<< Previous | Displaying results 4001-4050 of 6769 for "" | Next >>
In this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

In this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

In this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

In this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

In this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

Nazi Germany’s semi-official and fiercely antisemitic newspaper Der Stuermer warned of a Jewish program for world domination in this 1934 issue. The article—titled “Who is the Enemy?”—blamed Jews for destroying social order and claimed that Jews wanted war, while the rest of the world wanted peace. Der Stuermer, July 1934.

Cover of a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg.

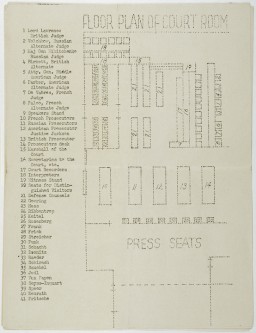
Floor plan of the courtroom. The plan appeared in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. 1945.
First page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hermann Göring, Rudolf Hess, Joachim von Ribbentrop, and Alfred Rosenberg, along with brief biographical information for each.

Third page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Julius Streicher, Wilhelm Keitel, Walter Funk, and Hjalmar Schacht., along with brief biographical information for each.

Fourth page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hjalmar Schacht, Karl Dönitz, Baldur von Schirach, Fritz Sauckel, and Albert Speer, along with brief biographical information for each.

Fifth page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Albert Speer, Franz von Papen, Alfred Jodl, Konstantin von Neurath, Artur Seyss-Inquart, Erich Raeder, and Hans Fritzsche, along with brief biographical information for each.

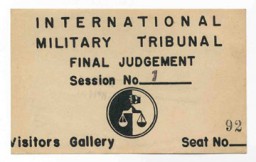
Pass for the visitors' gallery at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. Such passes were often shared among several people as they took turns observing the historic legal proceedings.

An insert prepared for American soldiers. This diagram, published in the overseas edition of "Newsmap for the Armed Forces," explains the indictment against the Nuremberg defendants. 1945.

Second page of a list of defendants at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. This material appears in a mimeographed program booklet distributed at the IMT. This page includes: Hans Frank, Ernst Kaltenbrunner, and Wilhelm Frick, along with brief biographical information for each.

Sorle and Shalomis Gorfinkel presented this card to their parents on the occasion of Rosh Hashanah 5704, the Jewish New Year 1943. The Gorfinkel family was part of the Mir Yeshiva community in Shanghai.

Wooden sandals worn by a member of the Mir Yeshiva in Shanghai. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Goblets used in Shanghai by the Caspary family for blessings (Kiddush) over wine on the Sabbath or Jewish holidays. The Orthodox Casparys ran a kosher restaurant frequented by yeshiva students from Poland. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

A page from the Mishneh Torah, one of many texts reprinted in Shanghai during the war. Yeshiva students spent part of each day listening to teachers lecture on the Talmud, the collection of ancient Rabbinic writings and commentaries composed of the Mishnah and the Gemara that form the basis of religious authority in Judaism. During the rest of the day, students paired up to review selections from the lecture. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

David Bloch, untitled woodblock print with watercolor, ca. 1945. Bloch, a German Jewish refugee, depicted typical shops in "Little Vienna," as Chusan Road in Hongkew became known. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Boy Scout handmade badges worn by German-Jewish refugee boys. British expatriates had transplanted the Boy Scouts to Shanghai before the refugees' arrival. Unlike most of the Polish Jewish refugees, German and Austrian Jews usually went to Shanghai as families, and enrollment in schools and youth organizations in the International Settlement grew rapidly. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Entry pass to the court building at the International Military Tribunal. This pass was issued to a U.S. military guard.

Back side of an entry pass to the court building at the International Military Tribunal. This pass was issued to a U.S. military guard. The pass is printed in each of the IMT's four official languages.

Cover of program booklet distributed at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg.

Reproduction of entry pass to the International Military Tribunal visitors' gallery for the sentencing of the defendants. October 1946.
Cover of booklet titled "What Shall Be Done with the War Criminals?" Published by the United States Armed Forces Institute, this was one of a series of 42 pamphlets created by the U.S. War Department under the series title "G.I. Roundtable." From 1943-1945, these pamphlets were created to "increase the effectiveness of the soldiers and officers and fighters during the war and as citizens after the war." Many of the pamphlets addressed the possibilities of a postwar world.

Second and third pages of a program booklet distributed during the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. Note the definitions of the conspiracy charge and crimes against peace, brought in the indictment.

Fourth and fifth pages of a program booklet distributed during the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. Page four defines the charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity. The fifth page begins the list of IMT defendants. Handwritten notes in the margin record each defendant's sentence as it was read aloud in the courtroom.

Courtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing's title is "Spectators at War Criminals Trial, Nuremberg, Germany." 1945.

Courtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing's title is "British Courier for the Correspondents." 1945.

Courtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing's title is "German defense counsel -- they are immediately in front of the defendants." 1945.

Courtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing depicts defendants Rudolf Hess and Wilhelm Keitel, with this accompanying text: "Hess looked very hollow cheeked and thin necked. He seemed to ignore the proceedings and kept his head down, absorbed in a book. Keitel tried to retain a rigid military bearing and strike haughty poses." Nuremberg, Germany, 1945.

Courtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing's title is "A few studies of the German defense counsel." 1945.

The front page of the New York World Telegram newspaper from Tuesday, October 1, 1946, announcing the sentences of the International Military Tribunal defendants.

First page of a program booklet distributed during the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. The dramatic text sets the scene in the courtroom.

Many observers at the IMT, aware of the historic nature of the trial, created scrapbooks to preserve their own record of the Nuremberg court. First Lieutenant Herman E. Klappert, Jr. was a photographer with the U.S. Army Signal Corps who assembled three such scrapbooks. Klappert's albums consist almost entirely of photographs that he printed himself. Also included in the albums are original autographs from the defendants and other principal figures at the trial, official identification cards issued to…

Many observers at the International Military Tribunal (IMT) at Nuremberg, aware of the historic nature of the trial, created scrapbooks to preserve their own record of the Nuremberg court. First Lieutenant Herman E. Klappert, Jr. was a photographer with the U.S. Army Signal Corps who assembled three such scrapbooks. Klappert's albums consist almost entirely of photographs that he printed himself. Also included in the albums are original autographs from the defendants and other principal figures at the…

Entry pass to the prison housing war criminals at the International Military Tribunal. This pass was issued to a U.S. military guard.

Back side of an entry pass to the prison housing war criminals at the International Military Tribunal. This pass was issued to a U.S. military guard.

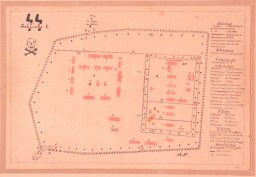
This map of the Treblinka I forced-labor camp was drawn by Holocaust survivor Manfred Kort in 1946. In 1990 Kort donated the map to the United States Holocaust Memorial Musem. In March 1997, at the request of the Office of Special Investigations, the Museum sent the original drawing to Chicago to be used as evidence at the trial of one Bronislaw Hajda. At the conclusion of Hajda's trial on April 10, 1997, the U.S. Department of Justice announced that "a federal judge in Chicago has revoked the naturalized…
Headphones used by defendant Hans Frank during the International Military Tribunal. Headphones like these enabled trial participants to hear simultaneous translation of the proceedings.

Headphones used by defendant Hermann Göring during the International Military Tribunal. Headphones like these enabled trial participants to hear simultaneous translation of the proceedings.

Headphones used by defendant Albert Speer during the International Military Tribunal. Headphones like these enabled trial participants to hear simultaneous translation of the proceedings.

Entry pass to a US military dining hall at Dachau, Germany. This card was issued to Anton Litwin, a member of the War Crimes Branch.

Affidavit signed by Rudolf Hoess attesting to the gassing of Jews while he was the commandant of the Auschwitz killing center. The German text reads: "I declare herewith under oath that in the years 1941 to 1943 during my tenure in office as commandant of Auschwitz Concentration Camp 2 million Jews were put to death by gassing and a 1/2 million by other means. Rudolf Hoess. May 14, 1946." The confession is also signed by Josef Maier of the US Chief of Counsel's office. A photoreproduction of the original…

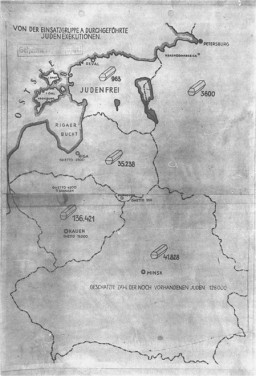
This map accompanied a secret undated German report on the mass murder of Jews by Einsatzgruppen A (mobile killing unit A). During the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg, the map was introduced as evidence by both the American and British prosecution teams. The document, entitled "Jewish Executions Carried Out by Einsatzgruppen A" and stamped "Secret Reich Matter," shows the number of Jews executed (symbolized by coffins) in the Baltic states and Belorussia by late 1941. The legend near the…
An August 6, 1972, Washington Post article about former concentration camp guard Hermine Braunsteiner Ryan, entitled "From a Dark Past, A Ghost the U.S. Won't Allow to Rest".

Courtroom sketch by artist David Rose of Nobel laureate and Holocaust survivor Elie Wiesel on the witness stand at the trial of Klaus Barbie. During his testimony, Wiesel stated that "The killer kills twice. First, by killing, and then by trying to wipe out the traces." June 2, 1987.

Evidence tag from the trial of Klaus Barbie in Lyon, France. This standard police form lists Barbie's infractions as crimes against humanity and complicity, concepts defined at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg decades earlier. The line in which the victims' names would be recorded is left blank. February 25, 1983.

Evidence tag from the trial of Klaus Barbie in Lyon, France. This standard police form lists Barbie's infractions as crimes against humanity and complicity, concepts defined at the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg decades earlier. The line in which the victims' names would be recorded is left blank. February 25, 1983.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.