Poking Pine City Displaced Persons Camp
For the Jews who survived the Holocaust, the end of World War II brought new challenges. Many could not or would not return to their former homelands, and options for legal immigration were limited. In spite of these difficulties, these Jewish survivors sought to rebuild their shattered lives by creating flourishing communities in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. In an unparalleled six-year period between 1945 and 1951, European Jewish life was reborn in camps such as Poking Pine City.
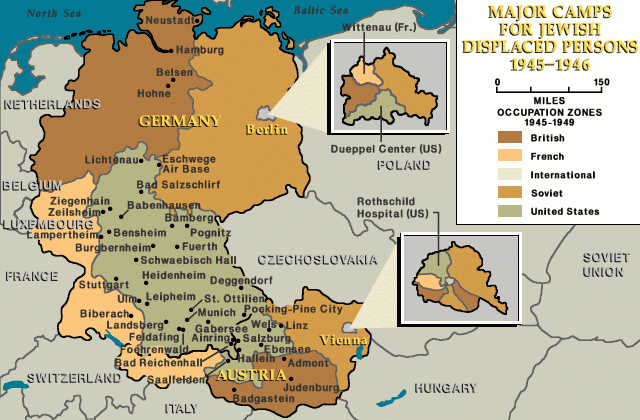
Located in the Bamberg district, Poking Pine City was the second largest displaced persons (DP) camp in Germany after Belsen. Opened in January 1946, the camp reached its maximum of 7,645 Jewish inhabitants on October 19, 1946.
The camp had several Talmud Torahs (religious elementary schools) with more than 200 pupils, as well as a Lubavitcher and a Klausenburger Yeshiva with a combined 500 pupils.
Poking Pine City’s cultural department featured theaters and sports clubs. A kosher kitchen for serving 200 people was also installed.
The camp closed on February 16, 1949.
Critical Thinking Questions
- What challenges did survivors face in the DP camps?
- What challenges did the Allies face in establishing and supervising DP camps?
- What responsibilities do (or should) other nations have regarding refugees from war and genocide?

