<< Previous | Displaying results 2901-2950 of 6719 for "" | Next >>
-
Students and members of the SA during the book burning in Berlin
PhotoStudents and members of the SA with armfuls of literature deemed "un-German" during the book burning in Berlin. Germany, May 10, 1933.

-
A book burning in Hamburg
PhotoIn Hamburg, members of the SA and students from the University of Hamburg burn books they regard as "un-German." Hamburg, Germany, May 15, 1933.

-
Book burning in Berlin
PhotoAt Berlin's Opernplatz (Opera Square), an SA man throws books into the flames at the public burning of books deemed "un-German." This image is a still from a motion picture. Berlin, Germany, May 10, 1933.

-
Public burning of "un-German" books in Berlin
PhotoPublic burning of "un-German" books in the Opernplatz (Opera Square) in Berlin. Students, some in SA uniform, march in a torchlight procession. Berlin, May 10, 1933.

-
Joseph Goebbels speaks during book burning
PhotoJoseph Goebbels, German propaganda minister, speaks on the night of book burning. Berlin, Germany, May 10, 1933.

-
Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels speaks during the book burning
PhotoPropaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels (at podium) praises students and members of the SA for their efforts to destroy books deemed "un-German" during the book burning at Berlin's Opernplatz (opera square). Germany, May 10, 1933.

-
Gavra Mandil celebrates his fourth birthday
PhotoGavra Mandil celebrates his fourth birthday with his parents, Mosa and Gabriela, and sister Irena. Novi Sad, Yugoslavia, September 6, 1940.

-
Yugoslav Jews in hiding
PhotoMr. Mandil and his son Gavra, Yugoslav Jews, while in hiding. The Mandil family escaped to Albania in 1942. After the German occupation in 1943, Mandil's Albanian apprentice hid the family, all of whom survived. Albania, between 1942 and 1945.
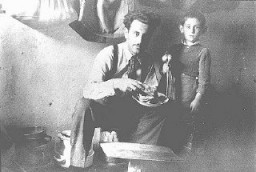
-
Sephardic synagogue in Berlin
PhotoAn interior view of the Sephardic synagogue on Luetzowstrasse. Berlin, Germany, before November 1938.

-
Bertolt Brecht
PhotoBertolt Brecht, author of the "Threepenny Opera" and a well-known leftist poet and dramatist, who emigrated from Germany in 1933. In exile, he co-edited an anti-Nazi magazine titled Das Wort. London, Great Britain, 1936.

-
Bertolt Brecht
PhotoBertolt Brecht (left), Marxist poet and dramatist, was a staunch opponent of the Nazis. He fled Germany shortly after Hitler's rise to power. Pictured here with his son, Stefan. Germany, 1931.

-
Lion Feuchtwanger in New York
PhotoAuthor Lion Feuchtwanger in New York, November 17, 1932. Feuchtwanger's 1930 novel Erfolg (Success) provided a thinly veiled criticism of the Beer Hall Putsch and Hitler's rise to leadership in the Nazi Party. He was targeted by the Nazis. After the Nazi takeover on January 30, 1933, his house in Berlin was illegally searched and his library was plundered during his lecture tour in the United States.

-
Lion Feuchtwanger arriving in New York
PhotoLion Feuchtwanger aboard the ship Excalibur, arriving in New York. United States, October 1940.

-

-
Helen Keller
PhotoPortrait of Helen Keller, ca. 1910. In 1933, Nazi students at more than 30 German universities pillaged libraries in search of books they considered to be "un-German." Among the literary and political writings they threw into the flames were the works of Helen Keller.

-
Portrait of Ernest Hemingway
PhotoErnest Hemingway in his World War I Red Cross Ambulance Corps uniform, ca. 1918.

-
Ernest Hemingway
PhotoPortrait of Ernest Hemingway by Helen Pierce Breaker. Paris, France, ca. 1928. In 1933, Nazi students at more than 30 German universities pillaged libraries in search of books they considered to be "un-German." Among the literary and political writings they threw into the flames were the works of Ernest Hemingway.

-
Cover of A Farewell to Arms
PhotoCover of Ernest Hemingway's A Farewell to Arms. (1929 cover. Princeton University Library.) In 1933, Nazi students at more than 30 German universities pillaged libraries in search of books they considered to be "un-German." Among the literary and political writings they threw into the flames during the book burning were the works of Ernest Hemingway.

-
Hemingway on a safari
PhotoAmerican novelist Ernest Hemingway on safari, ca. 1933. In 1933, Nazi students at more than 30 German universities pillaged libraries in search of books they considered to be "un-German." Among the literary and political writings they threw into the flames were the works of Ernest Hemingway.

-
Ernest Hemingway
PhotoAuthor Ernest Hemingway aboard the boat Pilar, ca. 1950. In 1933, Nazi students at more than 30 German universities pillaged libraries in search of books they considered to be "un-German." Among the literary and political writings they threw into the flames were the works of Ernest Hemingway.

-
American novelist Ernest Hemingway
PhotoErnest Hemingway, among the greatest American novelists, was a member of the "Lost Generation" of expatriate writers who were disillusioned by war. In 1933 the Nazis burned Hemingway's novels as part of the public book burning in Berlin. United States, ca. 1950.

-
Hidden child Gitta Rosenzweig
PhotoDuring a roundup for deportation in eastern Poland in 1942, Gitta Rosenzweig—then three or four years old—was sent into hiding. She ended up in a Catholic orphanage. In 1946, Ida Rosenshtein, a family friend and a survivor, learned of the child's whereabouts and sought to claim her. After denying that it held a Jewish child, the orphanage relinquished custody after Ida recognized Gitta and a local Jewish committee paid a "redemption" fee. Gitta is pictured here on the day she left the orphanage.

-
Portrait of Tsewie Herschel taken while he was living in hiding
PhotoPortrait of Tsewie Herschel seated in a chair, taken while he was living in hiding. Oosterbeek, the Netherlands, 1943–1944. Tsewie never knew his parents. Born in December 1942, he was hidden with the de Jong family in April 1943. That July, his parents were deported from the Netherlands to the Sobibór killing center. The de Jongs renamed Tsewie "Henkie," raised him as a Christian, and treated him as their son. Tsewie learned about his origins from his paternal grandmother, who reclaimed him…

-
Portrait of three-year-old Estera Horn
PhotoPortrait of three-year-old Estera Horn wrapped in a fur coat. Chelm, Poland, ca. 1940. Estera was born in January 1937. Her father was killed soon after the Germans invaded Poland. Estera and her mother, Perla Horn, were forced into the ghetto in Chelm. At the end of 1942, during the liquidation of the ghetto, Perla and Estera escaped from the ghetto. They hid in nearby villages. In late 1943, Perla asked a family in Plawnice to take care of Estera. Perla tried to hide with a group of Jews in the nearby…

-
Gavra Mandil class photo
PhotoGavra Mandil and his family narrowly escaped death in German-held Yugoslavia by fleeing to Italian-occupied Albania. There Gavra attended a school in Kavaja that had both Muslim and Christian pupils. He is seated on the far right in the first row. June 1943.

-
Hidden child in the Netherlands
PhotoJewish child Hans van den Broeke (born Hans Culp) in hiding in the Netherlands. He is 2 years old in this photograph.

-
Hiding under a different religion
PhotoSome Jewish children survived the Holocaust because they were protected by people and institutions of other faiths. Children quickly learned to master the prayers and rituals of their "adopted" religion in order to keep their Jewish identity hidden from even their closest friends. This photograph shows two hidden Jewish children, Beatrix Westheimer and her cousin Henri Hurwitz, with Catholic priest Adelin Vaes, on the occasion of Beatrix's First Communion. Ottignies, Belgium, May 1943.

-
Augusta Feldhorn in hiding
PhotoAugusta Feldhorn stands next to a nun while in hiding. Augusta, a Jewish child, was in hiding under an assumed Christian identity. Belgium. 1942-1945.

-
Page from the diary of Eugenia Hochberg
PhotoA page from the diary of Eugenia Hochberg, written while she was living in hiding in Brody, Poland. The page contains a timeline of important events that happened during the war, such as deaths and deportations of family and friends. Brody, Poland, July 1943–March 1944.

-
Suse Grunbaum at age one
PhotoPhotograph taken in December 1932 of Suse Grunbaum at age one. Soon after Hitler's 1933 seizure of power in Germany, two-year-old Suse and her parents fled to the Netherlands and settled in the town of Dinxperlo. In 1943, Jews in German-occupied Dinxperlo were ordered to assemble for deportation. Hearing of these plans, the Grünbaums went into hiding, finding refuge with Dutch farmers. The Hartemink family hid Suse and her mother for two years in their barn, first under the floorboards, then in a…

-
Lida Kleinman
PhotoPortrait of a young Jewish girl, Lida Kleinman sitting in her room in Lacko, Poland, 1935. In January 1942, Lida was sent into hiding. She hid under false identities in Catholic orphanages until the end of the war.

-
Henrietta and Herman Goslinski
PhotoIn 1942, Henrietta and Herman Goslinski went into hiding to avoid deportation from the Netherlands. Their rescuer could not, however, also take their infant daughter Berty. The Dutch resistance moved Berty frequently; she was eventually moved more than 30 times. During the two-and-a-half years apart, the parents saw Berty only once and received this single photograph of her taken while she was in hiding.

-
Jewish girls in hiding in a convent
PhotoA group of Jewish girls hiding, under assumed identities, in a convent. Ruiselede, Belgium, 1943-44.

-
Dawid Tennenbaum in hiding
PhotoIn 1942, eleven-year-old Dawid Tennenbaum went into hiding with his mother, settling in the Lvov region as Christians. Dawid disguised himself as a girl and as mentally disabled. This exempted him from attending school and prevented his being exposed.

-
Sisters Eva and Liane Münzer
PhotoSisters Eva and Liane Münzer. They were placed in hiding with a devout Catholic couple. In 1944, Eva and Liane were reported to the police as a result of a fight between their rescuers. The husband denounced his wife and the two Jewish girls. The three were immediately arrested and sent to the Westerbork camp. On February 8, 1944, eight- and six-year-old Eva and Liane were deported to Auschwitz, where they were murdered. Photograph taken in The Hague, the Netherlands, 1940.

-
Pierre Laval
PhotoPierre Laval, head of the government of Vichy France and Nazi collaborator. Shown here delivering a radio address. France, 1941–42.

-
Arrival of Jewish refugees from Germany
PhotoArrival of Jewish refugees from Germany. The Joint Distribution Committee (JDC) helped Jews leave Germany after the Nazi rise to power. France, 1936.

-
Seeking refuge in Argentina
PhotoA Jewish passenger prays on board a refugee ship from Germany bound for Argentina in 1938.

-
Jewish refugee children leave Berlin
PhotoJewish refugee children look out of the train window as they leave Berlin. They were on a Kindertransport from Germany. Schlesischen train station, Berlin, Germany, November 29-30, 1938.

-
Delegates to the Evian Conference
PhotoDelegates to the Evian Conference, where the fate of Jewish refugees from Nazi Germany was discussed. US delegate Myron Taylor is third from left. France, July 1938.

-
Site of the Evian Conference
PhotoThe Hotel Royal, site of the Evian Conference on Jewish refugees from Nazi Germany. Evian-les-Bains, France, July 1938.

-
The Evian Conference on Jewish refugees
PhotoThe Evian Conference on Jewish refugees. From left to right are French delegate Henri Berenger, United States delegate Myron Taylor, and British delegate Lord Winterton. France, July 8, 1938.

-
Arriving in New York
PhotoA group of German and Austrian Jewish refugee children arrives in New York on board the SS President Harding. New York, United States, June 3, 1939.

-
Looking out from the St. Louis
PhotoGerman Jewish refugees look through portholes of the St. Louis, in Havana harbor. Cuba refused to let the passengers disembark. Cuba, May or June, 1939.

-
German Jewish women wearing the compulsory Jewish badge
PhotoTwo German Jewish women wearing the compulsory Jewish badge. Germany, September 27, 1941.

-
Jewish couple wearing mandatory Jewish badges
PhotoA Jewish couple wearing the mandatory Jewish badge walks along a street in a German city. Germany, September 27, 1941.

-
Wearing the compulsory Jewish badge
PhotoAn elderly German Jewish woman wearing the compulsory Jewish badge. Berlin, Germany, September 27, 1941.

-
Jewish women at forced labor
PhotoJewish women deported from Bremen, Germany, are forced to dig a trench at the train station. Minsk, Soviet Union, 1941. (Source record ID: E9 NW 33/IV/2)

-
Poster in Hebrew for army recruitment and rescue efforts
PhotoA poster in Hebrew soliciting contributions from members of the Yishuv (the Jewish community of Palestine) for army recruitment and for efforts to rescue European Jewry. The Hebrew text reads "Give a hand in rescue, the Fund for Recruitment and Rescue." Palestine, July 22, 1943.

-
The refugee ship Pentcho
PhotoThis photograph shows the refugee ship Pentcho, carrying over 500 passengers bound for Palestine, sailing in the Aegean Sea. It had departed from Bratislava on May 18, 1940. In October 1940, while the Pentcho was sailing in Italian territory, its boiler exploded. The passengers and crew were able to get ashore and offload their supplies before the ship finally sank. On October 18 and 19, Italian authorities picked up the refugees and took them to Rhodes. They stayed there for over a year in a…

