You searched for: 公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建1wW6pnGvVO
<< Previous | Displaying results 101-150 of 653 for "公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建公募私募系统源码定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建1wW6pnGvVO" | Next >>
-
Edward Vebell courtroom sketch
ArtifactCourtroom sketch drawn during the International Military Tribunal by American artist Edward Vebell. The drawing's title is "British Courier for the Correspondents." 1945.

-
Home vandalized during Kristallnacht
PhotoA private Jewish home vandalized during Kristallnacht (the "Night of Broken Glass" pogrom). Vienna, Austria, November 10, 1938.

-
Mass execution site in Estonia
PhotoSite where members of Einsatzgruppe A and Estonian collaborators carried out a mass execution of Jews in September 1941. Kalevi-Liiva, Estonia, after September 1944.

-
Deportation from the Lodz ghetto
PhotoSS personnel stand guard while Lodz ghetto police board Jews onto a deportation train bound for Chelmno or Auschwitz. Lodz, Poland, between May and August 1944.

-
Burial of victims of the Kielce pogrom
PhotoMourners crowd around a narrow trench as coffins of pogrom victims are placed in a common grave, following a mass burial service. Kielce, Poland, after July 4, 1946.

-
Deportation from the Siedlce ghetto
PhotoJews assembled in the Siedlce ghetto during a deportation are forced to march toward the railway station. Siedlce, Poland, August 21–24, 1942.

-
Orphans arrive at a railroad station
PhotoJewish orphans arrive at the Marseille railroad station, en route to Palestine as part of postwar Brihah movement. Marseille, France, March 25, 1948.

-
An interior designer imprisoned for homosexuality
PhotoInterior designer from Duesseldorf who was charged with homosexuality and imprisoned for 18 months. Duesseldorf, Germany, date uncertain.

-
Advertisement for the Violetta women's club
DocumentA newspaper advertisement for the Damenklub Violetta, a Berlin club frequented by lesbians, 1928. Before the Nazis came to power in 1933, lesbian communities and networks flourished in Germany.

-
A Kripo agent's identifying warrant disc
ArtifactOfficial identification tag (warrant badge) for the Criminal Police (Kriminalpolizei or Kripo), the detective police force of Nazi Germany. These badges were generally suspended from a chain and included the officer's identification number on the reverse.

-
Reverse of a Kripo warrant disc listing the officer's number
ArtifactReverse of the official identification tag (warrant badge) for the Kriminalpolizei or Kripo, the detective police force of Nazi Germany. It reads Staatliche Kriminalpolizei (State Criminal Police) and identifies the officer's number as 8409.

-
The Times, August 17, 1921
ArtifactIn this London Times article, reporter Philip Graves compared passages from Maurice Joly’s Dialogue in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu (1864) side-by-side with the Protocols of the Elders of Zion in order to prove that the Protocols was plagiarized. Other investigations revealed that one chapter of a Prussian novel, Hermann Goedsche’s Biarritz (1868), also “inspired” the Protocols. Times (London), August 17, 1921.

-
Demonstrating the operation of the Dachau crematorium
PhotoSurvivors of the Dachau concentration camp demonstrate the operation of the crematorium by preparing a corpse to be placed into one of the ovens. Dachau, Germany, April 29–May 10, 1945. This image is among the commonly reproduced and distributed, and often extremely graphic, images of liberation. These photographs provided powerful documentation of the crimes of the Nazi era.

-
Sisters Eva and Liane Münzer
PhotoSisters Eva and Liane Münzer. They were placed in hiding with a devout Catholic couple. In 1944, Eva and Liane were reported to the police as a result of a fight between their rescuers. The husband denounced his wife and the two Jewish girls. The three were immediately arrested and sent to the Westerbork camp. On February 8, 1944, eight- and six-year-old Eva and Liane were deported to Auschwitz, where they were murdered. Photograph taken in The Hague, the Netherlands, 1940.

-
On the waiting list for American visas
DocumentSelmar and Elsa Biener joined the waiting list for US immigration visas in September 1938. Their waiting list numbers—45,685 and 45,686—indicate the number of people who had registered with the US consulate in Berlin. By September 1938, approximately 220,000 people throughout Germany, mostly Jews, were on the waiting list.

-
Pages from a child's diary
PhotoIllustrated page of a child's diary written in a Swiss refugee camp. The diary entry describes how they crossed the border into Switzerland. The text reads, "We came out of the woods and into a clearing: we had to be as quiet as possible because we were so close to the border. Oh! I almost forgot! Before we came out of the woods, they made us stand still for a quarter of an hour while they went to explore the area and to cut through the fence. Fortunately, shortly thereafter, we began to walk again. We saw…

-
View of the Sobibor killing center
PhotoRare image of the site of the Sobibor killing center, taken from an album of photos belonging to Sobibor deputy camp commandant Johann Niemann.

-

-
Deportation of Jews from Germany to Latvia
PhotoDeportation of Jews from Bielefeld in Germany to Riga in Latvia. Bielefeld, Germany, December 13, 1941.

-
Elie Wiesel speaks at a Days of Remembrance ceremony
PhotoElie Wiesel speaks at the Days of Remembrance ceremony, Washington, DC, 2002.

-
Soviet prisoners of war at forced labor
PhotoSoviet prisoners of war at forced labor build a road. Probably in the Soviet Union, about 1943.

-
Jadwiga Dzido's military entry permit
ArtifactReverse side of a military entry permit allowing Jadwiga Dzido to travel through occupied Germany to appear as a witness in the Medical Case trial at Nuremberg. 1946.

-
International Military Tribunal prison pass
ArtifactBack side of an entry pass to the prison housing war criminals at the International Military Tribunal. This pass was issued to a U.S. military guard.

-
White armband with blue Star of David
ArtifactWhite armband with a Star of David embroidered in blue thread, worn by Dina Offman from 1939 until 1941 while in the ghetto in Stopnica, Poland.

-
Torchlight parade in honor of Hitler's appointment as chancellor
PhotoFrom a window in the Reich Chancellery, German president Paul von Hindenburg watches a Nazi torchlight parade in honor of Adolf Hitler's appointment as German Chancellor. Berlin, Germany, January 30, 1933.

-
Ship used to deport Jews from Norway
PhotoThe Monte Rosa (right), one of the ships used to deport Jews from Norway to Germany. Norway, 1943.

-
Public burning of "un-German" books in Berlin
PhotoPublic burning of "un-German" books in the Opernplatz (Opera Square) in Berlin. Students, some in SA uniform, march in a torchlight procession. Berlin, May 10, 1933.

-
Adolf Hitler greets Paul von Hindenburg
PhotoAdolf Hitler, the newly appointed chancellor, greets German president Paul von Hindenburg. Berlin, Germany, January 30, 1933.

-
Jews captured during the Warsaw ghetto uprising
PhotoJews captured during the Warsaw ghetto uprising. Poland, April 19–May 16, 1943.

-
Postwar photo of a church in the village of Chelmno
PhotoPostwar photo of a church in the village of Chelmno. Jews were kept in this building en route to the Chelmno killing center. Chelmno, Poland, June 1945.

-
Jewish refugee children arrive in the United Kingdom
PhotoJewish refugee children, part of a Children's Transport (Kindertransport) from Germany, upon arrival in Harwich. Great Britain, December 12, 1938.

-
Deportation of Jews from Germany to Riga
PhotoJews in the town of Coesfeld, in northwestern Germany, assembled for deportation to the Riga ghetto. Coesfeld, Germany, December 10, 1941.

-
Agricultural training before emigration to Palestine
PhotoAn agricultural training farm to prepare Jewish refugees for life in Palestine, sponsored by the Joint Distribution Committee. Fuerth, Germany, June 13, 1946.

-
Footbridge that joined the two parts of the Lodz ghetto
PhotoThe footbridge over Zgierska Street that joined the two parts of the Lodz ghetto. The street itself was not part of the ghetto. Lodz, Poland, ca. 1941.

-
Regina at the Dueppel displaced persons camp
PhotoRegina (third from left) with friends while at the Dueppel displaced persons camp. Berlin, Germany, May 20, 1946.
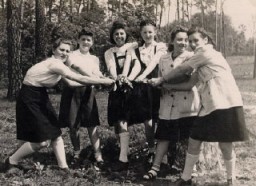
-
Page from an antisemitic German children's book
PhotoPage from the antisemitic German children's book, "Trau Keinem Fuchs..." (Trust No Fox in the Green Meadow and No Jew on his Oath). Germany, 1936.

-
Scene of destruction during World War I
PhotoHouses along the River Meuse damaged during the Battle of Verdun, December 1916. The battle was one of the longest and deadliest of World War I. © IWM (Q 67594)

-
Booklet about International Military Tribunal
ArtifactFourth and fifth pages of a program booklet distributed during the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg. Page four defines the charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity. The fifth page begins the list of IMT defendants. Handwritten notes in the margin record each defendant's sentence as it was read aloud in the courtroom.

-
Matchbox cover with Japanese propaganda illustration
ArtifactDuring the war the Japanese flooded Shanghai with anti-American and anti-British propaganda, including this image from a matchbox cover. It depicts Japanese planes flying in formation over the U.S. and British flags, with the Japanese flag rising in triumph. Shanghai, China, between 1943 and 1945. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Portrait by refugee artist Yonia Fain
ArtifactPortrait of Semek Kushner, in pencil, by Yonia Fain. Kushner's father and brother were killed in Shanghai near the end of the war during an American air raid on Hongkew. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Polish citizenship certificate issued to Samuel Solc
DocumentThis page of a Polish citizenship certificate issued to Samuel Solc contains two visas. The first (left), stamped by the British Passport control in Shanghai, allowed Samuel to travel to Palestine via Burma, India, Egypt, and Rangoon. The second visa (right) bears the British Mandate "Government of Palestine" stamp, dated February 6, 1942, and allowed Samuel to remain in Palestine permanently. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Defendant Hermann Göring listens to trial testimony
FilmDefendant Hermann Göring, seated at left in the dock, listens as US Chief Prosecutor Robert Jackson interrogates witness Albert Kesselring about the Luftwaffe (German Air Force).

-
Inauguration of Paul von Hindenburg as President of Germany
Timeline EventMay 12, 1925. On this date, German Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg is inaugurated, becoming the last president of the Weimar Republic.

-
Abraham Lewent describes conditions in the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Belongings of Jews who were deported from Vienna
PhotoBelongings of Jews who were deported from Vienna. Austria, 1941–42.

-
Jews from Bulgarian-occupied Macedonia before deportation
PhotoJews from Bulgarian-occupied Macedonia interned in the "Monopol" tobacco factory, which was used as a transit camp. They were ultimately deported to the Treblinka killing center. Skopje, Macedonia, March 1943.

-
Ruins of the old synagogue in Aachen
PhotoView of the old synagogue in Aachen after its destruction on Kristallnacht. Aachen, Germany, photo taken ca. November 10, 1938.

-
Book burning in Berlin, Germany, May 10, 1933
PhotoAt Berlin's Opernplatz, crowds of German students and members of the SA gather for the burning of books deemed "un-German." Berlin, Germany, May 10, 1933.

