
1940: Key Dates
February 12
German authorities deport approximately 1,000 German Jews from Stettin and other eastern German cities to Lublin District in the Generalgouvernement.
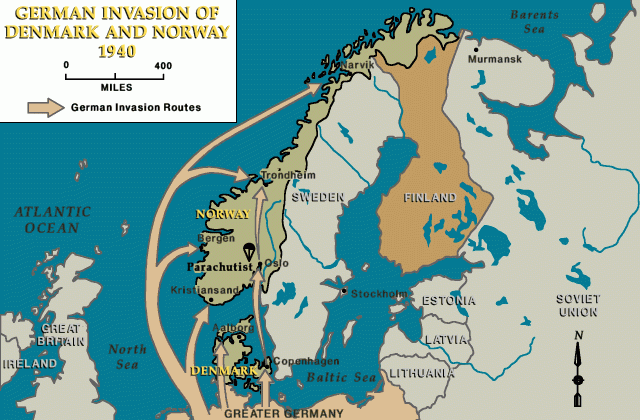
April 9
German forces invade Norway and Denmark.
April 30
German authorities seal the first major Jewish ghetto in Lodz, in District Wartheland.
May 10
German forces invade the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and France. By June 22, Germany will occupy all of these regions except for southern (Vichy) France.
May 20
SS authorities establish the Auschwitz concentration camp (Auschwitz I) outside the Polish city of Oswiecim, located in German-annexed Upper Silesia.
June 4
Having established Neuengamme as a subcamp of Sachsenhausen concentration camp in mid-December 1938, the SS Inspectorate of Concentration Camps designates the subcamp, located on the outskirts of the German city of Hamburg, an autonomous concentration camp.
June 10
Italy enters the war as an ally of Germany.
June 15-August 6
The Soviet Union occupies and incorporates the Baltic States (Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania), as Soviet Republics, into the USSR.
June 28
With German encouragement, the Soviet Union annexes the eastern provinces of Romania, Northern Bukovina and Bessarabia (today: Moldova).
July 16-July 30
German authorities expel more than 3,000 Alsatian Jews from Alsace to southern (Vichy) France.
August 30
Axis partners Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy arbitrate the fate of the Romanian province of Transylvania between Romania and Hungary, awarding northern Transylvania to Hungary. One week later, on September 6, Romanian King Carol II abdicates his throne over this issue, leaving power in the hands of an unstable coalition of the Romanian army under General Ion Antonescu and the fascist Legion of the Archangel Michael (also known as the Iron Guard) under Horia Sima.
September
Vichy French authorities establish or convert refugee camps in the south of France to detention camps for Jews and political prisoners. Among the best known of these camps are Gurs and Rivesaltes.
September 20
The first prisoners, including stateless Jews, arrive at the Breendonk detention camp, outside Antwerp in Belgium.
September 27
Germany, Italy, and Japan sign the Tripartite Pact, in which these countries promise mutual assistance if any one of the signatories is attacked by a country not already involved in the war.
November 15
German authorities order the Warsaw ghetto in the Generalgouvernement to be sealed. It is the largest ghetto in both area and population, confining more than 350,000 Jews (about 30 percent of the city's population) in an area of about 1.3 square miles, or 2.4 percent of the city's total area. At times, before the deportations of July 1942 begin, the actual population in Warsaw ghetto approaches 500,000.
November 20-24
Hungary (November 20), Romania (November 23), and Slovakia (November 24) sign the Tripartite Pact and became Axis partners. Bulgaria follows suit on March 1, 1941; the so-called Independent State of Croatia joins on June 15, 1941.

December 18
Hitler signs the first operational order for the planned German invasion of the Soviet Union.
Critical Thinking Questions
- Why did the Nazis resort to a system of ghettos?
- How do German actions against the Jews in 1940 illustrate the systematic and bureaucratic nature of the assault on the Jews of Europe?

