You searched for: nazi germany
<< Previous | Displaying results 976-1000 of 1276 for "nazi germany" | Next >>
-
Ritchie Boys
Article“Ritchie Boys” is a term used for American soldiers who trained at Camp Ritchie during World War II. Several thousand were Jewish refugees from Europe. Learn more.

-
Lewek Szabasson
ID CardLewek and his five brothers and sisters were born to religious Jewish parents in the town of Kozienice, situated in east central Poland near a birch forest. Lewek's father owned a sawmill, and when Lewek and his brothers were grown, they helped their father manage the family business. 1933-39: When Lewek was 15 he attended an agricultural school near Kozienice, because he wanted to immigrate to Palestine [Aliyah] to work the land. But after the Nazis rose to power in Germany in 1933, immigration…

-
Valtr Krakauer
ID CardValtr was the fourth of six children born to Jewish parents in a small Moravian town, where his father ran a dry-goods and clothing store. The Krakauers spoke both Czech and German at home. Valtr attended German-language schools and also played soccer for the Maccabi Jewish team. After graduating from secondary school, Valtr enrolled in a fashion-design school in the city of Brno. 1933-39: In Brno, Valtr founded a factory that produced ready-made clothes. He closely followed the rise of Nazism in Germany…

-
Books burn as Goebbels speaks
FilmIn their drive to rid the country of all that they deemed "un-German," the Nazis publically burned books in cities across Germany. Here in front of the Opera House in Berlin, a chanting crowd burns books written by Jews and leftist intellectuals. Joseph Goebbels, Hitler's minister of propaganda and public information, speaks of the intended "reeducation" of Germany.

-
Stutthof
ArticleLearn about the Stutthof camp from its establishment until liberation in May 1945, including conditions, forced labor, subcamps, and death marches.

-
German Invasion of Poland: Jewish Refugees, 1939
ArticleWhen Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, hundreds of thousands of Jewish and non-Jewish refugees fled the advancing German army. Learn about their experiences.

-
Josef Nassy
ArticleA Black expatriate artist living in Belgium upon the outbreak of WWII, Josef Nassy was held in German internment camps during the war. Learn about his experiences.
-
Mobile Killing Squads
ArticleLearn more about Nazi mobile killing squads (Einsatzgruppen) killing activities in the Soviet Union during World War II.
-
Page 2 of passport issued to Setty Sondheimer
DocumentSetty and Moritz Sondheimer and their two children fled Nazi Germany for Kovno, Lithuania, in 1934. There, Moritz opened a small factory manufacturing buttons and combs. This image shows page 2, containing an identification photograph, of a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer by the German Consulate in Kovno on January 29, 1938. With aid from Japanese diplomat Chiune Sugihara in obtaining Japanese transit visas, Setty and her family emigrated from Kovno in February 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition…

-
Deportation of Jews from Balti, Bessarabia
FilmThe Romanian government was allied with Nazi Germany, but it generally did not deport Romanian Jews to German-occupied territory. Instead, Romania systematically concentrated and deported the Jews of Bessarabia and northern Bukovina to Romanian-occupied areas of the Ukraine. Here, Jews from the Bessarabian town of Balti are assembled in collection camps during the deportations. By the end of May 1942, Romanian security forces had killed or deported most of the Jews in the area. Only about 200 Jews remained…

-
Evian Conference fails to aid refugees
FilmDelegates of 32 countries assembled at the Royal Hotel in Evian, France, from July 6 to 15, 1938, to discuss the problem of Jewish refugees. The refugees were desperate to flee Nazi persecution in Germany, but could not leave without having permission to settle in other countries. The Evian Conference resulted in almost no change in the immigration policies of most of the attending nations. The major powers--the United States, Great Britain, and France--opposed unrestricted immigration, making it clear…

-
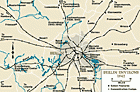
Berlin environs, 1942
MapBerlin was a center of Jewish life in Germany and—as the capital of the Reich—also the center for the planning of the "Final Solution," the decision to kill the Jews of Europe. The Wannsee Conference, named for the resort district in southwestern Berlin where it was held, took place in January 1942. High-ranking officials from the Nazi party, the SS, and the German state met to coordinate and finalize what they referred to as the "final solution to the Jewish problem." At the conference, these…
-
Thomas Buergenthal with his mother, Gerda, in Goettingen
PhotoThomas Buergenthal with his mother, Gerda, in Goettingen, Germany, 1950. With the end of World War II and collapse of the Nazi regime, survivors of the Holocaust faced the daunting task of rebuilding their lives. With little in the way of financial resources and few, if any, surviving family members, most eventually emigrated from Europe to start their lives again. Between 1945 and 1952, more than 80,000 Holocaust survivors immigrated to the United States. Thomas was one of them.

-
Thomas with his mother, Gerda, before Thomas's departure for the United States
PhotoThomas Buergenthal with his mother, Gerda, before Thomas's departure for the United States. Bad Neuheim, Germany, summer 1951. With the end of World War II and collapse of the Nazi regime, survivors of the Holocaust faced the daunting task of rebuilding their lives. With little in the way of financial resources and few, if any, surviving family members, most eventually emigrated from Europe to start their lives again. Between 1945 and 1952, more than 80,000 Holocaust survivors immigrated to the United…

-
Minsk
ArticleIn 1941, the Nazis occupied Minsk and established a ghetto there. Learn more about life in Minsk during World War II.

-
Karl Marx
ArticleKarl Marx was a political theorist and philosopher. He published “The Communist Manifesto” with Friedrich Engels. His works were burned in Nazi Germany in 1933.

-
Sachsenhausen: Key Dates
ArticleKey dates in the history of the Sachsenhausen camp in the Nazi camp system, from its establishment in 1936 to the postwar trial of camp staff in 1947.

-
Dora Oltulski
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Dora Oltulski.

-
David Broudo
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of David Broudo.

-

-
The 6th Armored Division during World War II
ArticleThe 6th Armored Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Buchenwald concentration camp in 1945.

-
The 104th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 104th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dora-Mittelbau concentration camp in 1945.

-
The 8th Armored Division during World War II
ArticleThe 8th Armored Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Halberstadt-Zwieberge subcamp of Buchenwald in 1945.
-
Massacre in Fort IX
Timeline EventOctober 29, 1941. On this date, German SS and police and Lithuanian police murdered 9,200 residents of the Kovno ghetto in Fort IX, Lithuania.

-
Prewar portrait of Golda Tenin with her daughter Paulina
PhotoPrewar portrait of Golda Tenin with her daughter Paulina, 1935. The Tenin family was living in the Ukrainian city of Odesa when it was occupied by Romania, an ally of Nazi Germany. In December 1941, Romanian authorities decided to make Odesa free of Jews. Two of Golda's children, Paulina and Rita, were murdered. Paulina was killed in January 1942, likely during deportation. Rita was killed after she was discovered in hiding with non-Jewish neighbors. Golda managed to survive.

