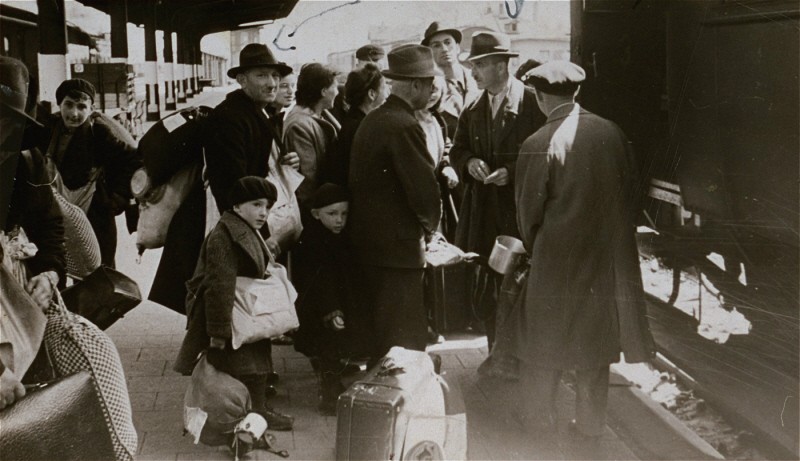

Theresienstadt
The Theresienstadt "camp-ghetto" existed for three and a half years, between November 24, 1941 and May 9, 1945. During its existence, Theresienstadt served three purposes:
- Theresienstadt served as a transit camp for Czech Jews whom the Germans deported to killing centers, concentration camps, and forced-labor camps in German-occupied Poland, Belorussia, and the Baltic States.
- It was a ghetto-labor camp. The SS deported and then incarcerated there certain categories of German, Austrian, and Czech Jews, based on their age, disability as a result of past military service, or domestic celebrity in the arts and other cultural life. To disguise the physical annihilation of the Jews deported from the Greater German Reich, the Nazi regime employed the general fiction, primarily inside Germany, that the deported Jews would be deployed at productive labor in the East. Since it seemed implausible that elderly Jews could be used for forced labor, the Nazis used Theresienstadt to hide the nature of the deportations.
- Theresienstadt served as a holding pen for Jews in the above-mentioned groups. It was expected that the poor conditions there would hasten the deaths of many deportees, until the SS and police could deport the survivors to killing centers in the East.

Theresienstadt served as a “settlement,” an assembly camp, and a concentration camp. It had recognizable features of both ghettos and concentration camps. In its function as a tool of deception, Theresienstadt was unique.
Nazi Deception
Theresienstadt served an important propaganda function for the Germans. The publicly stated purpose for the deportation of the Jews from Germany was their "resettlement to the east," where they would be compelled to perform forced labor. Since it seemed implausible that elderly Jews could be used for forced labor, the Nazis used the Theresienstadt ghetto to hide the nature of the deportations. In Nazi propaganda, Theresienstadt was cynically described as a "spa town" where elderly German Jews could "retire" in safety. The deportations to Theresienstadt were, however, part of the Nazi strategy of deception. The ghetto was in reality a collection center for deportations to ghettos and killing centers in Nazi-occupied eastern Europe.
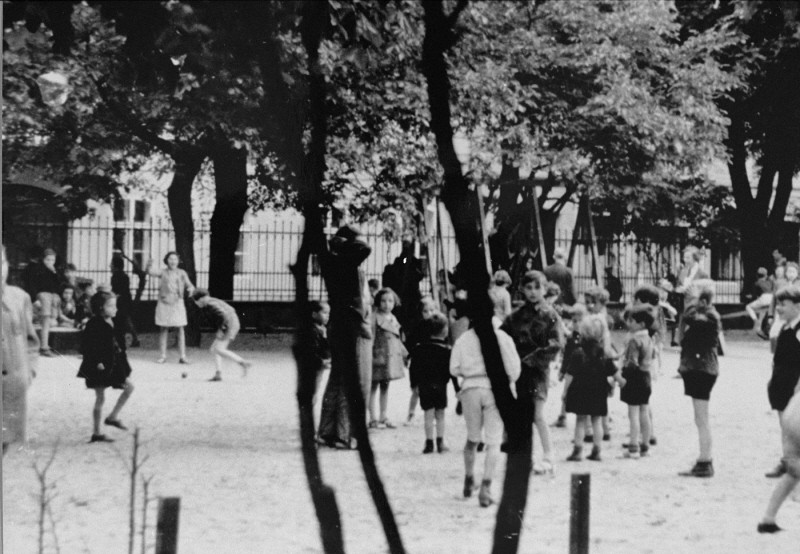
Succumbing to pressure following the deportation of Danish Jews to Theresienstadt, the Germans permitted the International Red Cross to visit in June 1944. It was all an elaborate hoax. The Germans intensified deportations from the ghetto shortly before the visit, and the ghetto itself was "beautified." Gardens were planted, houses painted, and barracks renovated. The Nazis staged social and cultural events for the visiting dignitaries. Once the visit was over, the Germans resumed deportations from Theresienstadt, which did not end until October 1944.
Deportations from Theresienstadt
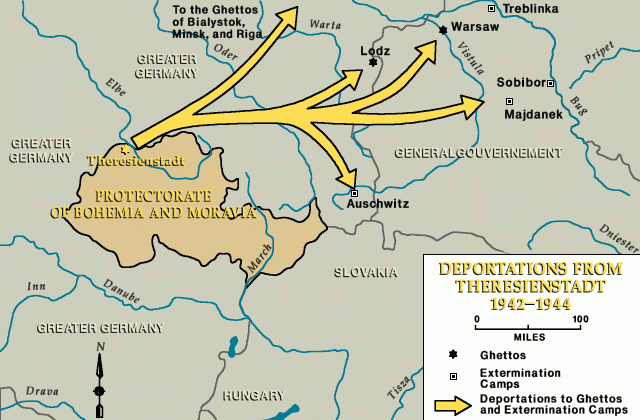
Beginning in 1942, SS authorities deported Jews from Theresienstadt to other ghettos, concentration camps, and killing centers in Nazi-occupied eastern Europe. German authorities either murdered the Jews upon their arrival in the ghettos of Riga, Warsaw, Lodz, Minsk, and Bialystok, or deported them further to killing centers. Transports also left Theresienstadt directly for the extermination camps of Auschwitz, Majdanek, and Treblinka. In the ghetto itself, tens of thousands of people died, mostly from disease or starvation. In 1942, the death rate within the ghetto was so high that the Germans built—to the south of the ghetto—a crematorium capable of handling almost 200 bodies a day.
Of the approximately 140,000 Jews transferred to Theresienstadt, nearly 90,000 were deported to points further east and almost certain death. Roughly 33,000 died in Theresienstadt itself.
Cultural Life at Theresienstadt
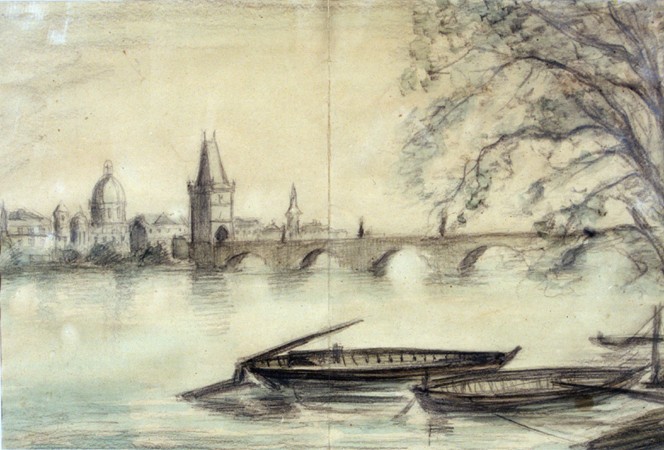

Despite the terrible living conditions and the constant threat of deportation, Theresienstadt had a highly developed cultural life. Outstanding Jewish artists, mainly from Czechoslovakia, Austria, and Germany, created drawings and paintings, some of them clandestine depictions of the ghetto's harsh reality. Writers, professors, musicians, and actors gave lectures, concerts, and theater performances. The ghetto maintained a lending library of 60,000 volumes.
Fifteen thousand children passed through Theresienstadt. Although forbidden to do so, they attended school. They painted pictures, wrote poetry, and otherwise tried to maintain a vestige of normalcy. Approximately 90 percent of these children perished in killing centers.
Conditions in the camp were harsh. Potatoes were as valuable as diamonds. I was hungry, scared and sick most of the time. For my eighth birthday, my parents gave me a tiny potato cake with a hint of sugar; for my ninth birthday, an outfit sewn from rags for my doll; and for my tenth birthday, a poem written by my mother.
—Inge Auerbacher
Critical Thinking Questions
- What was the role of Theresienstadt in the Nazi strategy of deception? How was it different from the majority of concentration camps and ghettos?
- Did other camps have multiple purposes? If so, what were they?
- Investigate the artwork produced in such extreme circumstances. What can be learned about the prisoners from their creations?
- Euphemisms, mild or indirect words or expressions substituted for ones considered to be too harsh or blunt, can hide dangerous or illegal behavior. What expressions did the Nazis use to disguise their intentions or policies?
- Review the visit to this camp by the Danish and International Red Cross delegations. How and why was the reality of the camp disguised from them?

