![A transport of Jewish prisoners marches through the snow from the Bauschovitz train station to Theresienstadt. [LCID: 69720]](https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/images/large/781755a6-1ba5-4d8e-8b2b-9f25bdf3687f.jpg)
Browse an alphabetical list of artifacts from the Holocaust and World War II. Each object tells a story about the history and demonstrates human experiences during the time period.
<< Previous | Displaying results 126-150 of 235 for "Artifact" | Next >>
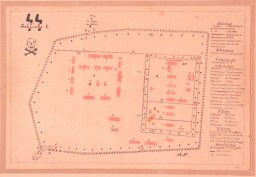
This map of the Treblinka I forced-labor camp was drawn by Holocaust survivor Manfred Kort in 1946. In 1990 Kort donated the map to the United States Holocaust Memorial Musem. In March 1997, at the request of the Office of Special Investigations, the Museum sent the original drawing to Chicago to be used as evidence at the trial of one Bronislaw Hajda. At the conclusion of Hajda's trial on April 10, 1997, the U.S. Department of Justice announced that "a federal judge in Chicago has revoked the naturalized…
During the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts a Japanese plane dropping a bomb on the U.S. and British flags. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

During the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts Japanese planes flying in formation over the U.S. and British flags, with the Japanese flag rising in triumph. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

During the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts a Japanese tank rolling over the U.S. and British flags. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

During the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt--dressed in rags, on a raft in the ocean, and holding onto the U.S. flag--in the view of a Japanese submarine periscope. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

During the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts a Japanese bomb landing in the United States heartland and knocking the stars off the U.S. flag. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

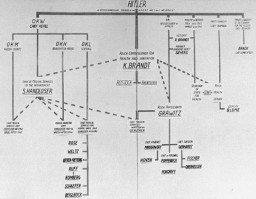
A diagram showing the medical chain of command in the Third Reich, drawn up as evidence for the Doctors Trial. Nuremberg, Germany, December 1946.
One of the ten metal boxes in which portions of the Oneg Shabbat archive were hidden and buried in the Warsaw ghetto. The boxes are currently in the possession of the Jewish Historical Institute in Warsaw. This view is of an open box without the lid.

One of the ten metal boxes in which portions of the Ringelblum Oneg Shabbat archives were hidden and buried in the Warsaw ghetto. The boxes are currently in the possession of the Jewish Historical Institute in Warsaw.

One of the two milk cans in which portions of the Ringelblum Oneg Shabbat archives were hidden and buried in the Warsaw ghetto. The milk cans are currently in the possession of the Jewish Historical Institute in Warsaw.

One of the milk cans used by Warsaw ghetto historian Emanuel Ringelblum to store and preserve the secret "Oneg Shabbat" ghetto archives.This milk can, identified as no. 2, was unearthed at 58 Nowolipki Street in Warsaw on December 1, 1950.

A page from the Mishneh Torah, one of many texts reprinted in Shanghai during the war. Yeshiva students spent part of each day listening to teachers lecture on the Talmud, the collection of ancient Rabbinic writings and commentaries composed of the Mishnah and the Gemara that form the basis of religious authority in Judaism. During the rest of the day, students paired up to review selections from the lecture. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Leon Jakubowicz, a shoemaker by training and a native of Lodz, began constructing this model of the Lodz ghetto soon after his arrival there from a prisoner-of-war camp in April 1940. The case holds a scale (1:5000) model of the ghetto, including streets, painted houses, bridges, churches, synagogue ruins, factories, cemeteries, and barbed wire around the ghetto edges. The model pieces are made from scrap wood. The case cover interior is lined with a collection of official seals, a ration card, and paper…

Nazi banner with a swastika. The swastika became the most recognizable symbol of Nazi propaganda, appearing on the Nazi flag, election posters, arm bands, medallions, and badges for military and other organizations.

Election poster reading "We workers have awakened: We’re voting National Socialist List 2 ," 1932.

Nazi propaganda poster titled “The Stalin Constitution?” printed October 10, 1943.The Nazis often used propaganda in occupied territories to secure the compliance and even support of local populations. In Ukraine and other occupied regions of the Soviet Union, the Nazis created propaganda that exploited preexisting discontent with the Soviet regime. They also tried to exploit preexisting anti-Jewish sentiment and sharpen divisions between Jews and non-Jews. One way of achieving this was by creating…

A March 3, 1967, New York Times article about Simon Wiesenthal entitled, "Relentless Nazi-Hunter."

The front page of the New York World Telegram newspaper from Tuesday, October 1, 1946, announcing the sentences of the International Military Tribunal defendants.

An illustration in the North-China Daily News following the arrival of a group of Jewish refugees in Shanghai, in Japanese-occupied China. August 24, 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Many of Julien Bryan's original 35mm nitrate film rolls were actively deteriorating when the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum acquired the collection in 2003.

First page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hermann Göring, Rudolf Hess, Joachim von Ribbentrop, and Alfred Rosenberg, along with brief biographical information for each.

Second page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hans Frank, Ernst Kaltenbrunner, and Wilhelm Frick, along with brief biographical information for each.

Third page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Julius Streicher, Wilhelm Keitel, Walter Funk, and Hjalmar Schacht., along with brief biographical information for each.

Fourth page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hjalmar Schacht, Karl Dönitz, Baldur von Schirach, Fritz Sauckel, and Albert Speer, along with brief biographical information for each.

Fifth page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Albert Speer, Franz von Papen, Alfred Jodl, Konstantin von Neurath, Artur Seyss-Inquart, Erich Raeder, and Hans Fritzsche, along with brief biographical information for each.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.