You searched for: Ghettos
<< Previous | Displaying results 1126-1150 of 1236 for "Ghettos" | Next >>
-
Berta Koselova Krakauerova
ID CardBerta was born to a Jewish family. Orphaned when she was a child, she was raised by her Uncle Poldi in Vienna. In 1899 she married Bernard Krakauer, a Jewish businessman from her hometown of Mikulov. As was the custom for orphans, Berta wore a black dress at her wedding. The couple settled in the town of Hodonin, where Bernard opened a dry goods and clothing store. They raised six children. 1933-39: With their children grown, Berta's husband retired in 1938. He sold the business and moved with Berta and…
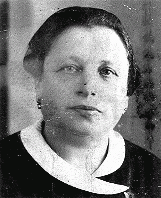
-
Felix Krakauer
ID CardFelix was one of six children born to Jewish parents in a small Moravian town, where his father ran a dry goods and clothing store. The family spoke Czech and German at home and Felix attended German-language schools. As a youth, he belonged to a Zionist club and liked to ski. He graduated from an international trade school in Vienna before settling down in the Moravian capital of Brno. 1933-39: During the 1930s Felix married a Christian woman from the town of Hodonin. When Felix's father retired in 1938,…

-
Judith Schwed
ID CardJudith was the older of two children born to Jewish parents in the town of Kiskunfelegyhaza in southeastern Hungary. Her mother, Anna, and her mother's sister, Kornelia, were close in age and had a contest to see who would be the first to have a baby. Judith's Aunt Kornelia won the contest and cousin Maria was born in December 1931, just three weeks before Judith. 1933-39: Judith's father had a prosperous wholesale business that sold goose meat, down, feathers and quilts. In 1939, the same year that…

-
Jocheved Kuzda Kasher
ID CardJocheved, or Jadza as she was called at home, was born in the industrial city of Lodz, Poland's second-largest city. Before the war, one-third of Lodz's inhabitants were Jewish. The Kuzdas kept a traditional Jewish home and placed importance on their children's education. Jocheved had two older sisters, Sarah and Regina. 1933-39: Jocheved was 9 when the war broke out in September 1939. Instead of starting school, she stayed at home listening to the bombs exploding. Her father and sister tried to get to…
-
A chart detailing physical characteristics of a Romani (Gypsy) individual
DocumentA chart detailing physical characteristics of a Romani (Gypsy) individual, c. 1938. Dr. Robert Ritter and his team created extensive family trees and genealogical charts in order to identify, register, and classify all Romani people living in Nazi Germany. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial…

-
Hana Mueller Bruml describes forced labor at Sackisch, a subcamp of Gross-Rosen
Oral HistoryIn 1942, Hana was confined with other Jews to the Theresienstadt ghetto, where she worked as a nurse. There, amid epidemics and poverty, residents held operas, debates, and poetry readings. In 1944, she was deported to Auschwitz. After a month there, she was sent to Sackisch, a Gross-Rosen subcamp, where she made airplane parts at forced labor. She was liberated in May 1945.

-
Bart Stern describes torture of prisoners during Hanukkah and a subsequent act of resistance to celebrate Hanukkah
Oral HistoryFollowing the German occupation of Hungary in March 1944, Bart was forced into a ghetto established in his home town. From May to July 1944, the Germans deported Jews from Hungary to the Auschwitz killing center in occupied Poland. Bart was deported by cattle car to Auschwitz. At Auschwitz, he was selected to perform forced labor, drilling and digging in a coal mine. As Soviet forces advanced toward the Auschwitz camp in January 1945, the Germans forced most of the prisoners on a death march out of the…

-
Helen Lebowitz Goldkind describes treatment of new prisoners at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryVolosianka was annexed by Hungary in 1939 and occupied by the Germans in 1944. Helen was about 13 when she and her family were deported to the Uzhgorod ghetto. They were then deported to various camps. Helen and her older sister survived Auschwitz, forced labor at a camp munitions factory, and Bergen-Belsen. When Helen was too weak to move, her sister would support her during roll call and drag her to work, knowing that labor was the only chance for survival.

-
Frima L. describes how her Holocaust experiences affect her life today
Oral HistoryWhile Frima's family was confined to a ghetto, Nazis used her father as an interpreter. He later perished. By pretending not to be Jews, Frima, her mother, and sister escaped a German mobile killing unit massacre. They were later discovered and jailed. Again, her mother devised an escape. Frima's mother and sister were smuggled to Romania, while Frima wandered in search of safekeeping until her mother could arrange to smuggle her out. In Romania, they were reunited and liberated.

-
Sam Spiegel describes life in a displaced persons camp
Oral HistoryIn 1942, Sam was forced into a ghetto in his hometown and assigned to work in a munitions factory. In 1944 he was transported to Auschwitz and then forced to work in a train factory. He survived eight days on a death march after the evacuation of Auschwitz by the Nazis. He was liberated by Soviet units in January 1945. He lived in a displaced persons camp in Germany where worked for the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration. In 1947, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Kate Bernath describes the psychology of survival in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryAfter the German invasion of Hungary in 1944, Kate and her family were deported first to the Kosice ghetto and then to the Auschwitz camp in Poland. Kate and other prisoners were sent on to the Plaszow camp, also in Poland. As partisan raids increased and the front drew closer, they were sent back to Auschwitz in August 1944. Kate was then selected for forced labor at a Messerschmidt factory in Augsburg, Germany. The prisoners were deported as Allied attacks intensified. Kate was eventually liberated after…

-
Mayer Adler describes surviving as a child in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryMayer grew up in a rural town that was occupied by Hungary in 1940. After Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944, Mayer and his family were forced into a ghetto. They were then deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland, where Mayer's parents and brothers perished. Mayer was selected for forced labor, and was later transferred to a satellite camp of Dachau, in Germany. He was liberated from Dachau in 1945. Sponsored by a children's committee, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Mayer Adler describes his family's preparations for deportation
Oral HistoryMayer grew up in a rural town that was occupied by Hungary in 1940. After Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944, Mayer and his family were forced into a ghetto. They were then deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland, where Mayer's parents and brothers perished. Mayer was selected for forced labor, and was later transferred to a satellite camp of Dachau, in Germany. He was liberated from Dachau in 1945. Sponsored by a children's committee, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Murray Pantirer describes one of Oskar Schindler's rescue efforts
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied Krakow in 1939. Murray's family was confined to the Krakow ghetto along with the rest of the Jewish population of the city. In 1942, Murray and a brother were deported for forced labor in the nearby Plaszow camp. In May 1944, his brother was transferred to Auschwitz and Murray was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp in Germany. Murray was later transferred to Bruennlitz, in the Sudetenland, as a forced laborer for German industrialist Oskar Schindler. Schindler helped the Jews who worked for…

-
Murray Pantirer describes the "Schindler Jews" in the Bruennlitz factory
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied Krakow in 1939. Murray's family was confined to the Krakow ghetto along with the rest of the Jewish population of the city. In 1942, Murray and a brother were deported for forced labor in the nearby Plaszow camp. In May 1944, his brother was transferred to Auschwitz and Murray was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp in Germany. Murray was later transferred to Bruennlitz, in the Sudetenland, as a forced laborer for German industrialist Oskar Schindler. Schindler helped the Jews who worked for…

-
Leopold Page describes meeting German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

-
Sam Itzkowitz describes a death march from Landsberg, a subcamp of Dachau, to the Bavarian Alps
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. When Makow was occupied, Sam fled to Soviet territory. He returned to Makow for provisions, but was forced to remain in the ghetto. In 1942, he was deported to Auschwitz. As the Soviet army advanced in 1944, Sam and other prisoners were sent to camps in Germany. The inmates were put on a death march early in 1945. American forces liberated Sam after he escaped during a bombing raid.

-
Irene Hizme describes medical experiments at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryIrene and Rene were born Renate and Rene Guttmann. The family moved to Prague shortly after the twins' birth, where they were living when the Germans occupied Bohemia and Moravia in March 1939. A few months later, uniformed Germans arrested their father. Decades later, Irene and Rene learned that he was killed at the Auschwitz camp in December 1941. Irene, Rene, and their mother were deported to the Theresienstadt ghetto, and later to the Auschwitz camp. At Auschwitz, the twins were separated and subjected…

-
Rene Slotkin describes medical experiments at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryRene and his twin sister Irene were born Rene and Renate Guttman. The family moved to Prague shortly after the twins' birth, where they were living when the Germans occupied Bohemia and Moravia in March 1939. A few months later, uniformed Germans arrested their father. Decades later, Rene and Irene learned that he was killed in the Auschwitz camp in December 1941. Rene, Irene, and their thier mother were deported to the Theresienstadt ghetto, and later to Auschwitz. There, the twins were separated and…

-
Hana Mueller Bruml describes arrival procedures at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryIn 1942, Hana was confined with other Jews to the Theresienstadt ghetto, where she worked as a nurse. There, amid epidemics and poverty, residents held operas, debates, and poetry readings. In 1944, she was deported to Auschwitz. After a month there, she was sent to Sackisch, a Gross-Rosen subcamp, where she made airplane parts at forced labor. She was liberated in May 1945.

-
Dorotka (Dora) Goldstein Roth describes retaliation against women for an escape from Stutthof
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, Dora's family fled to Vilna, Lithuania. When the Germans occupied Vilna, Dora's father was shot and the rest of the family was confined in the Vilna ghetto. Dora, her sister, and her mother were deported to the Kaiserwald camp in Latvia and then to the Stutthof concentration camp near Danzig. Her mother and sister perished in Stutthof. Dora herself was shot immediately before liberation, but she survived.

-
Morris Kornberg describes forced labor beginning after the German invasion of Poland
Oral HistoryMorris grew up in a very religious Jewish household and was active in a Zionist sports league. When the Germans invaded Poland in September 1939, Morris's town was severely damaged. Morris's family was forced to live in a ghetto, and Morris was assigned to forced labor. After a period of imprisonment in Konskie, a town about 30 miles from Przedborz, Morris was deported to the Auschwitz camp. He was assigned to the Jawischowitz subcamp of Auschwitz. In January 1945, Morris was forced on a death march and…

-
Boleslaw Brodecki describes hangings in a labor camp and their impact on the prisoners
Oral HistoryBoleslaw and his older sister were raised in a Jewish section of Warsaw. The Germans attacked Warsaw in September 1939. Boleslaw's father did not want to leave his ill relatives behind, so Boleslaw and his sister escaped on a train heading for the Soviet border. The Germans invaded Soviet territories in 1941, and in 1942 Boleslaw was imprisoned in a forced-labor camp. He was deported to the Theresienstadt ghetto, where he was liberated by Soviet forces in 1945.

-
Sam Spiegel describes conditions in a forced-labor camp
Oral HistoryIn 1942, Sam was forced into a ghetto in his hometown and assigned to work in a munitions factory. In 1944 he was transported to Auschwitz and then forced to work in a train factory. He survived eight days on a death march after the evacuation of Auschwitz by the Nazis. He was liberated by Soviet units in January 1945. He lived in a displaced persons camp in Germany where worked for the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration. In 1947, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Leopold Page describes an act of sabotage and clandestinely listening to radio broadcasts while in Bruennlitz
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

