<< Previous | Displaying results 326-350 of 1243 for "Ghettos" | Next >>
German troops occupied Lodz one week after Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. In early 1940, the Germans established a ghetto in the northeast section of the city. More than 20 percent of the ghetto's population died as a direct result of i...
Urszula was one of four children born to Franciszek and Jadwiga Kaczmarek, who lived in the industrial city of Poznan in western Poland. The family lived at 11 Smolnej Street. Like their parents, the Kaczmarek children were baptized in the Roman Catholic faith. 1933-39: As one of the older children in the family, Urszula helped her mother with the housework. She was 10 years old when the Germans invaded Poland on Friday, September 1, 1939. German planes bombed Poznan that same day, and German troops…

Baruch was known by his family and friends as Buzek. He came from the east central Polish town of Kozienice. Kozienice was a popular vacation spot situated near lakes and a birch forest. Baruch's father worked in the lumber business. 1933-39: Baruch attended public school, and in the afternoons he also went to Jewish religious school. On Friday nights for the sabbath, Baruch would go to his grandparents' house, where his relatives would gather to visit with one another. Baruch would run to his grandfather…

Pawel was the oldest of four children born to Roman Catholic parents in Poland's capital of Warsaw. Pawel's father had worked for the Polish merchant marine before starting his own textile business in 1930. The family moved to a comfortable apartment near the Royal Castle and the Vistula River. Pawel excelled in sports, including basketball and tennis. His favorite sport was rowing. 1933-39: In May 1939 Pawel became an army reserve officer and went to training camp near Augustow. On the morning of…
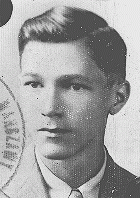
Fritz was one of three sons born to a Jewish family in the university city of Goettingen, where the Rosenbergs had lived since the 1600s. His father owned a linen factory. Fritz worked as a salesman there, and later he and his brothers inherited the business. In 1913 Fritz married Else Herz. By the early 1920s they had two sons and a daughter. 1933-39: In 1933 the Nazis came to power in Germany. A year later the Rosenbergs' factory was seized and three Nazis came to the family's home. An officer set a gun…
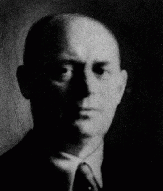
Inge was the only child of Berthold and Regina Auerbacher, religious Jews living in Kippenheim, a village in southwestern Germany near the Black Forest. Her father was a textile merchant. The family lived in a large house with 17 rooms and had servants to help with the housework. 1933-39: On November 10, 1938, hoodlums threw rocks and broke all the windows of Inge's home. That same day police arrested her father and grandfather. Inge, her mother and grandmother managed to hide in a shed until it was…

Fela was the older of two children born to Jewish parents living in Zakroczym, a town on the Vistula River near Warsaw. Her father was a respected attorney. As a young woman, Fela worked as a hat designer in Warsaw, until she married Moshe Galek when she was in her late 20s. She moved to the nearby town of Sochocin, where her husband owned a pearl-button factory. Fela and Moshe raised four daughters. 1933-39: In 1936 the Galeks moved to Warsaw, attracted by the city's cultural life. When Germany invaded…

Hela was born in the industrial city of Lodz. She grew up speaking Polish and Yiddish, and learned German and Russian at secondary school. After completing school she married, and moved with her husband to a house on her father-in-law's large estate in the nearby town of Ozorkow. Hela was active in planning events for Jewish organizations. She and her husband, Israel, had two daughters. 1933-39: After German troops occupied Ozorkow in 1939, Hela and her family were forced out of their home and moved in…

Hersh was born to a Jewish family in Kovno, the capital of independent Lithuania. Hersh's father was a mechanic in a textile factory, and his mother had worked as a hat designer until he was born. The Gordons lived on the first floor of Hersh's grandfather's apartment building. Eight-year-old Hersh was in the third grade at public elementary school. 1933-39: In the summers Hersh and his mother would go to his Aunt Ettel and Uncle Abraham in a small town not far away. They'd take a boat down the river to…

Ernest was one of three children born to a Jewish family in the commercial city of Breslau, which had one of the largest Jewish communities in Germany. His father, a World War I veteran, owned a factory that made matzah, the unleavened bread used during the Jewish holiday of Passover. Ernest was 12 when Hitler took power in 1933. 1933-39: Ernest often got in trouble at school because people called him names. "Christ-killer" and "your father kills Christian babies for Passover" were common taunts. Many…

Szlamach was one of six children born to Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish parents. Szlamach's father was a peddler, and the Radoszynski family lived in a modest apartment in Warsaw's Praga section on the east bank of the Vistula River. After completing his schooling at the age of 16, Szlamach apprenticed to become a furrier. 1933-39: During the 1930s Szlamach owned a fur business. Despite the Depression, he was hoping the economy would turn around so that he could make enough money to move into his own…

The Germans established Jewish Councils (Judenraete) in the ghettos during World War II. Jewish Councils were required to implement Nazi policies in the ghettos. This role meant impossible moral dilemmas. Council members had to decide whe...
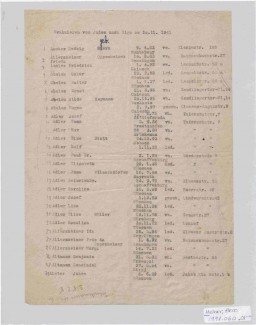
The SS compiled lists of Jews who were to be deported to ghettos, concentration camps, and killing centers. This document provides the names, birthdates, marital status, and addresses of Jews who were “evacuated” on November 20, 1941 from Germany to the Riga ghetto in German-occupied Latvia.
The Nazis made Jewish leaders responsible for the distribution of food supplies and other necessities allotted to ghetto residents. Due to grossly inadequate supplies, the Juedische Selbstverwaltung Theresienstadt (Jewish Administration of Theresienstadt) issued ration cards such as this one. The columns count points allotted for various goods identified by letters of the alphabet. Boxes were removed as residents exchanged points for food or other goods. This view shows the front of the card. Issued in the…

One of the ten metal boxes in which portions of the Ringelblum Oneg Shabbat archives were hidden and buried in the Warsaw ghetto. The boxes are currently in the possession of the Jewish Historical Institute in Warsaw.

One of the ten metal boxes in which portions of the Oneg Shabbat archive were hidden and buried in the Warsaw ghetto. The boxes are currently in the possession of the Jewish Historical Institute in Warsaw. This view is of an open box without the lid.

Jozef, also known as Josel, was one of six children born to Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish parents in the town of Zvolen in central Poland. Jozef became a shoemaker and married a Jewish neighbor. After living in Warsaw for several years, Jozef and his wife, Hannah, settled in the industrial city of Radom near their hometown. There, they raised their three sons. 1933-39: Jozef's three sons finished school and went to work at a young age. Jozef had stopped making shoes himself and was cutting and…

Irmgard was one of three children born to a Jewish family in the famous university city of Goettingen. The city had a small Jewish population, and only one synagogue. Irmgard's father, with his two brothers, owned a linen factory that had been founded by Irmgard's grandfather. Irmgard attended public school in the city. 1933-39: With the onset of the Depression in the 1930s, the family's factory went into decline. When the Nazis came to power in 1933, they confiscated the Rosenbergs' factory. Later, the…

The Germans established a ghetto in Warsaw in October 1940. All Jewish residents were required to live in the ghetto, which was sealed off from the rest of the city. Overcrowding, minimal rations, and unsanitary conditions led to disease, starvati...
The Germans established a ghetto in Warsaw in October 1940. All of Warsaw's Jews were required to live in the ghetto, which was sealed off from the rest of the city. Overcrowding, minimal rations, and unsanitary conditions led to disease, starvati...
We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.