You searched for: ust众筹理财项目定制开发【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建unit众筹理财项目定制开发【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建gnogu7gctt
<< Previous | Displaying results 351-400 of 1751 for "ust众筹理财项目定制开发【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建unit众筹理财项目定制开发【tg���������@ek7676】平台包网搭建gnogu7gctt" | Next >>
-
US veteran Tarmo Holma describes encountering camp survivors
Oral HistoryTarmo Holma is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
Charles Torluccio describes liberation and the role of medical staff
Oral HistoryCharles Torluccio is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
German American Bund - Photographs
Media EssayThe German-American Bund was an antisemitic, pro-Nazi group for Americans of German descent.
-
Elie Wiesel speaks at a Days of Remembrance ceremony
PhotoElie Wiesel speaks at the Days of Remembrance ceremony, Washington, DC, 2001.

-
Elie Wiesel speaks at a Days of Remembrance ceremony
PhotoElie Wiesel speaks at the Days of Remembrance ceremony, Washington, DC, 2002.

-
Manzanar
PhotoManzanar relocation center for Japanese Americans, photographed by Ansel Adams. Bird's-eye view of the grounds from the guard tower.

-
Frances Perkins
PhotoSecretary of Labor Frances Perkins testifies before the House Committee on migrant workers. Washington D.C., December 1940.

-
Alice (Eberstarkova) Masters describes going to a home for refugee children in England after arriving on a Kindertransport
Oral HistoryAlice grew up in a small village in Czechoslovakia. She was the middle of three daughters in a well-to-do, close-knit family. Her parents were religious and active in the Jewish community. After the German annexation of parts of Czechoslovakia in March 1939, antisemitism became more pronounced. Alice's uncle, a businessman who had moved to Great Britain, helped her parents arrange to send Alice and her two sisters on a Kindertransport (Children's Transport) to Britain. The sisters lived in a children's…

-
On the waiting list for American visas
DocumentThis document from the American Consul-General in Vienna certifies that the Trost family applied for American visas on September 15, 1938. It states that the family (Josef, Alice, Dorrit, and Erika) were placed on the waiting list for visas with the numbers 47291-47294.

-
John D. Rastelli describes entering occupied Austria and burial of the dead in Mauthausen
Oral HistoryJohn D. Rastelli is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
US veteran Ross Snowdon describes the camp quarry and barracks and the burial of the dead in Mauthausen
Oral HistoryRoss Snowdon is a veteran of the 11th Armored Division. During the invasion of German-held Austria, in May 1945 the 11th Armored (the "Thunderbolt" division) overran two of the largest Nazi concentration camps in the country: Mauthausen and Gusen.

-
US veteran Robert Patton describes Mauthausen upon liberation and his 2000 visit to the same site
Oral HistoryRobert Patton, of Chapel Hill, North Carolina, was with the 65th Infantry Division.

-
Kurt Pauly
ID CardKurt was born to Jewish parents in the city of Aachen, where his mother's family had resided since the 18th century. His father, though trained as a chef, worked as a butcher and also managed several stores for his father-in-law. The Paulys lived over one of those shops in the nearby suburb of Eilendorf. Kurt enjoyed large family gatherings, where he would play with his cousins, Anne and Margot Frank. 1933–39: When the Nazis came to power in 1933, the situation drastically changed for the Paulys.…

-
US Army Medic POW Diary Entry
Timeline EventApril 2, 1945. On this date, Anthony Acevedo wrote in his diary about his experience as a prisoner of war.

-
Liberation of Bergen-Belsen
Media EssayThe Bergen-Belsen concentration camp was liberated by British forces on April 15, 1945. Approximately 50,000 people died at Bergen-Belsen during the camp's existence. When liberating troops entered the camp, they witnessed evidence of Nazi atrocitie...
-
Liberator Vernon Tott
PhotoLiberator Vernon Tott (second from left) of the 84th Infantry was honored by some of the survivors he helped free from the Ahlem labor camp near Hanover, Germany. Tott's name was engraved on the Museum's Donor's Lounge wall with the inscription: "In honor of Vernon W. Tott, my liberator & hero." The ceremony in which Tott's name was unveiled came as a complete surprise to him. Washington, DC, November 2003.

-
French leader Charles de Gaulle in London
PhotoFrench leader Charles de Gaulle in London after France signed an armistice with Germany on June 22, 1940. De Gaulle refused to accept the armistice and led the Free France resistance movement. London, Great Britain, June 25, 1940.

-
Liberated Soviet and Polish prisoners at Mauthausen
PhotoSoviet and Polish prisoners with disabilities stand in front of a tank of the 11th Armored Division, US Third Army. This photograph was taken at the Mauthausen concentration camp immediately after liberation. Austria, May 5–7, 1945.

-
Camera and equipment that belonged to a US soldier
PhotoThis camera equipment belonged to Walter Hunkler, a sergeant assigned to a medical detachment of the 160th Field Artillery Battalion, which entered Dachau on April 29, 1945. He took photographs documenting the camp and the prisoners found there.

-
Children's artwork created at Weir Courtney
Media EssayAfter the war, Alice Goldberger cared for 24 refugee children at Lingfield House on the Weir Courtney Estate in England. She attempted to create a typical childhood for this group of young survivors of the Holocaust. Artwork created by the children...

-
Newspaper article "The Refugee Tragedy"
DocumentSan Francisco Chronicle newspaper article titled "The Refugee Tragedy." The article was based on an interview with Moses Beckelman of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee, an aid organization. It discussed the overcrowding of Polish and Lithuanian refugees stranded in Shanghai, Kobe (Japan), and Lisbon (Portugal), all stops en route to North and South America. The primary cause of this bottleneck was a lack of transit and entry visas, a result of most countries closing their borders to…

-
American troops, including African American soldiers from the 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion
PhotoAmerican troops, including African American soldiers from the Headquarters and Service Company of the 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion, 8th Corps, US 3rd Army, view corpses stacked behind the crematorium during an inspection tour of the Buchenwald concentration camp. Among those pictured is Leon Bass (the soldier third from left). Buchenwald, Germany, April 17, 1945.

-
American Student Reflects
Timeline EventNovember 11, 1938. On this date, Robert Harlan wrote about what he witnessed during Kristallnacht.

-
Seward Daily Gateway, April 14, 1933
DocumentSeward Daily Gateway (Alaska) article from April 14, 1933, titled "Great Bonfires of Forbidden Books in Germany to Blaze." This article from Berlin, written the month before the book burnings took place, reported that "Great bonfires will be burning on the campus of German universities in a few days, when the latest Nazi decree goes into effect. The Hitler regime is continuing its nationalistic crusade, has ordered that all books which deal with non-German subjects or espouse non-German causes, must be…

-
Flag graphic for US 104th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 104th Infantry Division's flag. The US 104th Infantry Division (the "Timberwolf" division) was activated in 1942. During World War II, they captured the cities of Cologne and Halle. The division also overran Nordhausen and the Dora-Mittelbau concentration camp. The 104th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 10th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 10th Armored Division's flag. The US 10th Armored Division is also known as the "Tiger" division. During World War II, they captured the cities of Trier and Oberammergau. The division also overran a Dachau subcamp. The 10th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 11th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 11th Armored Division's flag. The US 11th Armored Division (the "Thunderbolt" division) was formed in 1942. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the cities of Coburg, Bayreuth, and Linz. The division also overran the Mauthausen and Gusen concentration camps. The 11th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust…

-
Flag graphic for US 12th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 12th Armored Division's flag. The US 12th Armored Divison is also known as the "Hellcats" division. During World War II, they captured the cities of Ludwigshafen and Würzburg. The division also overran a subcamp of Dachau. The 12th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 29th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 29th Infantry Division's flag. The US 29th Infantry Division (the "Blue and Gray" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day, as well as the liberation of Dinslaken civilian labor camp. The 29th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1995 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 30th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 30th Infantry Division's flag. The US 30th Infantry Division (the "Old Hickory" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and also liberated Weferlingen, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 30th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 2012 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 3rd Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 3rd Armored Division's flag. The US 3rd Armored Division (the "Spearhead" division) was established in 1941. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Cologne. The division also discovered the Dora-Mittelbau concentration camp. The 3rd Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 4th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 4th Infantry Division's flag. The US 4th Infantry Division (the "Ivy" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day, the liberation of Paris, and the Battle of the Bulge. The division also captured the city of Nuremberg and discovered a Dachau subcamp near Haunstetten. The 4th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1992 by the United States Army Center of Military History and…

-
Flag graphic for US 65th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 65th Infantry Division's flag. The US 65th Infantry Division (the "Battle Axe" division) was established in 1943. During World War II, they took the cities of Regensburg, Passau, and Linz. The division also overran a subcamp of the Flossenbürg concentration camp. The 65th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1994 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 69th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 69th Infantry Division's flag. The US 69th Infantry Division ("Fighting 69th") was established in 1943. During World War II, they captured the city of Leipzig and uncovered Leipzig-Thekla, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 69th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 80th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 80th Infantry Division's flag. The US 80th Infantry Division (the "Blue Ridge" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge. The division entered Buchenwald concentration camp and liberated Ebensee, a subcamp of Mauthausen. The 80th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust…

-
Flag graphic for US 83rd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 83rd Infantry Division's flag. The US 83rd Infantry Division (the "Thunderbolt" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Halle. The division also encountered Langenstein, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 83rd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States…

-
Flag graphic for US 86th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 86th Infantry Division's flag. The US 86th Infantry Division (the "Blackhawk" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they discovered the Attendorn civilian forced-labor camp. The 86th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1996 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 8th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 8th Armored Division's flag. The US 8th Armored Division is also known as the "Iron Snake" or "Thundering Herd" division. During World War II, they liberated Halberstadt-Zwieberge, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 8th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1995 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 95th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 95th Infantry Division's flag. The US 95th Infantry Division (the "Victory" Division) was established in 1942. During World War II, they captured the cities of Metz and Dortmund. The division also undercovered a German prison and civilian labor camp in Werl. The 95th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1995 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 99th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 99th Infantry Division's flag. The US 99th Infantry Division (the "Checkerboard" or "Battle Babies" division) was established in 1942. During World War II, they were invovled in the Battle of the Bulge and liberated a Dachau subcamp near Mühldorf. The 99th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1992 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 9th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 9th Armored Division's flag. The US 9th Armored Division was known as the "Phantom" division. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and also liberated Zwodau and Falkenau an der Eger, two subcamps of Flossenbürg. The 9th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Displaced Persons Act
Timeline EventJune 25, 1948. On this date, the US Congress passed the Displaced Persons Act. This allowed approximately 400,000 displaced persons to immigrate to the US.

-
Arriving in New York
PhotoChildren aboard the President Harding look at the Statue of Liberty as they pull into New York harbor. They were brought to the United States by Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus. New York, United States, June 1939.

-
Ernst Toller
PhotoErnst Toller, German dramatist and revolutionary, emigrated from Germany to other European nations and then to the United States. New York, United States, May 1939.

-
Arriving in New York
PhotoChildren aboard the President Harding look at the Statue of Liberty as they pull into New York harbor. They were brought to the United States by Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus. New York, United States, June 1939.

-
Children's art: Drawing of people in a garden
ArtifactAlice Goldberger (1897-1986) was born in Berlin, Germany. Trained as a youth-work instructor, she ran a shelter for disadvantaged children and their families. When Hitler came to power, Alice, who was Jewish, had to give up her post. She immigrated to England in 1939. When war broke out, Alice was interned on the Isle of Man as an enemy alien. While there, she organized a children's facility.Hearing of Alice's work in the camp, psychoanalyst Anna Freud (daughter of Sigmund Freud) intervened to secure her…

-
US veteran James Rose describes his impressions of Dachau upon liberation
Oral HistoryJames A. Rose, of Toledo, Ohio, was with the 42nd (Rainbow) Division.

-
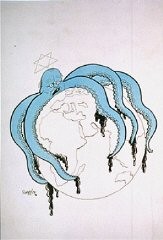
Nazi-era Antisemitic Propaganda Poster
PhotoNazi propaganda cartoon by Seppla (Josef Plank), a political cartoonist. Germany, date uncertain [probably during World War II]. Beginning in the 1920s, Nazi propagandists promoted the antisemitic myth that Jews were engaged in a massive conspiracy to take over the world. This false notion alleged that “international Jewry” used various people and groups as part of a plan for global conquest. At the time, an octopus extending its tentacles over the globe was a common visual metaphor for this…
-
Flag graphic for US 1st Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 1st Infantry Division's flag. The US 1st Infantry Division (the "Big Red One" division) was formed in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Allied invasions of North Africa and Italy, as well as D-Day and the Battle of the Bulge. Additionally, the division captured the city of Aachen and liberated Zwodau and Falkenau an der Eger, two subcamps of Flossenbürg. The 1st Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating…

-
Flag graphic for US 2nd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 2nd Infantry Division's flag. The US 2nd Infantry Division (the "Indianhead" division) was created in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day and the Battle of the Bulge. They also captured the cities of Leipzig and Hadamar. Additionally, the division overran Leipzig-Schönefeld, a subcamp of Buchenwald, and liberated prisoners at the Spergau/Zöschen camp. The 2nd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit…

