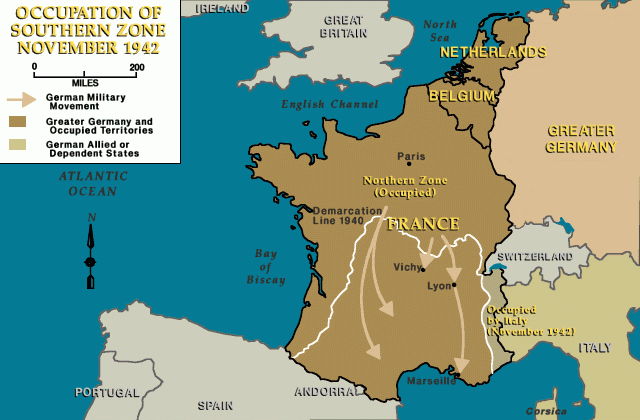
After the French surrender to German forces in June 1940, the Vichy regime (officially known as the French State) replaced the French Third Republic. Led by World War I hero Philippe Pétain, the Vichy government collaborated actively with the Nazi regime. It facilitated the deportation of Jews not only in the northern zone occupied by German forces, but also in France's free zone in the south, which the German army occupied only after the Allied invasion of North Africa in November 1942.
Following the Wannsee Conference of January 20, 1942, German authorities prepared for the deportation of Jews from France and other western European countries. An initial transport of more than 1,000 Jews left from Compiègne for Auschwitz on March 27, 1942. On May 29, 1942, German authorities issued a decree—to take effect on June 7—that Jews in occupied France wear the yellow star.
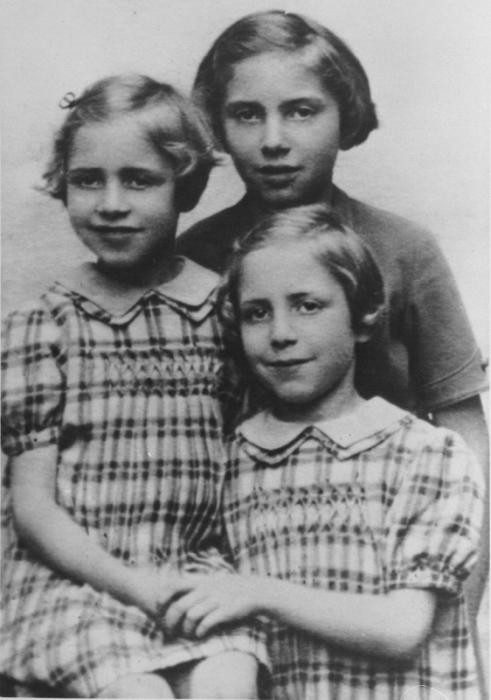

After securing the agreement of the Vichy government, German officials and French police conducted roundups of Jews in both the occupied and unoccupied zones of France throughout the summer of 1942. The Vél d'Hiv was part of a series of roundups codenamed Opération Vent printanier (Operation Spring Wind) that took place across the country in spring and summer of 1942.
Preparations for the Roundup
Planning for the Vél d'Hiv roundup took place among René Bousquet, secretary general of the French national police; Louis Darquier de Pellepoix, Commissioner for Jewish Affairs under the Vichy Régime; SS-Hauptsturmführer Theodor Dannecker, head of Adolf Eichmann's Judenreferat (Jewish Section) in France; and SS-Oberstürmführer Helmut Knochen, head of the German Security Police in France.
In order to guarantee the participation of the French police in the roundups, Nazi officials agreed to focus on foreign and stateless Jews, thus initially sparing the French Jewish population from deportation.
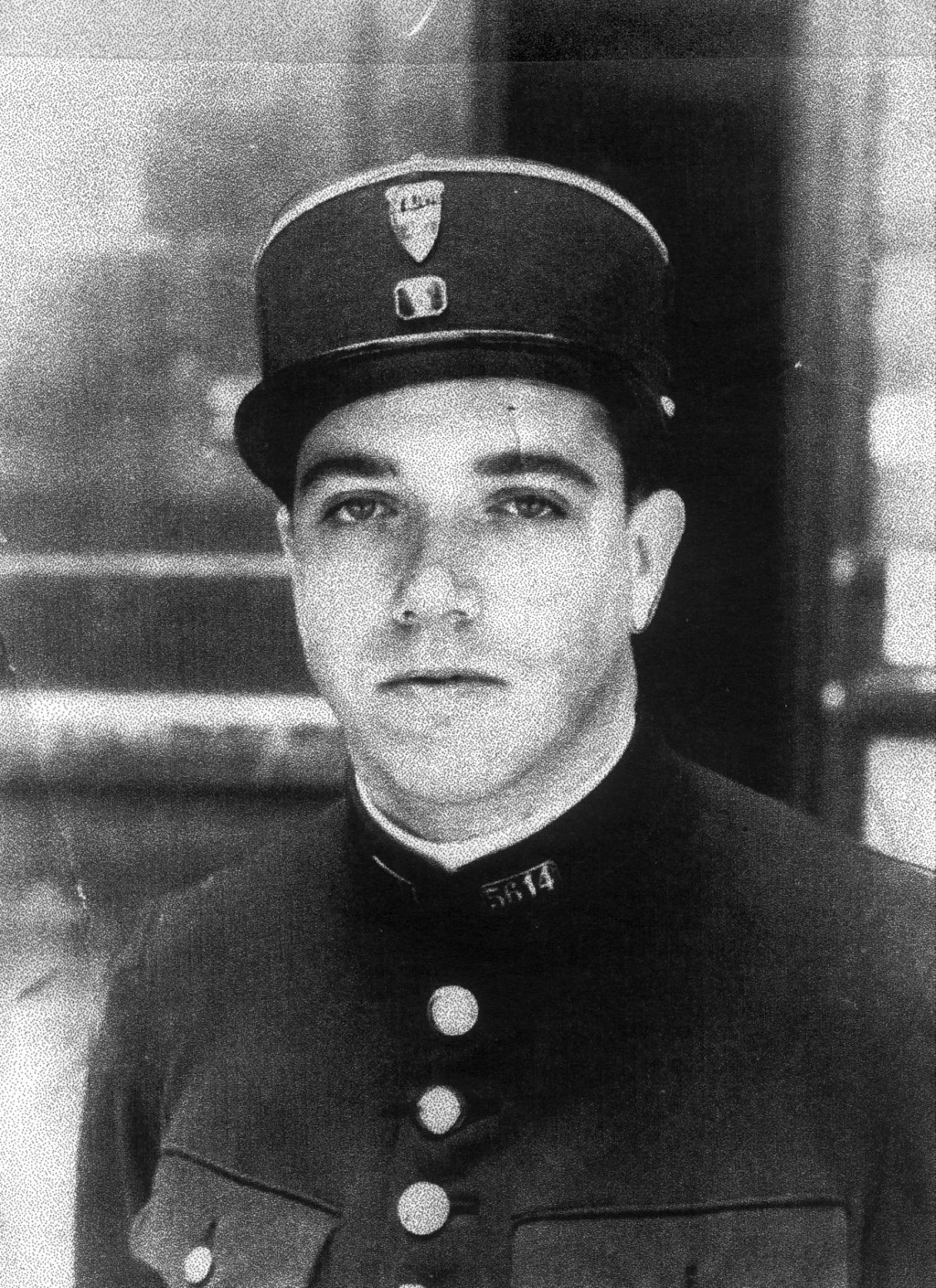
The Director of the local Paris Municipal Police, Emile Hennequin, sent precise expectations for the roundup to the police prefecture three days before the event. The roundup was originally set to take place from July 13–15, which included Bastille Day, the French national holiday. The holiday was not celebrated in the occupied zones of France, and in order to preclude local rioting, Nazi officials allowed French officials to delay the operation until July 16–17.
The German goal was that French police would round up 28,000 foreign and stateless Jews in the greater Paris area. They were to exempt “sensitive cases” such as British or American Jews. Although German authorities had originally agreed to exempt children under the age of 16, French Prime Minister Pierre Laval suggested for “humanitarian” reasons that children be arrested with their parents, unless a family member remained behind to care for them. Four thousand children were among those arrested in Paris.
In order to maintain a detailed record of the roundup, the police were to report the number of people they arrested each hour to their local prefecture.
July 16–17
Beginning in the early hours of July 16, French police rounded up thousands of men, women, and children throughout Paris. By the end of the day, the police had taken 2,573 men, 5,165 women, and 3,625 children from their homes. The roundup continued the following day, but with a much smaller number of arrests.
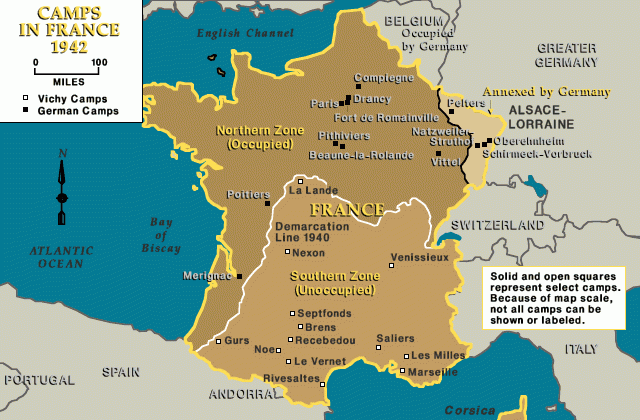
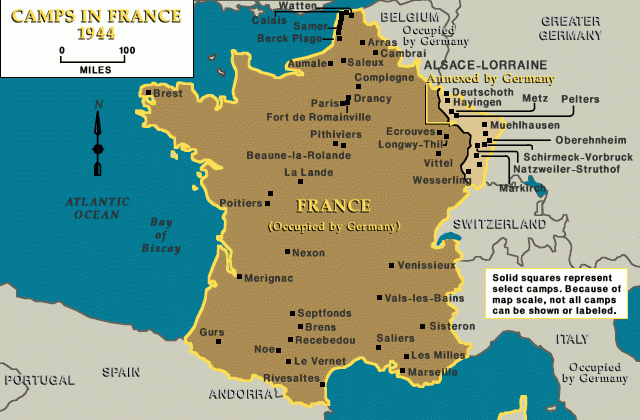
Approximately 6,000 of those rounded up were immediately transported to Drancy, in the northern suburbs of Paris. Drancy was at that point a transit camp for Jews being deported from France. The rest of the arrestees were detained at the Vélodrome d'Hiver (Winter Cycling Track), an indoor sporting arena in Paris's fifteenth arrondissement.
Officials could have held few illusions of the unsuitability of the “Vél d'Hiv” for holding such a large population indefinitely. With the outbreak of war in 1939, it had been used to intern German nationals, mainly German refugees. In 1940 it housed interned foreign women. In both instances, conditions were deplorable.

Following the roundup of Jews in greater Paris, some 7,000 Jews, among them almost 4,000 children, were crowded together in the sports arena. There was scarcely space to lie down and the incarcerated Jews faced appalling circumstances. No arrangements had been made for food, water, or sanitary facilities. Only two physicians a shift were allowed in to treat the internees. The glass ceiling of the arena contributed to a stifling environment by day, as all ventilation had been sealed to prevent escape, and led to chilly temperatures at night.
Aftermath
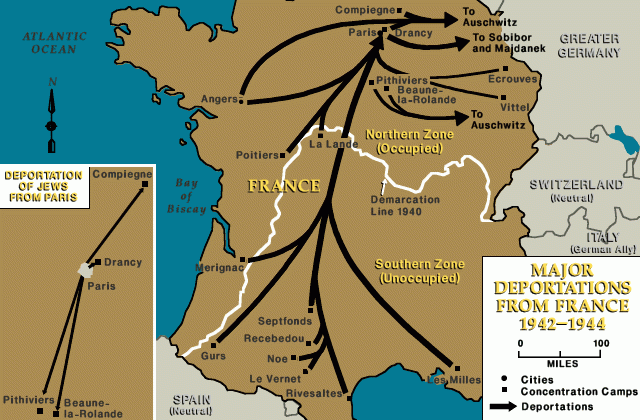
After five days, Jews incarcerated at the Vél d'Hiv were transferred to other transit camps outside Paris. At Drancy, Pithiviers, and Beaune-la-Rolande, French police guarded these men, women, and children until transport to concentration camps and killing centers in the east. At the end of July, the remaining adults were separated from their children and deported to Auschwitz. Over 3,000 children remained interned without their parents until they were deported, among adult strangers, to Auschwitz as well.
German authorities continued the deportations of Jews from French soil until August 1944. In all, some 77,000 Jews living on French territory perished in concentration camps and killing centers—the overwhelming majority of them at Auschwitz.
Postwar Trials
For his prominent role in the deportation of Jews from France, Pierre Laval, formerly the French Prime Minister, was arrested and tried after the liberation of France. He was shot by firing squad on 15 October 1945.
The fate of two German officials most involved in the Vél d'Hiv mirrored the common fates of high-ranking SS administrators. Theodor Dannecker was arrested by American officials in Bad Tölz, Bavaria, in December 1945, and committed suicide while in custody. Helmut Knochen, sentenced by a British court to 21 years in prison for a separate offense, was sentenced to death by a French court in 1954. The sentence was commuted to life imprisonment, and Knochen was released on orders of French President Charles de Gaulle in November 1962.
In 1949, René Bousquet, secretary general of the French police, was found guilty for his role in the complicit Vichy government, but his sentence was immediately commuted for "having actively and sustainably participated in the resistance against the occupier."
In 1991, French justice authorities in Paris indicted Bousquet for his participation in the deportation of Jews from France. Christian Didier, a mentally ill individual, assassinated Bousquet in his home in Paris on June 8, 1993, before proceedings could take place.
Acknowledging the Role of the State and Police
On July 16, 1995, on the fifty-third anniversary of the Vél d'Hiv roundup, French President Jacques Chirac acknowledged the role the state and its police had played in the persecution of Jews and other victims of the German occupation. “France,” Chirac said, “land of the Enlightenment and of Human Rights, land of hospitality and asylum, France, on that day, committed an irreparable act. It failed to keep its word and delivered those under its protection to their executioners.”