You searched for: poland
<< Previous | Displaying results 1401-1450 of 1568 for "poland" | Next >>
-
Leo Melamed describes train ride across the Soviet Union
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Alexander Schenker describes working as a lumberjack in a labor camp in Siberia
Oral HistoryFollowing the German invasion of Poland in September 1939, Alexander and his family fled eastward to Lvov. His father then fled to Vilna, hoping to obtain visas for the family to escape through Japan. The rest of the family was caught while trying to cross border into Lithuania in order to meet up with Alexander's father. They returned to Lvov. Alexander and his mother were later arrested for refusing to declare Soviet citizenship. They were sent to a labor camp in the Soviet interior. After their release…

-
Francis Akos describes experiences in the immediate aftermath of the Holocaust
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans occupied Hungary in March 1944, Francis was deported to Neuengamme, a concentration camp located on the outskirts of Hamburg, Germany. Later, as Allied forces advanced, Francis and other prisoners were transported from Neuengamme. They were placed on a cargo ship which sailed into Luebeck Bay, where the prisoners were crowded onto the "Cap Arcona." The "Cap Arcona" and other ships were bombed in early May 1945. Francis was rescued and came ashore in the German town of Neustadt, where…

-
Mayer Adler describes surviving as a child in Auschwitz
Oral HistoryMayer grew up in a rural town that was occupied by Hungary in 1940. After Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944, Mayer and his family were forced into a ghetto. They were then deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland, where Mayer's parents and brothers perished. Mayer was selected for forced labor, and was later transferred to a satellite camp of Dachau, in Germany. He was liberated from Dachau in 1945. Sponsored by a children's committee, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Mayer Adler describes his family's preparations for deportation
Oral HistoryMayer grew up in a rural town that was occupied by Hungary in 1940. After Germany occupied Hungary in March 1944, Mayer and his family were forced into a ghetto. They were then deported to the Auschwitz camp in Poland, where Mayer's parents and brothers perished. Mayer was selected for forced labor, and was later transferred to a satellite camp of Dachau, in Germany. He was liberated from Dachau in 1945. Sponsored by a children's committee, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Leopold Page describes meeting German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

-
Ludmilla Page describes German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Sam Itzkowitz describes a death march from Landsberg, a subcamp of Dachau, to the Bavarian Alps
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. When Makow was occupied, Sam fled to Soviet territory. He returned to Makow for provisions, but was forced to remain in the ghetto. In 1942, he was deported to Auschwitz. As the Soviet army advanced in 1944, Sam and other prisoners were sent to camps in Germany. The inmates were put on a death march early in 1945. American forces liberated Sam after he escaped during a bombing raid.

-
Leo Melamed describes going to school in prewar Bialystok
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Leo Melamed describes speaking several languages as a child in prewar Bialystok
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Leo Melamed describes the German occupation of Bialystok
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Leo Melamed describes fear after German occupation of Bialystok
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Leo Melamed describes fleeing by train from Bialystok to Vilna
Oral HistoryLeo was seven years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Before the war, Leo's father was a mathematics teacher and member of the Bialystok City Council. Fearing arrest, Leo's father fled Bialystok for Vilna just before the German occupation. Leo and his mother eventually joined his father in Vilna. After the Soviets occupied Vilna, Leo's father obtained transit visas to Japan. The family left Vilna in December 1940, traveled across the Soviet Union on the Trans-Siberian Express, and arrived…

-
Bella Jakubowicz Tovey describes antisemitic remarks made as she was forced to march into the Graeben camp
Oral HistoryBella was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in Sosnowiec. Her father owned a knitting factory. After the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, they took over the factory. The family's furniture was given to a German woman. Bella was forced to work in a factory in the Sosnowiec ghetto in 1941. At the end of 1942 the family was deported to the Bedzin ghetto. Bella was deported to the Graeben subcamp of Gross-Rosen in 1943 and to Bergen-Belsen in 1944. She was liberated in April 1945.

-
Dorotka (Dora) Goldstein Roth describes retaliation against women for an escape from Stutthof
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, Dora's family fled to Vilna, Lithuania. When the Germans occupied Vilna, Dora's father was shot and the rest of the family was confined in the Vilna ghetto. Dora, her sister, and her mother were deported to the Kaiserwald camp in Latvia and then to the Stutthof concentration camp near Danzig. Her mother and sister perished in Stutthof. Dora herself was shot immediately before liberation, but she survived.

-
Joseph Stanley Wardzala describes forced labor in Hannover
Oral HistoryJoseph and his family were Roman Catholics. After Germany invaded Poland in 1939, roundups of Poles for forced labor in Germany began. Joseph escaped arrest twice but the third time, in 1941, he was deported to a forced-labor camp in Hannover, Germany. For over four years he was forced to work on the construction of concrete air raid shelters. Upon liberation by US forces in 1945, the forced-labor camp was transformed into a displaced persons camp. Joseph stayed there until he got a visa to enter the…

-
Joseph Stanley Wardzala describes conditions at the forced-labor camp in Hannover
Oral HistoryJoseph and his family were Roman Catholics. After Germany invaded Poland in 1939, roundups of Poles for forced labor in Germany began. Joseph escaped arrest twice but the third time, in 1941, he was deported to a forced-labor camp in Hannover, Germany. For over four years he was forced to work on the construction of concrete air raid shelters. Upon liberation by US forces in 1945, the forced-labor camp was transformed into a displaced persons camp. Joseph stayed there until he got a visa to enter the…

-
Leo Bretholz describes arrival at the Drancy camp
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans annexed Austria in 1938, Leo attempted to flee. He eventually reached Belgium. In 1940 he was deported to the St.-Cyprien camp in France but escaped. In 1942 Leo was smuggled into Switzerland but was arrested and sent back to France, this time to the Rivesaltes and Drancy camps. He and a friend escaped from a train deporting them to Auschwitz in Poland. Leo joined the French underground in 1943. He arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
Leo Bretholz describes conditions in the Drancy camp
Oral HistoryAfter the Germans annexed Austria in 1938, Leo attempted to flee. He eventually reached Belgium. In 1940 he was deported to the St.-Cyprien camp in France but escaped. In 1942 Leo was smuggled into Switzerland but was arrested and sent back to France, this time to the Rivesaltes and Drancy camps. He and a friend escaped from a train deporting them to Auschwitz in Poland. Leo joined the French underground in 1943. He arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes conditions in the Westerbork camp in the Netherlands
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation--including the order to wear the Jewish…

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes deportations from the Westerbork camp in the Netherlands
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation—including the order to wear the…

-
Bella Jakubowicz Tovey describes conditions in Bergen-Belsen
Oral HistoryBella was the oldest of four children born to a Jewish family in Sosnowiec. Her father owned a knitting factory. After the Germans invaded Poland in 1939, they took over the factory. The family's furniture was given to a German woman. Bella was forced to work in a factory in the Sosnowiec ghetto in 1941. At the end of 1942 the family was deported to the Bedzin ghetto. Bella was deported to the Graeben subcamp of Gross-Rosen in 1943 and to Bergen-Belsen in 1944. She was liberated in April 1945, and…

-
Leopold Page describes an act of sabotage and clandestinely listening to radio broadcasts while in Bruennlitz
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

-
Ludmilla Page describes sabotage during production of munitions in Oskar Schindler's factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes a celebration of Oskar Schindler's birthday in Bruennlitz toward the end of the war
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes feeling different from other Polish children
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes her transition to living in London
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes how her teddy bear was given his name
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
Emanuel Tanay describes the establishment of the Miechow ghetto
Oral HistoryEmanuel and his family lived in the small town of Miechow, north of Krakow. After Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, persecution of Jews increased. The Germans established a ghetto in Miechow. Emanuel was forced to live in the ghetto. Emanuel, his mother, and his sister escaped from the ghetto before it was destroyed in 1942. He stayed in a monastery, under an assumed identity, along with members of the Polish underground. Emanuel left the monastery after about a year when a teacher began to suspect…

-
Leo Schneiderman describes conditions in the Lodz ghetto
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in September 1939. Leo and his family were confined to a ghetto in Lodz. Leo was forced to work as a tailor in a uniform factory. The Lodz ghetto was liquidated in 1944, and Leo was deported to Auschwitz. He was then sent to the Gross-Rosen camp system for forced labor. As the Soviet army advanced, the prisoners were transferred to the Ebensee camp in Austria. The Ebensee camp was liberated in 1945.

-
Abraham Klausner describes postwar efforts to reunite survivors
Oral HistoryRabbi Abraham Klausner was a US Army military chaplain. He arrived in the Dachau concentration camp in May 1945. He was attached to the 116th evacuation hospital unit and worked for about five years in displaced persons camps, assisting Jewish survivors.

-
Henry J. Kellermann describes the reactions of defendants during the Nuremberg Trial
Oral HistoryHenry received a Doctor of Law (J.D.) degree from the University of Berlin in 1937. Sponsored by the rabbi of the Baltimore Hebrew congregation, Henry immigrated to the United States in the same year. In 1945, the Office of Strategic Services (OSS) assigned him to prepare pre-trial briefs for the International Military Tribunal held in Nuremberg, Germany. He interrogated a number of witnesses and defendants. After the war, he held various diplomatic posts.

-
Sarah (Sheila) Peretz Etons describes her experiences as a child in hiding
Oral HistoryGermany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. After the German occupation, Sarah (then just three years old) and her mother were forced into a ghetto. One day, a Polish Catholic policeman warned them that the ghetto was about to be liquidated. He sheltered Sarah and her mother first in his house, then in a potato storage bunker, and then in a chicken coop on his property. Sarah hid there for more than two years, until the area was liberated by Soviet forces. After the war, Sarah emigrated from…

-
Morris Kornberg describes arrival at Auschwitz
Oral HistoryMorris grew up in a very religious Jewish household and was active in a Zionist sports league. When the Germans invaded Poland in September 1939, Morris's town was severely damaged. Morris's family was forced to live in a ghetto, and Morris was assigned to forced labor. After a period of imprisonment in Konskie, a town about 30 miles from Przedborz, Morris was deported to the Auschwitz camp. He was assigned to the Jawischowitz subcamp of Auschwitz. In January 1945, Morris was forced on a death march and…

-
Lilly Appelbaum Malnik describes death march from Auschwitz to Bergen-Belsen
Oral HistoryGermany invaded Belgium in May 1940. After the Germans seized her mother, sister, and brother, Lilly went into hiding. With the help of friends and family, Lilly hid her Jewish identity for two years. But, in 1944, Lilly was denounced by some Belgians and deported to Auschwitz-Birkenau via the Mechelen camp. After a death march from Auschwitz, Lilly was liberated at Bergen-Belsen by British forces.

-
Einsatzgruppen massacre sites in Ukraine and surrounding areas
MapIn the summer of 1941, following Germany's attack on the Soviet Union, the Germans began to perpetrate mass shootings of Jewish men, women, and children in territory seized from Soviet forces. These murders were part of the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question,” the mass murder of Europe’s Jews. Many of these mass shootings were organized and committed by task forces or special action groups, called Einsatzgruppen in German. Units of Einsatzgruppen followed the German army as it invaded the Soviet…
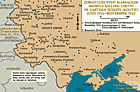
-
Miles Lerman describes the impact of his wartime experiences
Oral HistoryMiles Lerman was a Holocaust survivor, partisan fighter in the forests of Poland, international leader in the cause of Holocaust remembrance, and a "founding father" of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Hans Heimann describes internment in Italy
Oral HistoryThe Germans annexed Austria in March 1938. In 1939, Hans fled first to Hungary and then to Italy. He and his parents were interned in various towns. Hans's father became ill and died in 1940. In 1943, Hans and his mother were warned of German plans to deport Jews from Italy to Poland. They moved to smaller towns until liberation by the British in August 1943. Hans worked as an interpreter for the Allies until 1945, when he worked for the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee and helped resettle…

-
Guta Blass Weintraub describes Starachowice ghetto cultural life
Oral HistoryGuta and her family fled to Starachowice, Poland. There, the Germans ordered them and other Jews into a ghetto and put them to work in forced-labor factories. As an act of resistance at the Majowka camp, Guta attacked a Nazi guard preparing to shoot her and other prisoners at a mass grave. A bullet grazed her, but Guta pretended to be fatally wounded. Days later, Guta was deported to Auschwitz, then Ravensbrueck, where she was liberated. Her mother died only weeks short of freedom.

-
John Komski describes resistance activities in Krakow, including an underground newspaper
Oral HistoryJohn, who was born to a non-Jewish Polish family, graduated from an art academy. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, John was in Krakow. Food became scarce in Krakow, with long lines of people waiting for whatever food was available. John decided to join the resistance against the Germans. By early 1940, he and two of his friends felt that they were in danger and decided to try to escape to France. John was caught and arrested during this escape attempt. He survived imprisonment…

-
Resistance
Animated MapView an animated map describing acts of resistance to Nazi oppression, ranging from armed resistance to acts of spiritual preservation.
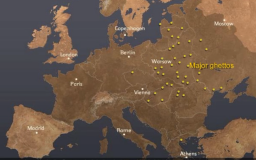
-
The Treatment of Soviet POWs: Starvation, Disease, and Shootings, June 1941–January 1942
ArticleThe Nazi treatment of Soviet prisoners of war (POWs) was determined by Nazi ideology. Cruel conditions included starvation, no medical care, and death.

-
Freemasonry under the Nazi Regime
ArticleNazi propaganda linked Jews and Freemasons and claimed there was a “Jewish-Masonic” conspiracy. Learn more about Freemasonry under the Nazi regime.

-
Auschwitz: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Auschwitz camp complex in German-occupied Poland.

-
Nazi Racism: In Depth
ArticleRacism, including racial antisemitism (prejudice against or hatred of Jews based on false biological theories), was an integral part of Nazism. Learn more
-
Third Reich
ArticleThe “Third Reich” is another name for Nazi Germany between 1933-1945. Learn more about life under Nazi rule before and during World War II.

-
World War I
ArticleThe experiences of World War I and its aftermath would profoundly shape the attitudes and actions of leaders and ordinary people during the Holocaust.

-
Kovno
ArticleKovno had a rich and varied Jewish culture. Learn about the Soviet and German occupations of Kovno, ghettoization, secret archives, and resistance in Kovno during WWII and the Holocaust.

-
Glossary of Terms and Individuals in the Nazi Judicial System
ArticleLearn more about the Holocaust Encyclopedia’s key terms and individuals in the Nazi judicial system.
-
Bulgaria
ArticleBulgaria joined the Axis alliance on March 1, 1941, after the Germans offered them Greek territory in Thrace. Learn about Bulgaria during WWII and the Holocaust.

