<< Previous | Displaying results 6701-6720 of 6720 for "" | Next >>
-
Protocols of the Elders of Zion: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events related to the Protocols of the Elders of Zion, the most notorious and widely distributed antisemitic publication of modern times.

-
Esther Lurie
ArticleArtist Esther Lurie documented life in the Kovno ghetto for its secret archives. Learn about her watercolors and sketches, the majority of which have never been found.

-
What Groups of People did the Nazis Target?
ArticleJews were the primary targets for mass murder by the Nazis and their collaborators. Nazi policies also led to the brutalization and persecution of millions of others.

-
The Eastern Front: The German War against the Soviet Union
ArticleOften referred to as the “eastern front,” the German-Soviet theater of war was the largest and deadliest of World War II. Learn more about the background and key events.

-
Axis Powers in World War II
ArticleThe three principal partners in the Axis alliance were Germany, Italy, and Japan. Learn more about the Axis powers in WW2.

-
Battle of the Bulge
ArticleThe Battle of the Bulge was a failed German counter-offensive against the Allied armies. Learn more about the Battle of the Bulge and its impact on WWII.

-
Emanuel Ringelblum and the Creation of the Oneg Shabbat Archive
ArticleEmanuel Ringelblum was a Warsaw-based historian and social welfare worker before WWII. Learn about the secret archive he would establish in the Warsaw ghetto.

-
The Bielski Partisans
ArticleUnder the protection of the Bielski partisan group, founded by brothers Tuvia, Asael, and Zus, over 1,200 Jews survived after fleeing into forests in western Belarus.

-
Der Stuermer, number 29, July 1934
ArtifactNazi Germany’s semi-official and fiercely antisemitic newspaper Der Stuermer warned of a Jewish program for world domination in this 1934 issue. The article—titled “Who is the Enemy?”—blamed Jews for destroying social order and claimed that Jews wanted war, while the rest of the world wanted peace. Der Stuermer, July 1934.

-
Antisemitism: Oral History Excerpts
Media EssayThe word antisemitism means prejudice against or hatred of Jews. The Holocaust is history’s most extreme example of antisemitism. In these oral histories, survivors......
-
What is Antisemitism?
ArticleThe word antisemitism means prejudice against or hatred of Jews. The Holocaust is history’s most extreme example of antisemitism. Learn more.

-
Breakfast menu from the SS Exeter, 1941
ArtifactThis breakfast menu comes from the SS Exeter, an American ocean liner. The ship carried the Shadurs, a Jewish refugee family, to the United States in February-March 1941. The Shadurs were among the many Jewish refugees who journeyed on the SS Exeter from Lisbon, Portugal, to New York during World War II. Joseph Shadur was twelve years old at the time. He marveled at the ship’s bountiful meals, especially in light of the hunger his family had faced on their journey to the port of Lisbon. The course of…

-
1936 Berlin Olympics torch holder
ArtifactThis Olympic torch holder was used during the 1936 Berlin Olympics. It is engraved with the 1936 Olympics torch relay route from Olympia, Greece, to Berlin, Germany.

-
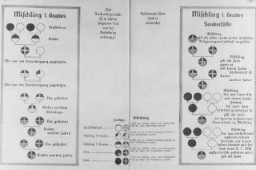
Classification System in Nazi Concentration Camps
ArticleThe Nazis used color-coded badges sewn onto uniforms to classify prisoners in the camp system and to easily identify the alleged reason for an individual’s incarceration.
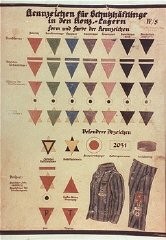
-
Antisemitism in History: Racial Antisemitism, 1875–1945
ArticleRacial antisemitism is the discriminatory idea that Jews are a separate and inferior race. This type of antisemitism dates back to the late 1800s.
-
Eugenics poster
PhotoEugenics poster entitled "The Nuremberg Law for the Protection of Blood and German Honor." The illustration is a stylized map of the borders of central Germany upon which is imposed a schematic of the forbidden degrees of marriage between Aryans and non-Aryans and the text of the Law for the Protection of German Blood. The German text at the bottom reads, "Maintaining the purity of blood insures the survival of the German people."
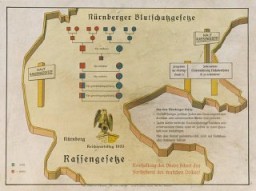
-
Gassing Operations
ArticleThe Nazis used poisonous gas to murder millions of people in gas vans or stationary gas chambers. The vast majority of those killed by gassing were Jews.

-
Trawniki: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Trawniki in German-occupied Poland.

-
Eugenics
Media EssayEugenics, or “racial hygiene” in the German context, was a scientific movement of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Eugenic theories provided the basis for the Nazi compulsory sterilization program and...

-

