<< Previous | Displaying results 3326-3350 of 6772 for "" | Next >>
Shortly after taking power in January 1933, Adolf Hitler and the Nazis took control of German newspapers, detailing how the news was to be reported.

The April 1, 1933, boycott of Jewish-owned businesses marked the beginning of a nationwide campaign by the Nazi Party against the entire German Jewish population.

Nazi ideology aimed to promote the myth of an ideal national community and label those who were to be excluded from it as enemies. Propaganda was essential in promoting such myths.

Learn about the provisions and impact of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, including the "War Guilt Clause" which held Germany responsible for starting World War I.
Anne Frank is among the most well-known of the six million Jews who died in the Holocaust. Discover who Anne Frank was and what happened to her.

The Diary of Anne Frank is often the first exposure readers have to the history of the Holocaust. Learn about Anne's diary, including excerpts and images.

Börgermoor was part of the Nazi regime’s early system of concentration camps. It was located in the Emsland region of Prussia.
Ghettos separating Jews from the rest of the population were part of the Nazi plan to destroy Europe's Jews. Read about ghettoization during the Holocaust.

Adolf Hitler established himself as absolute Führer, or leader, of the Nazi Party by 1921. Learn more about Hitler in the years 1919-1924.

Under Adolf Hitler, the Nazi regime was responsible for the mass murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other victims. Learn about Hitler in the years 1924-1930.

Under Adolf Hitler's leadership, the Nazi regime was responsible for the mass murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other victims. Learn about Hitler in the years 1930-1933.

The German invasion of Poland in the fall of 1939 triggered WWII. Learn more about key dates and events, causes, and related Holocaust history.

Survivors of the Holocaust faced huge obstacles in rebuilding their lives. Learn about the challenges they faced in the aftermath of the Holocaust.

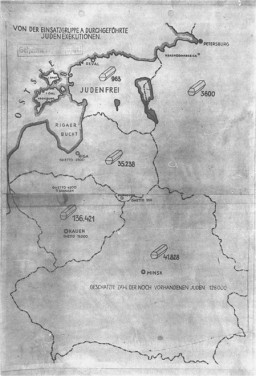
Einsatzgruppen, often called “mobile killing units,” are best known for their role in the murder of Jews in mass shooting operations during the Holocaust.
The liberation of concentration camps toward the end of the Holocaust revealed unspeakable conditions. Learn about liberators and what they confronted.

Germany started World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, by invading Poland. War would continue until 1945. Learn more about WWII and genocide in Europe.

The search for refuge frames both the years before the Holocaust and its aftermath. Learn about obstacles refugees faced when searching for safe havens.

The Third Reich began with the Nazi rise to power in 1933 and ended with the German surrender in 1945. Learn more about Nazi Germany during World War II.

Children were especially vulnerable to Nazi persecution. Learn more about the fates of Jewish and non-Jewish children.

Nazi Germany and its allies established over 44,000 concentration camps and incarceration sites during the Holocaust. Read about the Nazi camp system.

The term Final Solution to the Jewish Question was a euphemism used by Nazi Germany’s leaders. It referred to the mass murder of Europe’s Jews.

The United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941, following the attack on Pearl Harbor. Learn more about World War II in the Pacific.

As Allied forces approached Nazi camps in the last months of WWII, the SS organized brutal “death marches” (forced evacuations) of concentration camp inmates.

Thousands of Nazi criminals were never arrested. Learn more about the postwar efforts to bring Nazi perpetrators to justice.

German physicians conducted inhumane experiments on prisoners in the camps during the Holocaust. Learn more about Nazi medical experiments during WW2.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.