You searched for: usd交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建used交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建ivkcss1pgu
<< Previous | Displaying results 1691-1700 of 1782 for "usd交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建used交易程序後臺源碼【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建ivkcss1pgu" | Next >>
-
Hanne Hirsch Liebmann describes a Children's Aid Society (OSE) visit and life in Le Chambon-sur-Lignon
Oral HistoryHanne's family owned a photographic studio. In October 1940, she and other family members were deported to the Gurs camp in southern France. In September 1941, the Children's Aid Society (OSE) rescued Hanne and she hid in a children's home in Le Chambon-sur-Lignon. Her mother perished in Auschwitz. In 1943, Hanne obtained false papers and crossed into Switzerland. She married in Geneva in 1945 and had a daughter in 1946. In 1948, she arrived in the United States.

-
Julian Noga describes conditions in Flossenbürg
Oral HistoryJulian's Catholic parents had settled in the United States, but his mother returned to Poland. In 1939, Julian was deported to Austria to do farm labor after he was caught for hiding a rifle. On the farm he met the landowner's daughter, Frieda, his future wife. He was arrested in 1941 because relationships between Austrians and Poles were considered illegal and in 1942 he was deported to the Flossenbürg camp in Germany. During a forced march in 1945, he was liberated by US forces. Julian and Freida…

-
Henny Fletcher Aronsen describes living conditions in the Kovno ghetto
Oral HistoryHenny was born into an upper-middle-class Jewish family in Kovno, Lithuania. She and her brother attended private schools. In June 1940 the Soviets occupied Lithuania, but little seemed to change until the German invasion in June 1941. The Germans sealed off a ghetto in Kovno in August 1941. Henny and her family were forced to move into the ghetto. Henny married in the ghetto in November 1943; her dowry was a pound of sugar. She survived several roundups during which some of her friends and family were…

-
Abraham Lewent describes hiding during a raid in which his mother and sisters were seized for deportation from Warsaw to Treblinka
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Ruth Berkowicz Segal describes finding her father in Vilna after he fled Soviet-occupied eastern Poland
Oral HistoryWhen German forces invaded Poland in September 1939, Ruth's father fled to eastern Poland. Upon the Soviet occupation of eastern Poland, he fled to Lithuania. Ruth left Warsaw with two friends to find her father and later joined him in Vilna. After Soviet forces occupied Lithuania, Ruth and her father obtained transit visas for Japan, but only Ruth obtained a Soviet exit visa. Her father insisted she leave and not wait for him. Ruth traveled by the Trans-Siberian Railroad across the Soviet Union to…

-
Herbert A. Friedman describes finding two child survivors after liberation
Oral HistoryHerbert graduated from Yale in 1938. He became a rabbi and worked very closely with American Jewish leader Stephen S. Wise. He became a chaplain in the US Army during World War II. In the spring of 1945, he went to Europe. When the war ended, he was recruited by David Ben-Gurion into the Aliyah Bet ("illegal" immigration) operation of the Hagana. This involved smuggling Jews from eastern Europe through Germany to Palestine. He worked with displaced persons, mainly in Berlin and the American zone of…

-
Susan Bluman describes items she took with her when she left Warsaw
Oral HistorySusan was 19 years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Her boyfriend, Nathan, was in Lvov when the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland. Nathan sent a guide to Warsaw to bring Susan to the Soviet zone of occupied Poland. Her parents reluctantly agreed after Susan promised to return to Warsaw within two weeks. Upon her arrival in Lvov, Susan married Nathan. The couple then fled across the Lithuanian border to Vilna, where they stayed for a year. They received a visa for transit through Japan…
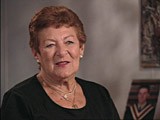
-
Felix Horn describes postwar emigration with the Brihah movement and adjustment to life after the war
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Cecilie Klein-Pollack describes survival with her sister in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryCecilie was the youngest of six children born to a religious, middle-class Jewish family. In 1939, Hungary occupied Cecilie's area of Czechoslovakia. Members of her family were imprisoned. The Germans occupied Hungary in 1944. Cecilie and her family had to move into a ghetto in Huszt and were later deported to Auschwitz. Cecilie and her sister were chosen for forced labor; the rest of her family was gassed upon arrival. Cecilie was transferred to several other camps, where she labored in factories. Allied…

-
Thomas Buergenthal describes being reprieved from a massacre of children while he was in a forced-labor camp in Kielce
Oral HistoryThomas's family moved to Zilina in 1938. As the Slovak Hlinka Guard increased its harassment of Jews, the family decided to leave. Thomas and his family ultimately entered Poland, but the German invasion in September 1939 prevented them from leaving for Great Britain. The family ended up in Kielce, where a ghetto was established in April 1941. When the Kielce ghetto was liquidated in August 1942, Thomas and his family avoided the deportations to Treblinka that occurred in the same month. They were sent…

