<< Previous | Displaying results 91-100 of 1017 for "" | Next >>
Learn more about the end of Nazi tyranny in Europe and the liberation of camps and other sites of Nazi crimes. This article includes dates of liberation of some of the camps.

Between 1933-1939, Nazi eugenics and racial hygiene led to policies like mass sterilization and criminalizing marriage between Jews and non-Jews.

The Protocols of the Elders of Zion is the most widely distributed antisemitic publication of modern times. Although repeatedly discredited, it continues to circulate.

After WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Foehrenwald DP camp.

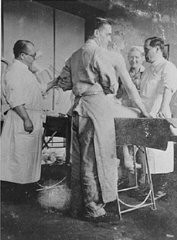
Carl Clauberg, one of many German doctors involved in Nazi crimes, conducted medical experiments at Auschwitz toward developing a method of mass sterilization. Learn more.
Adolf Hitler's Nazi aimed to purify the genetic makeup of the German population through measures known as racial hygiene or eugenics.

Based on their ideas about race, the Nazis mass murdered people with disabilities; people perceived as threats in occupied Poland; and Jewish people. Learn more.

After WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Eschwege DP camp.

After WWII, many Holocaust survivors, unable to return to their homes, lived in displaced persons camps in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Read about Bergen-Belsen DP camp.

Halle an der Saale was a satellite camp of Buchenwald concentration camp. It was established by the Nazis in Saxony, Germany in 1941.
We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.