<< Previous | Displaying results 6401-6450 of 6705 for "" | Next >>
-
Flag graphic for US 4th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 4th Armored Division's flag. The US 4th Armored Division is also known as the "Breakthrough" division. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and overran Ohrdruf, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 4th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 4th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 4th Infantry Division's flag. The US 4th Infantry Division (the "Ivy" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day, the liberation of Paris, and the Battle of the Bulge. The division also captured the city of Nuremberg and discovered a Dachau subcamp near Haunstetten. The 4th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1992 by the United States Army Center of Military History and…

-
Flag graphic for US 63rd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 63rd Infantry Division's flag. The US 63rd Infantry Division (the "Blood and Fire" division) was established in 1943. During World War II, they took the town of Heidelberg and liberated several Kaufering subcamps. The 63rd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 2000 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 65th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 65th Infantry Division's flag. The US 65th Infantry Division (the "Battle Axe" division) was established in 1943. During World War II, they took the cities of Regensburg, Passau, and Linz. The division also overran a subcamp of the Flossenbürg concentration camp. The 65th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1994 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 69th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 69th Infantry Division's flag. The US 69th Infantry Division ("Fighting 69th") was established in 1943. During World War II, they captured the city of Leipzig and uncovered Leipzig-Thekla, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 69th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 6th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 6th Armored Division's flag. The US 6th Armored Division is also known as the "Super Sixth." During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and overran the Buchenwald concentration camp. The 6th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 71st Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 71st Infantry Division's flag. The US 71st Infantry Division (the "Red Circle" division) was established in 1943. During World War II, they were involved in taking the cities of Coburg, Bayreuth, and Regensburg. The division also liberated Gunskirchen, a subcamp of Mauthausen. The 71st Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 80th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 80th Infantry Division's flag. The US 80th Infantry Division (the "Blue Ridge" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge. The division entered Buchenwald concentration camp and liberated Ebensee, a subcamp of Mauthausen. The 80th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust…

-
Flag graphic for US 82nd Airborne Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 82nd Airborne Division's flag. The US 82nd Airborne Division (the "All American" division) was established in 1918 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day and Battle of the Bulge. The division also overran Wöbbelin, a subcamp of Neuengamme. The 82nd Airborne Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1991 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 83rd Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 83rd Infantry Division's flag. The US 83rd Infantry Division (the "Thunderbolt" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Halle. The division also encountered Langenstein, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 83rd Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States…

-
Flag graphic for US 84th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 84th Infantry Division's flag. The US 84th Infantry Division (the "Railsplitter" division) was established in 1917. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and captured the city of Hannover. The division also uncovered Hannover-Ahlem and Salzwedel, two satellite camps of the Neuengamme concentration camp. The 84th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and…

-
Flag graphic for US 86th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 86th Infantry Division's flag. The US 86th Infantry Division (the "Blackhawk" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they discovered the Attendorn civilian forced-labor camp. The 86th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1996 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 89th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 89th Infantry Division's flag. The US 89th Infantry Division (the "Rolling W" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they captured the town of Eisenach and the city of Zwickau. The division overran Ohrdruf, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 89th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 8th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 8th Armored Division's flag. The US 8th Armored Division is also known as the "Iron Snake" or "Thundering Herd" division. During World War II, they liberated Halberstadt-Zwieberge, a subcamp of Buchenwald. The 8th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1995 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 8th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 8th Infantry Division's flag. The US 8th Infantry Division (the "Golden Arrow" or "Pathfinder" division) was established in 1918 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they captured the cities of Rennes and Brest. The division also encountered Wöbbelin, a subcamp of Neuengamme. The 8th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1988 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum…

-
Flag graphic for US 90th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 90th Infantry Division's flag. The US 90th Infantry Division (the "Tough Ombre" division) was established in 1917 and fought in World War I. During World War II, they were involved in D-Day and the Battle of the Bulge. The division also captured the city of Mainz and overran Flossenbürg concentration camp. The 90th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1985 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States…

-
Flag graphic for US 95th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 95th Infantry Division's flag. The US 95th Infantry Division (the "Victory" Division) was established in 1942. During World War II, they captured the cities of Metz and Dortmund. The division also undercovered a German prison and civilian labor camp in Werl. The 95th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1995 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 99th Infantry Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 99th Infantry Division's flag. The US 99th Infantry Division (the "Checkerboard" or "Battle Babies" division) was established in 1942. During World War II, they were invovled in the Battle of the Bulge and liberated a Dachau subcamp near Mühldorf. The 99th Infantry Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1992 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Flag graphic for US 9th Armored Division
PhotoA digital representation of the United States 9th Armored Division's flag. The US 9th Armored Division was known as the "Phantom" division. During World War II, they were involved in the Battle of the Bulge and also liberated Zwodau and Falkenau an der Eger, two subcamps of Flossenbürg. The 9th Armored Division was recognized as a liberating unit in 1993 by the United States Army Center of Military History and the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM).

-
Former gas chamber in the Auschwitz main camp
PhotoPostwar photograph of gas chamber for mass murder in the Auschwitz main camp. Poland, ca. 1947. In mid-August 1940, Auschwitz concentration camp authorities put into operation a crematorium adjacent to a morgue. This building was located just outside the boundaries of the Auschwitz main camp. In September 1941, the morgue was converted to a gas chamber for mass murder where several hundred people could be killed at a time. This gas chamber was used until December 1942, though the crematorium remained…

-
Thomas Buergenthal with one of his grandchildren
PhotoThomas with Eliza, one of his grandchildren. 1996. With the end of World War II and collapse of the Nazi regime, survivors of the Holocaust faced the daunting task of rebuilding their lives. With little in the way of financial resources and few, if any, surviving family members, most eventually emigrated from Europe to start their lives again. Between 1945 and 1952, more than 80,000 Holocaust survivors immigrated to the United States. Thomas was one of them.

-
German General Headquarters, World War I
PhotoPictured from left to right: Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, Kaiser Wilhelm II, and General Erich Ludendorff study maps during World War I. January 1917.

-
Paul von Hindenburg, 1917
PhotoField Marshal Paul von Hindenburg walks along a flower-covered path on his 70th birthday. On either side, crowds of children cheer. October 2, 1917. Hindenburg will later be elected president of Germany in 1925, during the Weimar Republic. © IWM Q 23976

-
Demonstration in Berlin, November 1918
PhotoA public demonstration is held on the Unter den Linden in Berlin on November 9, 1918. On this day, Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicated the throne after a recent naval mutiny in Kiel inspired widespread revolution. © IWM Q 88164

-
British soldiers transfer Jewish refugee children from the ship Theodor Herzl
PhotoIn April 1947, the British Navy intercepted the ship Theodor Herzl en route from Europe to British-controlled Mandatory Palestine. On board were hundreds of Holocaust survivors, including children, seeking a home. This photograph shows British soldiers transferring some of the Jewish refugee children to a vessel for deportation to Cyprus detention camps. Haifa port, British-controlled Mandatory Palestine, April 1947.

-
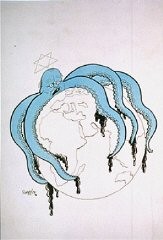
Nazi-era Antisemitic Propaganda Poster
PhotoNazi propaganda cartoon by Seppla (Josef Plank), a political cartoonist. Germany, date uncertain [probably during World War II]. Beginning in the 1920s, Nazi propagandists promoted the antisemitic myth that Jews were engaged in a massive conspiracy to take over the world. This false notion alleged that “international Jewry” used various people and groups as part of a plan for global conquest. At the time, an octopus extending its tentacles over the globe was a common visual metaphor for this…
-
Adolf Hitler passes through the Brandenburg Gate on his way to the opening ceremonies of the Olympic Games
PhotoAdolf Hitler passes through the Brandenburg Gate on the way to the opening ceremonies of the Olympic Games. Berlin, Germany, August 1, 1936.

-
Dr. Robert Ritter visits a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoDr. Robert Ritter talks to several residents in a Zigeunerlager ("Gypsy camp"). Hamburg, Germany, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

-
Sophie Ehrhardt performs a racial examination on a Romani woman
PhotoSophie Ehrhardt, a German hygienist working with Dr. Robert Ritter, performs a racial examination on a Romani woman. Berlin, Germany, c. 1936-1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most…

-
Dr. Robert Ritter and Eva Justin examine a young boy interned in a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoDr. Robert Ritter and Eva Justin examine a young boy interned in a Zigeunerlager (“Gypsy camp”). Cologne, Germany, c. 1937-1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people…

-
The “Gypsy camp” in Hodonín u Kunštátu
PhotoThe “Gypsy camp” in Hodonín u Kunštátu (Hodonin bei Kunstadt), Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (Czech Republic), 1942.

-
US Army unit at Camp Ritchie
PhotoOtto Perl poses with his US Army unit at Camp Ritchie, Maryland, circa 1945. Born in Austria, Perl served in the Austrian Army until March 1938, when he was dismissed because he was Jewish. With the help of a friend, Perl was able to obtain a US visa. He reached New York in 1940. Several thousand of the soldiers who trained at Camp Ritchie were Jewish refugees who had immigrated to the United States to escape Nazi persecution.

-
Two US soldiers cross the Rhine River
PhotoTwo American soldiers cross the Rhine River into Germany on March 29, 1945. In the foreground is Jack Caminer, who emigrated from Germany to the United States in 1938. After he was drafted into the US Army, Caminer was sent to Camp Ritchie to prepare for intelligence work. Caminer participated in the liberation of Ohrdruf.

-
SS men guard Soviet POWs near the Babyn Yar killing site
PhotoSS men guard Soviet prisoners of war doing forced labor near the Babyn Yar killing site. The photograph was taken within days of the mass murder of over 33,000 Jews on September 29-30, 1941. Kyiv (Kiev), German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
An SS guard speaks with local Ukrainian women while Soviet POWs perform forced labor nearby
PhotoAn SS guard speaks with local Ukrainian women while Soviet prisoners of war carry out forced labor. A German Propaganda Company photographer took this image shortly after the SS murdered over 33,000 Jews on September 29-30,1941 at the nearby Babyn Yar killing site. Kyiv (Kiev), German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
Belongings of a Jewish family murdered at Babyn Yar
PhotoBelongings of a Jewish family murdered by an SS mobile killing squad at Babyn Yar. On September 29-30, 1941, the SS killed more than 33,000 Jews from Kyiv (Kiev). A German Propaganda Company photographer took this image within days of the massacre. Kyiv, German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
Belongings of Jews murdered at Babyn Yar
PhotoThe SS ordered Jews to undress prior to the mass shootings at the nearby Babyn Yar killing site. In two days, September 29-30, 1941, they shot more than 33,000 Jews from Kyiv (Kiev). This photograph, taken by a member of a German Propaganda Company, shows just some of the belongings of these victims. Kyiv, German-occupied Soviet Union, After September 30, 1941.

-
Belongings of Jewish victims murdered at Babyn Yar
PhotoClothing belonging to Jewish victims murdered by the SS at the nearby Babyn Yar killing site. Prior to the mass shootings, the SS ordered Jews to undress and leave their belongings. They then marched or drove the victims to the killing site. A German photographer took this image within days of the mass shootings. Kyiv (Kiev), German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
An SS guard examines clothing of victims of the Babyn Yar mass shootings
PhotoAn SS guard examines piles of clothing belonging to the more than 33,000 Jews murdered at the nearby Babyn Yar killing site. The SS forced the victims to undress and leave their belongings behind. The Jews were then marched or driven to the shooting site. Kyiv (Kiev), German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
SS guards search through clothing of victims of the Babyn Yar mass shootings
PhotoSS men search through massive piles of clothing belonging to the more than 33,000 Jews murdered at the nearby Babyn Yar killing site. The SS forced the victims to undress and leave their belongings behind. The Jews were then marched or driven to the shooting site. Kyiv (Kiev), German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
SS men or German officers on a cliff near the Babyn Yar killing site
PhotoSS men or German police officers on one of the sandy cliffs near the Babyn Yar killing site. Below them are unidentified men, perhaps Soviet prisoners of war or local Ukrainians, who sorted through the huge piles of clothing belonging to the more than 33,000 Jews from Kyiv (Kiev) who were murdered at Babyn Yar. Kyiv, German-occupied Soviet Union, after September 30, 1941.

-
Léon Degrelle
PhotoLéon Degrelle, an extreme right-wing Belgian politician and Nazi collaborator. Photo dated 1933–1945.

-
Johann Niemann at the Bernburg "euthanasia" center
PhotoStaff member Johann Niemann in his room at the Bernburg "euthanasia" center. For the picture, he turned his family photo on the bedside table in the direction of the photographer. Niemann later became the deputy commandant of Sobibor, one of three "Operation Reinhard" killing centers.

-
Nazi collaborator Léon Degrelle with Belgian Volunteer fighters
PhotoBelgian politician Léon Degrelle (center) stands in formation with fighters from the Belgian Volunteers who are on their way to fight in the Soviet Union. Belgium, August 15, 1941. During World War II, Degrelle founded a collaborationist military force that fought on the eastern front.

-
Portrait of Żegota member Andrzej Klimowicz
PhotoWartime portrait of Andrzej Klimowicz, Poland. Andrzej Klimowicz (1918–1996) aided and rescued Jews in Warsaw throughout the duration of the German occupation of Poland. He eventually became a member of the Council for Aid to Jews (codenamed “Żegota”), a clandestine organization that coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. Under the auspices of Żegota, Andrzej played a role in providing Jews in Warsaw with forged identity papers and hiding places outside the walls of the…

-
Eva Justin interviews a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp"
PhotoA color photograph of Eva Justin interviewing a Romani woman interned in a "Gypsy camp." Vienna, Austria, 1940. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.” Ritter worked with a small team of racial hygienists. Among them were Eva Justin and Sophie Ehrhardt. Most of the people whom Ritter studied and…

-
Portrait of Żegota member Irena Sendler
PhotoPortrait of Irena Sendler in Warsaw, Poland, circa 1939. Irena Sendler (1910–2008) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Irena Sendler (Sendlerowa) was working as a social worker in Warsaw when World War II broke out in 1939. After…

-
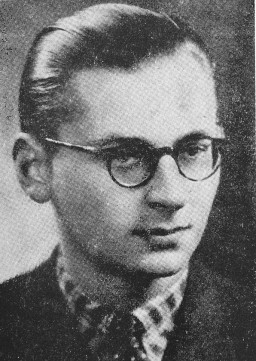
Portrait of Żegota co-founder Władysław Bartoszewski
PhotoPortrait of Władysław Bartoszewski, Poland, unknown date. Władysław Bartoszewski (1922–2015) was a co-founder and member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. After World War II broke out in September 1939, Władysław worked as a janitor…
-
People crowded around an antisemitic "Pesti Ujság" newspaper display
PhotoVisitors view the exhibition of the Arrow Cross newspaper, Pesti Ujság, at the International Fair in Budapest. The headline reads: "For a Hungary without Jews." Budapest, Hungary, approximately 1941-1942. The Arrow Cross was Hungary's largest fascist political movement after 1935. In the 1939 parliamentary elections it won over 20% of the vote and had more than 250,000 members. Its ideology was ultra-nationalistic and fiercely antisemitic. The Arrow Cross viewed Jews as an "anti-national" "race"…

-
Election officers in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
PhotoElection officers count votes late into the night after the second round of the 2006 presidential and provincial elections in Bunia, Ituri, Democratic Republic of the Congo.

