You searched for: bergen-belsen
<< Previous | Displaying results 161-170 of 193 for "bergen-belsen" | Next >>
-
Charles (Karel) Bruml
ID CardCharles was born to a Jewish family in Prague, the capital of Czechoslovakia. His father owned several shoe factories there. Prague's Jewish minority enjoyed a great deal of cultural freedom because of the new democratic Republic. Though antisemitism still existed in Czechoslovakia, Prague was a relatively tolerant city. 1933-39: Charles' father's business thrived in Prague, and they lived well. Charles enjoyed painting as a child and decided to study at an art school in the city. On the morning of March…

-
Genya Rotenberg
ID CardGenya and her brother, Nahum, were raised by Jewish parents in Lodz, Poland's second-largest city and an industrial center. Before the war, one-third of Lodz's inhabitants were Jewish. Genya's parents placed emphasis on their children's education. 1933-39: In 1939, when Genya was 9, the Germans occupied Lodz. After that, it was forbidden for "Jews, Gypsies and dogs" to be in public places. Since Jews weren't allowed to go to school, her parents arranged to tutor her secretly at home, but she couldn't keep…
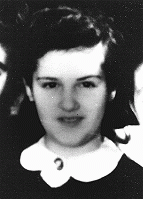
-
Helen Lebowitz Goldkind describes German humiliation of her grandfather in the Uzhgorod ghetto
Oral HistoryIn 1938-39, Hungary annexed the area of Czechoslovakia in which Helen lived. After Germany occupied Hungary in 1944, Helen and her family were deported to the Uzhgorod ghetto. As Jews, they were soon transferred to various camps, where much of the family perished. Although at times Helen was too weak to walk, she and her older sister survived Auschwitz, forced labor at a camp munitions factory, and Bergen-Belsen.

-
Rifka Muscovitz Glatz describes emotions surrounding the establishment of the state of Israel
Oral HistoryRifka was raised in a religious family in Debrecen. In the early 1940s, her family moved to Cluj (Kolozsvar) in Northern Transylvania, annexed to Hungary from Romania in 1940. In 1944, she and her family were forced to leave their house in Cluj. They were rounded up by Hungarian troops helping the Nazis and taken to a brick factory where they stayed for a month. In June 1944, Rifka was transported to the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp. Eight months later she was transported to Switzerland. She sailed to…

-
Fela Warschau describes reading lists of names to find surviving family members
Oral HistoryFela was liberated at Bergen-Belsen by the British army in 1945. She went to a displaced persons (DP) camp administered by the Americans in Feldafing, near Munich. She married in the DP camp in 1946, and eventually immigrated to the United States.

-
Helen Lebowitz Goldkind describes treatment of new prisoners at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryVolosianka was annexed by Hungary in 1939 and occupied by the Germans in 1944. Helen was about 13 when she and her family were deported to the Uzhgorod ghetto. They were then deported to various camps. Helen and her older sister survived Auschwitz, forced labor at a camp munitions factory, and Bergen-Belsen. When Helen was too weak to move, her sister would support her during roll call and drag her to work, knowing that labor was the only chance for survival.

-
Bella Jakubowicz Tovey describes antisemitic remarks made as she was forced to march into the Graeben camp
Oral HistoryBella was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in Sosnowiec. Her father owned a knitting factory. After the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, they took over the factory. The family's furniture was given to a German woman. Bella was forced to work in a factory in the Sosnowiec ghetto in 1941. At the end of 1942 the family was deported to the Bedzin ghetto. Bella was deported to the Graeben subcamp of Gross-Rosen in 1943 and to Bergen-Belsen in 1944. She was liberated in April 1945.

-
Ruth Moser Borsos describes forced-labor assignments in Westerbork
Oral HistoryRuth moved to the Netherlands after Kristallnacht (the "Night of Broken Glass") in 1938. She and her father had permits to sail to the United States, but Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940 and they could not leave. Ruth was deported to the Westerbork camp in 1943 and to the Bergen-Belsen camp in Germany in 1944. After an exchange agreement with the Allies broke down, Ruth was interned near the Swiss border until liberation by French forces in 1945.

-
Ruth Moser Borsos describes the process of selection for deportations from Westerbork to Auschwitz
Oral HistoryRuth moved to the Netherlands after Kristallnacht (the "Night of Broken Glass") in 1938. She and her father had permits to sail to the United States, but Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940 and they could not leave. Ruth was deported to the Westerbork camp in 1943 and to the Bergen-Belsen camp in Germany in 1944. After an exchange agreement with the Allies broke down, Ruth was interned near the Swiss border until liberation by French forces in 1945.

-
Bella Jakubowicz Tovey describes the confiscation of her family's property
Oral HistoryBella was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in Sosnowiec. Her father owned a knitting factory. After the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, they took over the factory. The family's furniture was given to a German woman. Bella was forced to work in a factory in the Sosnowiec ghetto in 1941. At the end of 1942 the family was deported to the Bedzin ghetto. Bella was deported to the Graeben subcamp of Gross-Rosen in 1943 and to Bergen-Belsen in 1944. She was liberated in April 1945, and…

