You searched for: https://www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html%20t%C3%BAi%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20nam%20,%20%C3%81o%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p?www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html?%20Giay%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20,%20mu%20dior%20Dior,%20giay%20lu?i%20dior%20nam,%20T%C3%BAi%20c%C3%B4ng%20s?%20Dior%20Like%20Auth%20so%20mi%20dior%20nam
<< Previous | Displaying results 1351-1400 of 1747 for "https://www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html%20t%C3%BAi%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20nam%20,%20%C3%81o%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p?www.duybrand.com/brand-1-c0.html?%20Giay%20Dior%20sieu%20c?p%20,%20mu%20dior%20Dior,%20giay%20lu?i%20dior%20nam,%20T%C3%BAi%20c%C3%B4ng%20s?%20Dior%20Like%20Auth%20so%20mi%20dior%20nam" | Next >>
-
The History of the Swastika
ArticleThe swastika is an ancient symbol that was in use in many different cultures for many years before Adolf Hitler made it the centerpiece of the Nazi flag.

-

-
Leah Hammerstein Silverstein describes working under a false non-Jewish identity in a German hospital in Krakow
Oral HistoryLeah grew up in Praga, a suburb of Warsaw, Poland. She was active in the Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir Zionist youth movement. Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Jews were forced to live in the Warsaw ghetto, which the Germans sealed off in November 1940. In the ghetto, Leah lived with a group of Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir members. In September 1941, she and other members of the youth group escaped from the ghetto to a Ha-Shomer ha-Tsa'ir farm in Zarki, near Czestochowa, Poland. In May 1942, Leah became a courier…

-
Thomas Buergenthal describes operations of international tribunals
Oral HistoryJudge Thomas Buergenthal was one of the youngest survivors of the Auschwitz and Sachsenhausen concentration camps. He immigrated to the United States at the age of 17. Judge Buergenthal devoted his life to international and human rights law. He served as chairman of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum’s Committee on Conscience; was named the Lobingier Professor of Comparative Law and Jurisprudence at the George Washington University Law School; and served for a decade as the American judge at…

-
Suse Gruenbaum Schwarz describes preparation for and hiding during a Nazi raid
Oral HistorySuse's family moved to the Netherlands in 1933. After invading the Netherlands in 1940, the Germans imposed anti-Jewish measures. From 1942, Suse could not attend school. The family went into hiding in 1943, Suse and her mother on one farm and her father on another. Later, her father and another couple came to hide with Suse. They were liberated in 1945. Suse arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
Budy: An Auschwitz Subcamp
ArticleBudy was one of more than 40 subcamps that the SS administered as part of the Auschwitz camp complex. Learn more.
-
Miriam Peleg explains why Żegota was important
Oral HistoryMiriam Peleg (1913–1996) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Born Maria Hochberg, Miriam was from a Polish-Jewish family. She grew up in a small town about 70 miles east of Kraków. As early as the summer of 1940, Miriam obtained…

-
Sarah Judelowitz
ID CardSarah, born Sarah Gamper, was one of four children born to a Jewish family in the Baltic port city of Liepaja. Her parents owned a general store there. At the outbreak of World War I, Sarah was studying piano at a conservatory in Russia. During World War I, she remained there to serve as a nurse. She returned to Liepaja, and after marrying Herman Judelowitz in 1920, settled there. 1933-39: Sarah and Herman operated a shoe store in the front of their small shoe workshop. By 1935 they had three daughters,…

-
Frances Perkins
ArticleFrances Perkins was FDR's secretary of labor. Learn about her role in the rescue of European Jews whose lives were threatened by the Nazi regime.

-
Truman proclaims victory in Europe
FilmWorld War II began with the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 and ended in Allied victory in Europe with the German surrender in May 1945. May 8 was proclaimed VE (Victory in Europe) Day. In this footage, United States president Harry S. Truman proclaims victory in Europe and promises to continue the war in the pacific until the unconditional surrender of Japan.

-
British army chaplain describes Bergen-Belsen upon liberation
FilmBritish troops liberated the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp in Germany in April 1945. They filmed statements from members of their own forces. In this British military footage, British army chaplain T.J. Stretch recounts his impressions of the camp.

-
Allied prisoner of war describes work details
FilmMost Allied prisoners of war (POWs) were treated well compared to inmates of concentration camps. But, as former Dutch POW Captain Boullard explains here at Dachau concentration camp, some were subject to severe beatings and forced to work in harsh labor assignments.

-
Hanne Hirsch Liebmann describes harassment and anti-Jewish sentiment in Germany
Oral HistoryHanne's family owned a photographic studio. In October 1940, she and other family members were deported to the Gurs camp in southern France. In September 1941, the Children's Aid Society (OSE) rescued Hanne and she hid in a children's home in Le Chambon-sur-Lignon. Her mother perished in Auschwitz. In 1943, Hanne obtained false papers and crossed into Switzerland. She married in Geneva in 1945 and had a daughter in 1946. In 1948, she arrived in the United States.

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes how the teddy bear brings her back to the past
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
William (Bill) Zeck describes translation and witnesses during war crimes trials
Oral HistoryBefore joining the US Army, Zeck—a lawyer—worked for the Board of Economic Warfare. In 1946, he was hired to work on preparations for the Nuremberg trials. In his search for documents pertaining to the I. G. Farben company's involvement in the war, Zeck also met attorney Belle Mayer, his future wife. Both Zeck and Mayer were involved in preparing the indictment in the I. G. Farben trial held at Nuremberg.

-
Historian Peter Black describes the importance of legal consequences
Oral HistoryIn the 1980s and 1990s, historian Peter Black worked for the US Department of Justice Office of Special Investigations, as part of a team tracking and prosecuting suspected war criminals. Black later served as the Senior Historian at the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Ruth Meyerowitz describes her memories of the Auschwitz crematoria
Oral HistoryIn Frankfurt, Ruth's family faced intensifying anti-Jewish measures; her father's business was taken over and Ruth's Jewish school was closed. In April 1943, Ruth and her family were deported to Auschwitz. Ruth was selected for forced labor and assigned to work on road repairs. She also worked in the "Kanada" unit, sorting possessions brought into the camp. In November 1944, Ruth was transferred to the Ravensbrueck camp system, in Germany. She was liberated in May 1945, during a death march from the…

-
Miles Lerman describes roles of women in the underground
Oral HistoryMiles Lerman was a Holocaust survivor, partisan fighter in the forests of Poland, international leader in the cause of Holocaust remembrance, and a "founding father" of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Rallying the Nation
ArticleThe Nazis used propaganda to promote their ideas and beliefs about a "national community." Read more about the principles, goals, and strategies of Nazi propaganda.

-
Gardelegen
ArticleIn April 1945, US troops encountered a barn on the outskirts of Gardelegen where the SS and its accomplices had massacred over 1,000 concentration camp prisoners.

-
The SA
ArticleThe SA (Sturmabteilung) was a paramilitary organization integral to Hitler’s ascension to power. Learn more about the rise and fall of the SA.

-
Eugenics
ArticleTheories of eugenics shaped many persecutory policies in Nazi Germany. Learn about the radicalization and deadly consequences of these theories and policies

-
Frank Liebermann
ArticleExplore Frank Liebermann’s biography and learn about his experiences of antisemitism in his home town in Germany before World War II.

-
The 84th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 84th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating two Neuengamme subcamps, Hannover-Ahlem and Salzwedel, in 1945.
-
Danzig - Photographs
Media EssayFollowing World War I, the Treaty of Versailles (1918) declared Danzig to be a free city administered by Poland and the League of Nations. Germany resented the loss of this largely German city. After invading Poland in September 1939, Nazi Germany annexed Danzig.
-
Martin Niemöller
Media EssayMartin Niemöller was a prominent Protestant pastor in Germany who emerged as an outspoken public foe of Adolf Hitler. His postwar words, “First they came for the socialists, and I did not speak out…” continue to be used in popular culture and public...
-
Treblinka: Maps
Media EssayThe Treblinka killing center was one of four camps linked to Operation Reinhard. Known as Treblinka II, it opened in July 1942 about a mile from from Treblinka I, the labor camp. The Germans killed an estimated 925,000 Jews at Treblinka II, as well...
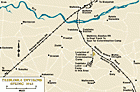
-
Annexation of Austria
FilmGerman troops entered Austria on March 12, 1938. The annexation of Austria to Germany was proclaimed on March 13, 1938. In this German newsreel footage, Austrians express overwhelming enthusiasm for the Nazi takeover of their country.

-
Insignia of the 84th Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 84th Infantry Division. The 84th Infantry Division derives its nickname, "Railsplitter" division, from the divisional insignia, an ax splitting a rail. This design was created during World War I, when the division was known as the "Lincoln" division to represent the states that supplied soldiers for the division: Illinois, Indiana, and Kentucky. All figured prominently in the life of President Abraham Lincoln, of log-splitting legend.

-
Insignia of the 86th Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 86th Infantry Division. The 86th Infantry Division developed the blackhawk as its insignia during World War I, to honor the Native American warrior of that name who fought the US Army in Illinois and Wisconsin during the early nineteenth century. The nickname "The Blackhawks" or "Blackhawk" division is derived from the insignia.

-
Insignia of the 90th Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 90th Infantry Division. Called the "Tough Ombres," the 90th Infantry Division was raised from draftees from the states of Texas and Oklahoma during World War I. The divisional insignia incorporates the letters "T" and "O" to symbolize both states. These letters later yielded the nickname "Tough Ombres," symbolizing the esprit de corps of the unit. The 90th was also sometimes called the "Alamo" division during World War II.

-
Insignia of the 83rd Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 83rd Infantry Division. The 83rd Infantry Division received its nickname, the "Thunderbolt" division, after a division-wide contest for a new nickname held in early 1945. The earlier nickname, "Ohio," was based on the division's insignia (which includes the name "Ohio," where the division was raised during World War I). A new nickname was desired to represent the nationwide origins of the division's personnel during World War II.

-
Insignia of the 101st Airborne Division
PhotoInsignia of the 101st Airborne Division. The nickname of the 101st Airborne Division, "Screaming Eagles," originates from the division's insignia, a bald eagle on a black shield. "Old Abe" was the eagle mascot of a Wisconsin regiment during the Civil War. The 101st was formed as a reserve unit in Wisconsin shortly after World War I and included "Old Abe" as part of the division's insignia.

-
Insignia of the 42nd Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 42nd Infantry Division. The nickname of the 42nd Infantry Division, the "Rainbow" division, reflects the composition of the division during World War I. The division was drawn from the National Guards of 26 states and the District of Columbia. It represented a cross section of the American people, as the rainbow represents a cross section of colors.

-
Insignia of the 36th Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 36th Infantry Division. The 36th Infantry Division, the "Texas" division, was raised from National Guard units from Texas and Oklahoma during World War I. The "T" in the division's insignia represents Texas, the arrowhead Oklahoma. The division was also sometimes called the "Lone Star" division, again symbolizing its Texas roots.

-
Insignia of the 29th Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 29th Infantry Division. "Blue and Gray" was coined as the nickname of the 29th Infantry Division by the division's commander during World War I. The name commemorates the lineage of the mid-Atlantic states' National Guard units that formed the division, many with service on both sides during the Civil War.

-
Insignia of the 80th Infantry Division
PhotoInsignia of the 80th Infantry Division. The nickname of the 80th Infantry Division, the "Blue Ridge" division, reflects the home states of the majority of soldiers who formed the division during World War I: Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Virginia. The Blue Ridge Mountains run through these three states.

-
Erich Mühsam
PhotoIdentification picture of Erich Mühsam taken in the Oranienburg concentration camp. Mühsam, an anarchist and a pacifist, worked as an editor and writer; he was imprisoned during World War I for opposing the war. Arrested during the massive roundup of Nazi political opponents following the Reichstag fire (February 27, 1933), Mühsam was tortured to death in Oranienburg on July 11, 1934. Oranienburg, Germany, February 3, 1934.

-
Reversal of Fortune: Robert Kempner
ArticleLawyer Robert Kempner was expelled from Germany in 1935. After WWII, he would return to serve as assistant US chief counsel during the IMT at Nuremberg.

-
James Ingo Freed: Architect of the Museum
ArticleArchitect James Ingo Freed designed the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

-
Rut Berlinska
ArticleChildren's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking experiences of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Rut Berlinska.
-
Latvia
ArticleBetween 1940 and 1944, Latvia was occupied by the Soviets and then by the Germans. These occupations had grave consequences for Jews in Latvia. Learn more.

-
Artist on the Blacklist: Ludwig Meidner
ArticleLudwig Meidner was an Expressionist artist and poet. He was on the list of banned writers and artists in Nazi Germany. Monographs about him were burned in 1933.

-
Alfred Kerr
ArticleGerman Jewish writer Alfred Kerr was a well known theater critic during the Weimar period. His works were burned during the Nazi book burnings of 1933.
-
Yitzhak Gitterman
ArticleYitzhak Gitterman was a director of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee in Poland and a member of the underground Jewish Fighting Organization.

-
Hermann Göring
ArticleBrief overview of the charges against Hermann Göring, highest ranking Nazi official tried during the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg.

-
Nazi Hunting: Simon Wiesenthal
ArticleHolocaust survivor Simon Wiesenthal dedicated his life to raising public awareness of the need to hunt and prosecute Nazis who had evaded justice.
-
Russian Revolution, 1917
ArticleThe Russian Revolution consisted of two separate revolutions in 1917: the February Revolution and the Bolshevik Revolution. Learn more.

-
Werner Hegemann
ArticleWerner Hegemann was a city planner and author. The Nazis opposed his views of American architecture and German historical figures. His book was burned in 1933.
-
Morris Hillquit
ArticleMorris Hillquit was a prominent theoretician of the socialist movement in the United States. His work was burned in the Nazi book burnings of 1933. Learn more.

