Tarnow
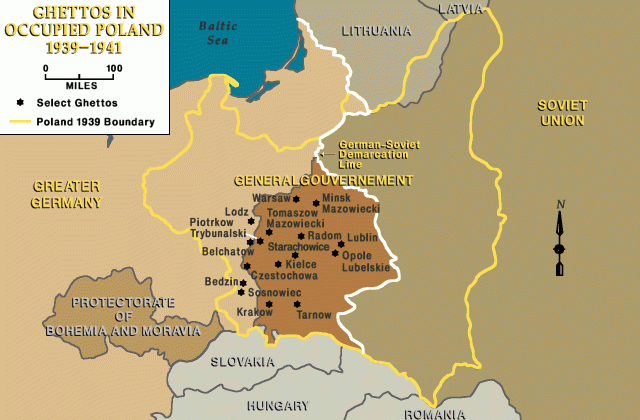
During the Holocaust, the creation of ghettos was a key step in the Nazi process of brutally separating, persecuting, and ultimately destroying Europe's Jews. Ghettos isolated Jews from the non-Jewish population and from other Jewish communities. Living conditions were miserable. Among them was the Tarnow ghetto.
Before World War II, about 25,000 Jews lived in Tarnow, a city in southern Poland, 45 miles east of Krakow (Cracow). Jews—whose recorded presence in the town went back to the mid-fifteenth century—comprised about half of the town's total population. A large portion of Jewish business in Tarnow was devoted to garment and hat manufacturing. The Jewish community was ideologically diverse and included both religious Hasidim and secular Zionists.
Immediately following the German occupation of the city on September 8, 1939, the harassment of the Jews began. German units burned down most of the city's synagogues on September 9 and drafted Jews for forced-labor projects. Tarnow was incorporated into the Generalgouvernement (the territory in the interior of occupied Poland). Many Tarnow Jews fled to the east, while a large influx of refugees from elsewhere in Poland continued to increase the town's Jewish population. In early November, the Germans ordered the establishment of a Jewish council (Judenrat) to transmit orders and regulations to the Jewish community. Among the duties of the Jewish council were enforcement of special taxation on the community and providing workers for forced labor.
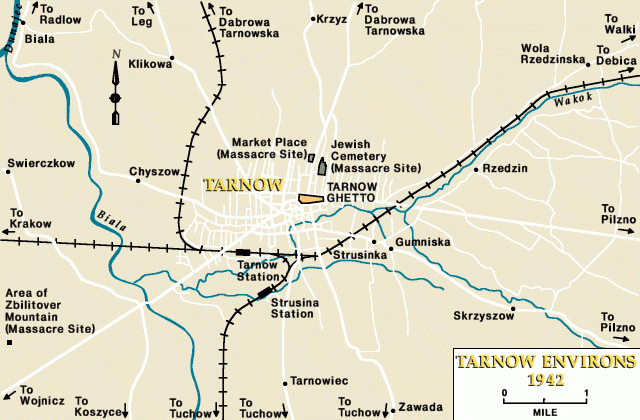
During 1941, life for the Jews of Tarnow became increasingly precarious. The Germans imposed a large collective fine on the community. Jews were required to hand in their valuables. Roundups for labor became more frequent and killings became more commonplace and arbitrary. Deportations from Tarnow began in June 1942, when about 13,500 Jews were sent to the Belzec killing center. During the deportation operations, German SS and police forces massacred hundreds of Jews in the streets, in the marketplace, in the Jewish cemetery, and in the woods outside the town.
We heard the columns of Jews under German, German escort at night. It was going constantly. They were passing our house because this was already on the outskirts of the city, the cemetery, and they were marching them to the woods behind the, uh, the, uh, uh, city. And as we found out later they, uh, they were all shot over there.
—Martin Spett
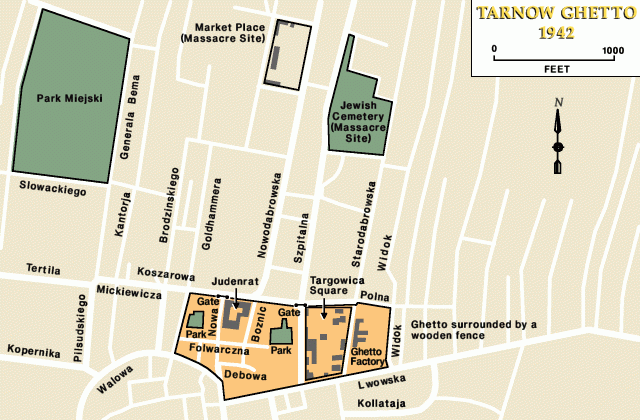
After the June deportations, the Germans ordered the surviving Jews in Tarnow, along with thousands of Jews from neighboring towns, into a ghetto. The ghetto was surrounded by a high wooden fence. Living conditions in the ghetto were poor, marked by severe food shortages, a lack of sanitary facilities, and a forced-labor regimen in factories and workshops producing goods for the German war industry.
In September 1942, the Germans ordered all ghetto residents to report at Targowica Square, where they were subjected to a Selektion (selection) in which those deemed "unessential" were selected out for deportation to the Belzec killing center. About 8,000 people were deported. Thereafter, deportations from Tarnow to killing centers continued sporadically; the Germans deported a group of 2,500 in November 1942.
It was, you know, like after a real pogrom, you know. Households, the doors open, broken glass, uh, pillowcases ripped up and, you know, the feathers in the air.
—Leah Hammerstein Silverstein
In the midst of the 1942 deportations, some Jews in Tarnow organized a resistance movement. Many of the resistance leaders were young Zionists involved in the Ha-Shomer Ha-Tsa'ir youth movement. Many of those who left the ghetto to join the partisans fighting in the forests later fell in battle with SS units. Other resisters sought to establish escape routes to Hungary, but with limited success.
The Germans decided to destroy the Tarnow ghetto in September 1943. The surviving 10,000 Jews were deported, 7,000 of them to Auschwitz and 3,000 to the Plaszow concentration camp in Krakow. In late 1943, Tarnow was declared "free of Jews" (judenrein). By the end of the war, the overwhelming majority of Tarnow Jews had been murdered by the Germans. Although some 700 Jews returned to the city after liberation, virtually all of them soon left to escape local antisemitism.
Critical Thinking Questions
- Learn about the lives of the Jews in the community of Tarnow before 1939.
- Learn about the history of the Jewish community in your country.