You searched for: ���������������������������������������������������������������������cxfk69���just
<< Previous | Displaying results 126-150 of 572 for "���������������������������������������������������������������������cxfk69���just" | Next >>
-
Miriam Lewent describes conditions in Siberia
Oral HistoryMiriam and her family fled their home when the Germans invaded Poland in 1939. They were interned by Soviet forces and deported to Siberia. Near the city of Tomsk, Miriam cut trees to earn food rations. When the Soviet Union went to war with Germany in June 1941, the Soviets released Miriam and her family. They sold their Red Cross rations for train fare and intended to return to Poland, but most of the family settled in Kazakhstan during the rest of the war. There, her father taught Hebrew to Jewish…

-
Gerda Weissmann Klein describes her birthday celebration in the Bielsko ghetto
Oral HistoryIn 1939, Gerda's brother was deported for forced labor. In June 1942, Gerda's family was deported from the Bielsko ghetto. While her parents were transported to Auschwitz, Gerda was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp system, where for the remainder of the war she performed forced labor in textile factories. Gerda was liberated after a death march, wearing the ski boots her father insisted would help her to survive. She married her American liberator.

-
Abraham Lewent describes food shortages after the invasion of Warsaw
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Steven Springfield describes 1945 death march from Burggraben in the Stutthof camp system
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied Riga in 1941, and confined the Jews to a ghetto. In late 1941, at least 25,000 Jews from the ghetto were massacred at the Rumbula forest. Steven and his brother were sent to a small ghetto for able-bodied men. In 1943 Steven was deported to the Kaiserwald camp and sent to a nearby work camp. In 1944 he was transferred to Stutthof and forced to work in a shipbuilding firm. In 1945, Steven and his brother survived a death march and were liberated by Soviet forces.

-
Lucille Szepsenwol Camhi describes obtaining Japanese transit visas from Chiune Sugihara in Kovno
Oral HistoryLucille's father died three months before she was born. Lucille's mother decided to immigrate to the United States with Lucille and her sister, Fejga. They completed all the paperwork, but were unable to get their final papers because of the German invasion of Poland in 1939. Volozhin was in the Soviet-occupied zone of Poland. Lucille and her sister feared arrest by the Soviets because they were members of a Jewish Zionist youth group. The girls fled to Vilna, where their mother later joined them. Their…

-
Mayer Adler describes surviving as a child in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryMayer grew up in a rural town that was occupied by Hungary in 1940. After Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944, Mayer and his family were forced into a ghetto. They were then deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland, where Mayer's parents and brothers perished. Mayer was selected for forced labor, and was later transferred to a satellite camp of Dachau, in Germany. He was liberated from Dachau in 1945. Sponsored by a children's committee, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Liny Pajgin Yollick describes fleeing to France from Antwerp
Oral HistoryIn May 1940, the Germans occupied the Netherlands. In 1942, it took Liny, her mother, and her sister six months to escape to southern France. They pretended to be Protestant, obtained visas to travel through Spain and Portugal, and were on one of the last trains to cross into Spain after the Germans took over southern France. They boarded a Portuguese ship bound for Dutch Guiana (Suriname). Liny was placed in a refugee camp, and then worked in the Dutch embassy in Washington D.C. She eventually settled in…

-
Leo Melamed describes going to school in prewar Bialystok
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Preben Munch-Nielsen describes the Danish people's responsibility to help their Jewish fellow citizens
Oral HistoryPreben was born to a Protestant family in Snekkersten, a small fishing village. The Germans invaded Denmark in 1940. Preben became a courier in the resistance. When the Gestapo (German Secret State Police) began hunting down Jews in Denmark in October 1943, Preben helped hide refugees in houses near the shore and led them to boats which took them to Sweden. Preben himself had to take refuge in Sweden in November 1943. He returned to Denmark in May 1945.

-
Ruth Meyerowitz describes deportation to and conditions in Ravensbrück
Oral HistoryIn Frankfurt, Ruth's family faced intensifying anti-Jewish measures; her father's business was taken over and Ruth's Jewish school was closed. In April 1943, Ruth and her family were deported to Auschwitz. Ruth was forced to work on road repairs. She also worked in the "Kanada" unit, sorting possessions brought into the camp. In November 1944, Ruth was transferred to the Ravensbrueck camp system, in Germany. She was liberated in May 1945, during a death march from the Malchow camp.

-
Darrell Romjue describes how US troops encoutered camps such as Mauthausen
Oral HistoryDarrell Romjue is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
Ernest G. Heppner describes learning about the Holocaust and the fate of his relatives
Oral HistoryErnest's family owned a factory that made matzah, the unleavened bread eaten during Passover. In February 1939, three months after Kristallnacht (the "Night of Broken Glass" pogroms), Ernest and his mother fled to Shanghai, one of few havens for refugees without visas. His father and sister stayed behind in Germany; they perished during the Holocaust. A brother escaped to England. Ernest and his mother found work in Shanghai. In 1947, he came to the United States with his wife, whom he met and married in…

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes how her teddy bear was given his name
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
William (Welek) Luksenburg describes the first night of the German invasion of Poland
Oral HistoryShortly after the German invasion of Poland in September 1939, William's family was ordered into a ghetto and his brother went to a work camp. William bribed officials to discharge his brother from a hospital destined for evacuation to Auschwitz. Later, after escaping from a prison camp to tend to his brother, William was jailed. He was sent to Blechhammer, Gleiwitz (where he met his future wife), and other camps. William collapsed during a death march near the Austrian border, but was then liberated. His…

-
Leo Schneiderman describes conditions in the Lodz ghetto
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. Leo and his family were confined to a ghetto in Lodz. Leo was forced to work as a tailor in a uniform factory. The Lodz ghetto was liquidated in 1944, and Leo was deported to Auschwitz. He was then sent to the Gross-Rosen camp system for forced labor. As the Soviet army advanced, the prisoners were transferred to the Ebensee camp in Austria. The Ebensee camp was liberated in 1945.

-
US nurse Pat Lynch describes caring for starving and critically ill camp survivors
Oral HistoryPat was one of thousands of US nurses who served in evacuation hospitals during the liberation of concentration camps in Europe. She cared for camp survivors, many of whom were in critical condition upon liberation.

-
US nurse Pat Lynch describes treating survivors in a subcamp of Dachau
Oral HistoryPat was one of thousands of US nurses who served in evacuation hospitals during the liberation of concentration camps in Europe. She cared for camp survivors, many of whom were in critical condition upon liberation.

-
Lily Mazur Margules describes death march from a labor camp near Stutthof
Oral HistoryLily was forced into a ghetto after the Germans occupied Vilna in 1941. She was forced to work until the liquidation of the ghetto in 1943 when she was deported to the Kaiserwald camp near Riga, Latvia. From there she was sent to work in the Duenawerke labor camp. She was deported by ship across the Baltic Sea to the Stutthof camp and was taken to a nearby labor camp. Lily was liberated during a death march which ended in the town of Krumau, East Prussia, in 1945.

-
Barbara Ledermann Rodbell describes Anne Frank's parents
Oral HistoryDescribes Anne Frank's parents

-
Hans Heimann describes internment in Italy
Oral HistoryThe Germans annexed Austria in March 1938. In 1939, Hans fled first to Hungary and then to Italy. He and his parents were interned in various towns. Hans's father became ill and died in 1940. In 1943, Hans and his mother were warned of German plans to deport Jews from Italy to Poland. They moved to smaller towns until liberation by the British in August 1943. Hans worked as an interpreter for the Allies until 1945, when he worked for the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee and helped resettle…

-
The Treatment of Soviet POWs: Starvation, Disease, and Shootings, June 1941–January 1942
ArticleThe Nazi treatment of Soviet prisoners of war (POWs) was determined by Nazi ideology. Cruel conditions included starvation, no medical care, and death.

-
The Nazification of the German Police, 1933–1939
ArticleThe Nazis utilized the German police for mass repression and genocide. Learn more about the Nazification of the police force from 1933-1939.

-
Oskar Schindler
ArticleOskar Schindler's actions to protect Jews during the Holocaust saved over 1,000 Jews from deportation. Learn more about Schindler's List.
-
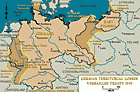
Treaty of Versailles
ArticleLearn about the provisions and impact of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, including the "War Guilt Clause" which held Germany responsible for starting World War I.
-
Railcar: Interior
ArtifactMany different kinds of railway cars were used for deportations. They varied in size and weight. The railway car on display in the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum's Permanent Exhibition is of just one type used. The dimensions of the railway car in the Museum's exhibition are as follows: Total length 31 feet 6 inches (9.6 meters); interior space for deportees 26 feet 2 inches (8 meters). Total height 14 feet (4.3 meters) from the bottom of the wheel to the highest point of the car; interior space…

