January 30, 1933
Adolf Hitler is Appointed Chancellor
The Nazi Party assumes control of the German state.

1933–1938

During Kristallnacht, groups of Nazis vandalized storefronts of Jewish-owned businesses on Potsdamer Straße, a commercial street in central Berlin. These businesses were among the thousands of stores and homes damaged during the nationwide anti-Jewish riot. Berlin, Germany, November 10, 1938.
—Bildarchiv Preussischer KulturbesitzFollowing Adolf Hitler’s appointment as German chancellor on January 30, 1933, the Nazis and their allies transformed Germany from a multi-party republic into a one-party dictatorship. The Nazi dictatorship implemented radical racial, political, and social policies. During the first six years of Hitler’s rule, German Jews felt the effects of legislation that transformed them from “citizens” to “outcasts.” In the 1930s, the regime also targeted a variety of alleged “enemies of the state” within German society.
January 30, 1933
Adolf Hitler is Appointed Chancellor
The Nazi Party assumes control of the German state.

February 28, 1933
Reichstag Fire Decree
President Hindenburg suspends constitutional protections in Germany.
![The Reichstag (German parliament) building burns in Berlin. [LCID: 38104]](/images/small/4bd2d2f2-3ff1-4258-86cf-4de905e098b6.jpg)
March 22, 1933
Establishment of Dachau Camp
The SS establishes the Dachau concentration camp in March 1933.

April 01, 1933
Anti-Jewish Boycott
Members of the Nazi Party and its affiliated organizations organize a nationwide boycott of Jewish-owned businesses in Germany.

April 07, 1933
Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service
German law excludes Jews and other political opponents from civil service positions.

April 25, 1933
Law Limits Jews in Public Schools
The Law against Overcrowding in Schools and Universities limits the number of Jewish students in public schools.

April 26, 1933
Rumbold Dispatch
The British ambassador to Germany warns the British government about the principles outlined in Hitler’s Mein Kampf.

May 10, 1933
Book Burning
Books deemed "un-German" are publicly burned throughout Germany.

July 14, 1933
Law for the "Prevention of Offspring with Hereditary Diseases"
New German law mandates the forced sterilization of certain individuals with physical and mental disabilities.

September 17, 1933
Central Organization of German Jews Formed
German Jewish organizations join together to form the Reichsvertretung der deutschen Juden.
October 04, 1933
Editors Law
New German law forbids non-“Aryans” to work in journalism.
![A pedestrian stops to read an issue of the antisemitic newspaper "Der Stuermer" (The Attacker) in a Berlin display box. [LCID: 02629]](/images/small/21168f2c-61a8-4033-8b72-6662080a15b7.jpeg)
November 24, 1933
Law against "Dangerous Habitual Criminals"
A new German law allows courts to order indefinite imprisonment.
June 30, 1934
Röhm Affair
Hitler orders the purge of the top leadership of the SA, the Nazi Party paramilitary formation.
August 02, 1934
Death of German President von Hindenburg
Adolf Hitler becomes President of Germany.
![Reich President Paul von Hindenburg meets with Chancellor Adolf Hitler. [LCID: 08401]](/images/small/11bcf86a-b31d-457f-b0db-98e070c147cf.jpg)
August 19, 1934
Referendum Confirms Hitler's New Title and Powers
Hitler becomes the absolute dictator of Germany.
![A crowd cheers Adolf Hitler as his car leaves the Reich Chancellery following a meeting with President Paul von Hindenburg. [LCID: 80706]](/images/small/7712da59-53b8-4bb8-a558-a4c3e44aeb89.jpeg)
April 01, 1935
Ban on Jehovah's Witness Organizations
The German government bans all organizations of the Jehovah's Witness Christian denomination.

June 18, 1935
Anglo-German Naval Agreement
The United Kingdom and Germany sign an agreement allowing the German navy to expand beyond the terms of the Treaty of Versailles.

June 28, 1935
Revision of Paragraph 175
Paragraphs 175 and 175a and the Nazi campaign against homosexuality.

September 15, 1935
Nuremberg Race Laws
The Nuremberg Laws of 1935 herald a new wave of antisemitic legislation that brings immediate and concrete segregation.
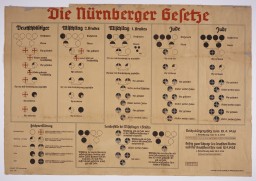
December 1935
Creation of Lebensborn Program
The Lebensborn (“Fount of Life”) program is created at the direction of Heinrich Himmler in order to combat Germany’s falling birth rate.

June 1936
Formation of the Center for Research on Racial Hygiene and Demographic Biology
Robert Ritter becomes head of a new eugenics research center focusing on racially classifying Roma and Sinti.

June 06, 1936
Decree on “Combating the Gypsy Plague”
Minister of the Interior for the Reich and Prussia Wilhelm Frick issues a decree on “Combating the Gypsy Plague.”
July 16, 1936
Marzahn Camp for Roma and Sinti Established
German authorities order the roundup of Roma and Sinti in Berlin, confining them in a new camp in the Marzahn suburb.

August 01, 1936
Olympic Games Open in Berlin
The Nazi dictatorship camouflages its racist, militaristic character while hosting the Summer Olympics.
![On August 1, 1936, Hitler opened the 11th Summer Olympic Games. [LCID: 21678]](/images/small/58ee0871-44e7-4ee6-801e-77a0f979bee8.jpeg)
August 03, 1936
Jesse Owens Competes in Olympic Games
Owens' victory in the 100-meter dash is the first of four gold medals he wins at the 1936 Olympic games.
![American Olympic runner Jesse Owens and other Olympic athletes compete in the twelfth heat of the first trial of the 100m dash. [LCID: 14523a]](/images/small/0eefaa06-6a60-46ab-832d-cc86b1f5a8de.jpeg)
May 28, 1937
Neville Chamberlain Takes Office
Neville Chamberlain succeeds Stanley Baldwin as British prime minister.

May 1937–September 1939
British Policy of Appeasement
Prime Minister Chamberlain follows a policy of appeasement towards Nazi Germany.
![British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and German Chancellor Adolf Hitler greet each other at the Munich conference. [LCID: 74614]](/images/small/0fcb90e8-79de-436a-b8e8-a4bb761ee4ab.jpeg)
July 15, 1937
Buchenwald Concentration Camp Opens
The first prisoners arrive at the Buchenwald concentration camp near Weimar, Germany.

November 08, 1937
Antisemitic Exhibition Opens in Munich
Joseph Goebbels and Julius Streicher open the antisemitic exhibition Der Ewige Jude (The Eternal Jew) at the library of the German Museum in Munich, Germany.
![Nazi officials attend the opening of "Der ewige Jude" (The Eternal Jew), an antisemitic exhibition in Munich. [LCID: 44201]](/images/small/6409121f-9414-4122-ae35-fd1f94227b8d.jpg)
March 11–13, 1938
German Annexation of Austria
On March 11–13, 1938, Nazi Germany took over and annexed Austria in an event known as the Anschluss.
![The Loos Haus building in Vienna decorated with signs encouraging Austrian incorporation into greater Germany. [LCID: 64403]](/images/small/dc7ba6b3-8d7b-4a07-866d-54d6e07545ea.jpg)
March 14, 1938
Helen Baker Diary Entry
An American woman describes what she witnessed as Hitler entered Vienna.

March 14, 1938
Winston Churchill speaks before the House of Commons
Days after Nazi Germany annexed Austria, Churchill delivers a warning about German aggression.
May 29, 1938
The First Jewish Law in Hungary
Hungary adopts a comprehensive anti-Jewish law, restricting the number of Jews in certain sectors of the economy.

July 06, 1938
Evian Conference
Delegates from 32 countries attend a conference in Evian, France, to discuss the growing refugee crisis.
![Delegates to the Evian Conference, where the fate of Jewish refugees from Nazi Germany was discussed. [LCID: 47173]](/images/small/cd4af96b-f86a-416a-9a8b-da8769352c56.jpeg)
August 17, 1938
Law on Alteration of Family and Personal Names
A new German law requires Jews bearing first names of “non-Jewish” origin to adopt an additional name: “Israel” for men and “Sara” for women.

September 15, 1938
Neville Chamberlain Meets with Hitler at Berchtesgaden
Chamberlain travels to Germany to negotiate with Hitler during the Sudetenland crisis.
![Czechoslovakia 1933, Sudetenland indicated [LCID: cze69080]](/images/small/f753b610-cbe2-44ad-b9d8-2b6a13795c57.gif)
September 29, 1938
Munich Agreement
Germany, Italy, Great Britain, and France sign the Munich agreement.
![British prime minister Neville Chamberlain (left), German chancellor Adolf Hitler (center), and French premier Edouard Daladier (right) ... [LCID: 13454]](/images/small/13069304-58d4-4f79-8bb1-110e8ec9b616.jpeg)
September 30, 1938
Chamberlain’s “Peace for Our Time” Speech
The British Prime Minister addresses the public after signing the Munich Agreement with Germany, Italy, and France.

October 05, 1938
German Jews' Passports Declared Invalid
The Reich Ministry of the Interior invalidates all German passports held by Jews. Jews must surrender their old passports, which will become valid only after the letter “J” has been stamped on them.

October 05, 1938
Churchill’s “Disaster of the First Magnitude” Speech
Member of Parliament Winston Churchill condemns the Munich Agreement.
November 09–10, 1938
Kristallnacht
In a nationwide anti-Jewish riot called Kristallnacht, Nazis and other Germans burned synagogues, vandalized Jewish homes and businesses, and assaulted or killed hundreds of Jews.

November 11, 1938
American Student Reflects
Robert Harlan witnessed Kristallnacht. He recorded his observations while traveling to help the parents of a Jewish friend whose house was ransacked.
November 12, 1938
Exclusion of Jews from German Economic Life
A new German decree closes all Jewish-owned businesses.
![Windows of a Jewish-owned business in Berlin painted with the word "Jude" (Jew). [LCID: 00239]](/images/small/6675e69f-1c67-4213-bdb2-3a724f708a49.jpg)
December 02, 1938
First Kindertransport Arrives in Great Britain
In desperation, Jewish parents send their unaccompanied children abroad to escape Nazi persecution.

December 08, 1938
Himmler Decree on “Combating the Gypsy Plague”
Heinrich Himmler orders that Nazi Germany’s policies regarding Roma and Sinti should be developed according to Nazi racial principles.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.