You searched for: krakow
<< Previous | Displaying results 51-100 of 152 for "krakow" | Next >>
-
Max Diamant's identity card (inside)
DocumentMax Diamant obtained this identity card from the German health department located in Krakow (Krakau), occupied Poland, in July 1942. This view shows the interior pages, which identify him as a Jew and detail his personal information, such as occupation (dental assistant), birthdate (June 23, 1915), birthplace (Vienna), and current address in Przemysl, Poland.

-
-
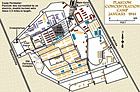
Entrance to the Plaszow camp
PhotoView of the entrance to the Plaszow camp. Plaszow, Poland, 1943-1944.

-
Heinrich Himmler and Hans Frank
PhotoSS chief Heinrich Himmler (left) and Hans Frank, head of the Generalgouvernement in occupied Poland. Krakow, Poland, 1943.

-
Writers and Poets in the Ghettos
ArticleSongs, verses, and writings of writers and poets in the ghettos reflect efforts to preserve culture, humanity, and documentation, as well as acts of defiance. Explore examples.

-
Shimshon and Tova Draenger
PhotoShimshon and Tova Draenger, members of the underground in the Kraków and Warsaw ghettos and partisans in the Wisnicz Forest. Krakow, Poland, date uncertain.

-
Our Town is Burning
SongMordecai Gebirtig, born in 1877 in Krakow, Poland, was a Yiddish folk poet and songwriter. He wrote "Undzer shtetl brent!" in 1936, following a pogrom in the Polish town of Przytyk. During the war, the song became popular in the Krakow ghetto and inspired young people to take up arms against the Nazis. It was sung in many ghettos and camps, and translated into Polish and several other languages. Gebirtig was killed in June 1942 during a roundup for deportation from the Krakow ghetto. Today, "Undzer…
-
German Administration of Poland
ArticleGermany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Learn about the administrative units that Germany established after annexing and occupying parts of prewar Poland.

-
Shifrele's Portrait
SongYiddish folk poet and songwriter Mordecai Gebirtig was born in 1877 in Krakow, Poland. He wrote "Shifrele's Portrait" was written in Krakow in December 1939, shortly after the outbreak of World War II. Gebirtig's eldest daughter, Shifre, lived in Lvov, and was separated from her family when the Soviets annexed Lvov. In this brief song, Gebirtig, gazing at his daughter's photograph, imagines himself in conversation with her. She assures him that the war will end soon, and that parent and child will be…
-
Rescue and Resistance
ArticleWhile some European Jews survived the Holocaust by hiding or escaping, others were rescued by non-Jews. Learn more about these acts of resistance.
-
Belzec: Key Dates
ArticleExplore key events in the history of the Belzec killing center in the Nazi camp system. It was constructed for the sole purpose of murdering Jews.

-
Płaszów - Photographs
Media EssayThe Płaszów camp was established in 1942 under the authority of the SS and police leaders in Krakow (Cracow). Płaszów was initially a forced-labor camp for Jews, but became a concentration camp in 1944. The largest...
-
German destruction of symbols of the Polish state
PhotoThe Germans destroyed symbols of the Polish state. Here, German soldiers stand by the toppled Grunwald monument in Krakow. Poland, 1940.

-
Tarnow
ArticleLearn about the prewar Jewish community of Tarnow, German occupation, deportations and killings of the Jewish population, ghettoization, and resistance.

-
Miriam Peleg describes why she joined Żegota
Oral HistoryMiriam Peleg (1913–1996) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Born Maria Hochberg, Miriam was from a Polish-Jewish family. She grew up in a small town about 70 miles east of Kraków. As early as the summer of 1940, Miriam obtained…

-
Moses Rechnitz: Maps
Media EssayMoses Rechnitz was born to Jewish parents in the Polish town of Bedzin on June 3, 1923. Moses was 16 years old when German troops invaded Poland in September 1939. By 1941, he was a slave laborer on a German railroad construction project outside o...
-
Execution of Poles near Bochnia
PhotoGerman police execute a group of Poles at the edge of the Uzbornia Grove just outside of Bochnia. Altogether, 51 residents of Bochnia and the vicinity were shot in reprisal for an assault on a German police station by members of the Polish underground organization "Orzel Bialy" (White Eagle) on 16 December 1939. Bochnia, Krakow, Poland, December 18, 1939.

-
German Order Policemen stand guard over a group of Jewish men
PhotoMembers of the German Order Police stand guard over a group of Orthodox Jewish men, 1942. The men have been rounded-up either for forced labor or public humiliation. Krakow, in German-occupied Poland.

-
Collections Highlight: Selma Schwarzwald and her Bear, "Refugee"
ArticleWhile living under an assumed identity after escaping from the Lvov ghetto, Selma Schwarzwald received a toy bear that she kept with her for many years. Read about Refugee the bear.

-
Norman Salsitz and Amalie Petranka shortly after they met
PhotoNorman Salsitz and Amalie Petranka shortly after they met (under their assumed identities of, respectively, Felicja Milaszewska and Tadeusz Zaleski). Krakow, Poland, March 15, 1945. With the end of World War II and collapse of the Nazi regime, survivors of the Holocaust faced the daunting task of rebuilding their lives. With little in the way of financial resources and few, if any, surviving family members, most eventually emigrated from Europe to start their lives again. Between 1945 and 1952, more than…

-
Theo Markus Verderber
PhotoTheo Markus Verderber's mother, Gelle, was among the Jews of Polish nationality expelled from Germany in October 1938. Theo and his younger brother were born in Germany, but went with their mother to a refugee camp in the border town of Zbaszyn. Hungry and cold, the refugees were stranded on the border, unwelcome in either Germany or Poland. Theo was ultimately chosen to join a Kindertransport to England, arriving there in February 1939. His mother, sister and youngest brother remained in…

-
Your Kitten is Hungry
SongMordecai Gebirtig, born in 1877 in Krakow, Poland, was a Yiddish folk poet and songwriter. Gebirtig had three daughters, for whom he wrote and performed his poems. The words were set to improvised melodies, and most of his songs resemble entries in a diary. Many of Gebirtig's poems contain themes of eastern European Jewish life in the 1920s and 1930s. The lullaby "Your Kitten is Hungry" dates from the early 1920s. The lyrics, addressed to a hungry child, evoke the themes of hunger and deprivation.
-
Avreml the Pickpocket
SongMordecai Gebirtig, born in 1877 in Krakow, Poland, was a Yiddish folk poet and songwriter. Gebirtig had three daughters, for whom he wrote and performed his poems. The words were set to improvised melodies, and most of his songs resemble entries in a diary. Many of Gebirtig's poems contain themes of eastern European Jewish life in the 1920s and 1930s. The lyrics to "Avreml the Pickpocket" address two social issues, crime and the collapse of family life, arguing that both find their roots in poverty and…
-
Auschwitz Camp Established
Timeline EventMay 20, 1940. On this date, SS authorities established the Auschwitz concentration camp complex.

-
Armed Jewish Resistance: Partisans
ArticleFacing overwhelming odds, Jews throughout occupied Europe attempted armed resistance against the Germans and their Axis partners.

-
Helena Manaster
ID CardHelena was the eighth of 10 children born to a Jewish family in the town of Lesko. Her father was a landowner. When Helena was a young girl the family moved to nearby Orelec, where they had a summer home. As there were no schools in Orelec, Helena and her siblings continued attending school in Lesko. Later, Helena traveled three hours by train daily to attend the nearest high school, which was in Przemysl. 1933-39: The German army invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. By the beginning of October the…
-
Pinchas Gerszonowicz
ID CardPinchas was born into a large family living in the town of Miechow in south central Poland. His father was a machinist and locksmith. Pinchas spent long days studying, either learning Hebrew in the Jewish school or taking general subjects at the public school. He belonged to the Zionist youth organization, Ha Shomer ha-Tsa'ir, and played left wing for a Jewish soccer team. 1933-39: At 13 Pinchas finished school and started work as an apprentice machinist and blacksmith in a building contractor's shop.…

-
Jehuda Gerszonowicz
ID CardThe third of eight children, Jehuda was born in the predominantly Jewish town of Wodzislaw, about 45 miles north of Krakow. Jehuda's father was a mechanic and locksmith, and had trained Jehuda and his brothers in the trade. Jehuda eventually opened his own shop in the nearby town of Miechow. He had eight children--five sons and three daughters--by two marriages. 1933-39: All this summer Jehuda has been glued to the radio, as the number of skirmishes between the German and Polish border guards have…

-
Jan Komski
ID CardJan was born to a Catholic family in the small Polish town of Bircza. His father, a World War I veteran, moved the family to Brzozow shortly after the war. Brzozow was a small manufacturing town in southeastern Poland. After graduating from secondary school, Jan enrolled at the Academy of Fine Arts in Cracow. 1933-39: Cracow was a beautiful old city; Jan studied its remarkable churches and synagogues in his classes. By September 1939, however, the war engulfed the beauty of Cracow. He left to escape the…

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes the Tarnow ghetto after a roundup
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Murray Pantirer describes one of Oskar Schindler's rescue efforts
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied Krakow in 1939. Murray's family was confined to the Krakow ghetto along with the rest of the Jewish population of the city. In 1942, Murray and a brother were deported for forced labor in the nearby Plaszow camp. In May 1944, his brother was transferred to Auschwitz and Murray was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp in Germany. Murray was later transferred to Bruennlitz, in the Sudetenland, as a forced laborer for German industrialist Oskar Schindler. Schindler helped the Jews who worked for…

-
Murray Pantirer describes the "Schindler Jews" in the Bruennlitz factory
Oral HistoryThe Germans occupied Krakow in 1939. Murray's family was confined to the Krakow ghetto along with the rest of the Jewish population of the city. In 1942, Murray and a brother were deported for forced labor in the nearby Plaszow camp. In May 1944, his brother was transferred to Auschwitz and Murray was sent to the Gross-Rosen camp in Germany. Murray was later transferred to Bruennlitz, in the Sudetenland, as a forced laborer for German industrialist Oskar Schindler. Schindler helped the Jews who worked for…

-
Leopold Page describes meeting German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

-
Ludmilla Page describes German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Leopold Page describes an act of sabotage and clandestinely listening to radio broadcasts while in Bruennlitz
Oral HistoryLeopold was a teacher in Krakow, Poland, when World War II began in 1939. While serving in the Polish army, he was captured by Germans. Leopold escaped from a prisoner-of-war transport. Soon after, he met the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. The two became friends. Leopold was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto. He later worked in Schindler's factory in Bruennlitz. He and the other Jews who worked there were treated relatively well and protected from the Nazis. After the war, Leopold moved to the…

-
Ludmilla Page describes sabotage during production of munitions in Oskar Schindler's factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes a celebration of Oskar Schindler's birthday in Bruennlitz toward the end of the war
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Emanuel Tanay describes the establishment of the Miechow ghetto
Oral HistoryEmanuel and his family lived in the small town of Miechow, north of Krakow. After Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, persecution of Jews increased. The Germans established a ghetto in Miechow. Emanuel was forced to live in the ghetto. Emanuel, his mother, and his sister escaped from the ghetto before it was destroyed in 1942. He stayed in a monastery, under an assumed identity, along with members of the Polish underground. Emanuel left the monastery after about a year when a teacher began to suspect…

-
Invasion of Poland, Fall 1939
ArticleThe German invasion of Poland in the fall of 1939 triggered WWII. Learn more about key dates and events, causes, and related Holocaust history.

-
Portrait of three-year-old Estera Horn
PhotoPortrait of three-year-old Estera Horn wrapped in a fur coat. Chelm, Poland, ca. 1940. Estera was born in January 1937. Her father was killed soon after the Germans invaded Poland. Estera and her mother, Perla Horn, were forced into the ghetto in Chelm. At the end of 1942, during the liquidation of the ghetto, Perla and Estera escaped from the ghetto. They hid in nearby villages. In late 1943, Perla asked a family in Plawnice to take care of Estera. Perla tried to hide with a group of Jews in the nearby…

-
Gross-Rosen
ArticleLearn about the Gross-Rosen camp, including its establishment, prisoner population, subcamps, forced labor, and liberation.

-
Einsatzgruppen and other SS and Police Units in the Soviet Union
ArticleLearn more about how and why Nazi German SS and police units, including the Einsatzgruppen, perpetrated mass killings of Jews in the occupied-Soviet Union.

-
Rejoice, Make Merry, Children
SongMordecai Gebirtig, born in 1877 in Krakow, Poland, was a Yiddish folk poet and songwriter. Gebirtig had three daughters, for whom he wrote and performed his poems. The words were set to improvised melodies, and most of his songs resemble entries in a diary. Many of Gebirtig's poems contain themes of eastern European Jewish life in the 1920s and 1930s. The lyrics to "Rejoice, Make Merry, Children" contain a springtime motif that recurred in other Gebirtig works. In the lyrics, an elderly narrator urges…
-
Miriam Peleg explains why Żegota was important
Oral HistoryMiriam Peleg (1913–1996) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Born Maria Hochberg, Miriam was from a Polish-Jewish family. She grew up in a small town about 70 miles east of Kraków. As early as the summer of 1940, Miriam obtained…

-
Fred Bachner describes flight to eastern Poland upon the German invasion of Poland in September 1939
Oral HistoryFred was born to Polish Jewish parents in Berlin, where his father owned a factory. After the Kristallnacht ("Night of Broken Glass") pogrom in November 1938, Fred's father and brother were deported to Poland. It was not until June 1939, when Poland allowed Fred and his mother to enter the country, that the family was reunited in Krakow. Fred and his family tried to flee upon the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 but were told to return to their homes. They were forced into the Krakow ghetto, and…

-
Ludmilla Page describes conditions in Oskar Schindler's munitions factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes starvation in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes bombings in Praga and Warsaw after the outbreak of World War II
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes the emotions she felt upon arrival in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem after the war
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Morris Zaidband
ID CardMorris was one of five children born to a Jewish family in the Polish town of Oswiecim, 33 miles west of Cracow [Krakow]. Morris' father sold ladies' undergarments. Morris worked as a jeweler. 1933-39: In September 1939 Germany invaded Poland. Morris's family started to flee eastward but two weeks later the Germans overtook them and they were sent home. When they returned, the Germans were already beating Jews who didn't show them "respect." One day, when German guards came to their house to deport…

