You searched for: warsaw
<< Previous | Displaying results 351-400 of 487 for "warsaw" | Next >>
-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes conditions in the Westerbork camp in the Netherlands
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation--including the order to wear the Jewish…

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes deportations from the Westerbork camp in the Netherlands
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation—including the order to wear the…

-
Elie Wiesel Timeline and World Events: 1928–1951
ArticleSurvivor Elie Wiesel devoted his life to educating the world about the Holocaust. Learn about key events in the world and his life from 1928–1951.

-
Resistance in the Smaller Ghettos of Eastern Europe
ArticleLearn more about Jewish resistance efforts in the smaller ghettos of eastern Europe and the obstacles and limitations Jews faced.

-
Non-Jewish Resistance
ArticleA variety of non-Jewish groups and individuals resisted the Nazi regime, both in Germany and in German-occupied territory. Learn more.

-
Sachsenhausen
ArticleIn July 1936, the SS opened the Sachsenhausen concentration camp as the principal concentration camp for the Berlin area.

-
Rescue in Denmark
ArticleThe Danish resistance movement, assisted by many ordinary citizens, coordinated the flight of some 7,200 Jews to safety in nearby neutral Sweden. Learn more about rescue in Denmark.

-
1944: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1944 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Portrait of three-year-old Estera Horn
PhotoPortrait of three-year-old Estera Horn wrapped in a fur coat. Chelm, Poland, ca. 1940. Estera was born in January 1937. Her father was killed soon after the Germans invaded Poland. Estera and her mother, Perla Horn, were forced into the ghetto in Chelm. At the end of 1942, during the liquidation of the ghetto, Perla and Estera escaped from the ghetto. They hid in nearby villages. In late 1943, Perla asked a family in Plawnice to take care of Estera. Perla tried to hide with a group of Jews in the nearby…

-
Ghettos in occupied Poland, 1939-1941
MapGermany occupied western Poland in fall 1939. Much of this territory was annexed to the German Reich. Eastern Poland was not occupied by German forces until June 1941. In south-central Poland the Germans set up the Generalgouvernement (General Government), where most of the early ghettos were established. Ghettos were enclosed districts of a city in which the Germans forced the Jewish population to live under miserable conditions. Ghettos isolated Jews by separating Jewish communities both from the…
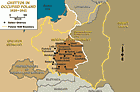
-
Jewish Uprisings in Ghettos and Camps, 1941–44
ArticleUnder the most adverse conditions, Jewish prisoners initiated resistance and uprisings in some of the ghettos and camps, including Bialystok, Warsaw, Treblinka, and Sobibor.

-
Einsatzgruppen and other SS and Police Units in the Soviet Union
ArticleLearn more about how and why Nazi German SS and police units, including the Einsatzgruppen, perpetrated mass killings of Jews in the occupied-Soviet Union.

-
Jewish Community of Kalisz in the Interwar Years
ArticleLearn about the vibrant Jewish community of Kalisz between World War I and World War II.

-
Plight of Jewish Children
ArticleDuring the Holocaust, some children went into hiding to escape Nazi persecution. They faced constant fear, dilemmas, and danger.

-
Coining a Word and Championing a Cause: The Story of Raphael Lemkin
ArticlePolish-Jewish lawyer Raphael Lemkin introduced the word genocide in 1944 and lobbied tirelessly for its addition as a crime in international law.

-
Shalom Yoran
ArticleRead the Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation's short biography of Shalom Yoran.

-
Documentation on the Persecution of Roma (Gypsies)
ArticleRoma (Gypsies) were persecuted in Europe before and during World War II. This history is well documented in archives throughout Europe and the United States. Learn more.

-
Blanka Rothschild describes returning to Lodz after the war to look for family members
Oral HistoryBlanka was an only child in a close-knit family in Lodz, Poland. Her father died in 1937. After the German invasion of Poland, Blanka and her mother remained in Lodz with Blanka's grandmother, who was unable to travel. Along with other relatives, they were forced into the Lodz ghetto in 1940. There, Blanka worked in a bakery. She and her mother later worked in a hospital in the Lodz ghetto, where they remained until late 1944 when they were deported to the Ravensbrueck camp in Germany. From Ravensbrueck,…

-
The Lodz Ghetto
Animated MapView an animated map of key events in the history of the Lodz ghetto in occupied Poland, from establishment by the Germans in 1940 until destruction in 1944.
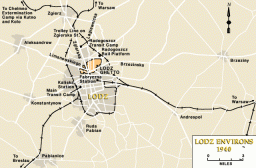
-
World War II: In Depth
ArticleGermany started World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, by invading Poland. War would continue until 1945. Learn more about key events in the history of WWII.

-
Ruth Berkowicz Segal describes receiving visa to leave Lithuania
Oral HistoryWhen German forces invaded Poland in September 1939, Ruth's father fled to eastern Poland. Upon the Soviet occupation of eastern Poland, he fled to Lithuania. Ruth left Warsaw with two friends to find her father and later joined him in Vilna. After Soviet forces occupied Lithuania, Ruth and her father obtained transit visas for Japan, but only Ruth obtained a Soviet exit visa. Her father insisted she leave and not wait for him. Ruth traveled by the Trans-Siberian Railroad across the Soviet Union to…

-
Susan Bluman describes fleeing to Vilna after the occupation of Poland
Oral HistorySusan was 19 years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Her boyfriend, Nathan, was in Lvov when the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland. Nathan sent a guide to Warsaw to bring Susan to the Soviet zone of occupied Poland. Her parents reluctantly agreed after Susan promised to return to Warsaw within two weeks. Upon her arrival in Lvov, Susan married Nathan. The couple then fled across the Lithuanian border to Vilna, where they stayed for a year. They received a visa for transit through Japan…

-
Susan Bluman describes obtaining a transit visa from Chiune Sugihara
Oral HistorySusan was 19 years old when Germany invaded Poland in September 1939. Her boyfriend, Nathan, was in Lvov when the Soviet Union occupied eastern Poland. Nathan sent a guide to Warsaw to bring Susan to the Soviet zone of occupied Poland. Her parents reluctantly agreed after Susan promised to return to Warsaw within two weeks. Upon her arrival in Lvov, Susan married Nathan. The couple then fled across the Lithuanian border to Vilna, where they stayed for a year. They received a visa for transit through Japan…

-
Raszka (Roza) Galek Brunswic describes her decision, while posing as a Polish Catholic, to work on a farm in Germany
Oral HistoryRoza's family moved to Warsaw in 1934. She had just begun college when Germany invaded Poland in 1939. In 1940, the Germans sealed the Warsaw ghetto, where her parents were shot during a roundup. Roza escaped and went into hiding. From her hiding place she saw the burning of the ghetto in the 1943 uprising. She had false papers stating she was a Polish Catholic (Maria Kowalczyk), and was deported by cattle train to Germany in June 1943. She worked on a farm until liberation in 1945.

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes the importance of bonds of friendship among young people imprisoned in the Westerbork camp
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation--including the order to wear the Jewish…

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes Zionist and cultural activities in the Westerbork camp
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation--including the order to wear the Jewish…

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes her years in Poland living under a false identity
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
Combating Holocaust Denial: Evidence of the Holocaust presented at Nuremberg
ArticleAt the Nuremberg trials, Allied prosecutors submitted documentation left by the Nazi state itself. This evidence is a lasting refutation of attempts to deny the Holocaust.

-
1942: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1942 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
The Order Police
ArticleThe Order Police (Ordnungspolizei, Orpo) were Nazi Germany’s uniformed police forces. They became perpetrators of horrific crimes and played a significant role in the Holocaust.

-
The Krakow (Cracow) Ghetto during the Holocaust
ArticleThe Krakow ghetto in German-occupied Poland held over 15,000 Jews. Learn more about Krakow and the ghetto’s history during the Holocaust and WWII.

-
Wladyslaw Piotrowski
ID CardWladyslaw was born to Catholic parents in Russian-occupied Poland. He grew up in Plock, a town located in a rural area north of Warsaw. Wladyslaw married in 1918 and he and his wife, Marie, raised four children. 1933-39: Wladyslaw worked as a bookkeeper, and then as an accountant for a local farmers' cooperative. In 1931 he was sent to the town of Wyszogrod to close a failing branch of the farmers cooperative. A year later, he organized a new, successful cooperative in Wyszogrod with local farmers and…

-
Benjamin Frydmacher
ID CardBenjamin was born in the industrial city of Lublin to a large, Yiddish-speaking Jewish family. He attended public school, and after he graduated at the age of 14, he apprenticed at the same tannery where his father was the tannery master. 1933-39: After completing his apprenticeship, Benjamin became the assistant tannery master. After his father's death in 1938, he became the production tannery master. He and his wife, Gucia, lived with his mother at 50 Lubartowska Street. In 1938 the Frydmachers had a…

-
Rozia Grynbaum
ID CardRozia was the second-oldest of nine children born to religious Jewish parents in Starachowice, a town in east-central Poland. Their small one-story house served as both the family's residence and their tailor shop. The tailoring was often done in exchange for goods such as firewood or a sack of potatoes. Rozia worked in the shop sewing women's clothing. 1933-39: Rozia married a Jewish tailor from Radom, a large town some 60 miles south of Warsaw. The couple settled in Starachowice, and they ran a tailor…
-
Mayer List
ID CardMayer was born into a Jewish family in a village near Warsaw. His family was active there in the workers' movement. They decided to emigrate when Mayer was a child; his father hoped to find work in Argentina. As a young man, Mayer was arrested for being a communist. In prison, he organized a hunger strike. The police released him to keep him from recruiting the other prisoners to communism. 1933-39: Mayer joined one of the International Brigades and went to Spain to fight in the civil war against Franco…

-
Edwarda Kleinfeld Rorat describes emotions upon liberation
Oral HistoryAfter the German invasion in 1939, Edwarda and her family left Warsaw and moved to a small village near Lublin. Her parents were murdered by German soldiers in 1942. Edwarda was eventually taken in by the Rorat family. The Rorats owned a village store. She lived under their protection throughout the war and continued to live with them after liberation. She completed her education in Poland and later immigrated to the United States.

-
Doris Greenberg describes conditions in Ravensbrück
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in 1939 and established a ghetto in Warsaw in 1940. After her parents were deported, Doris hid with her sister and other relatives. Doris's sister and an uncle were killed, and she learned that her parents had been killed. Her grandmother committed suicide. Doris was smuggled out of the ghetto and lived as a non-Jewish maid and cook, but was ultimately deported to the Ravensbrück camp. Upon arrival there, Doris and her friend Pepi contemplated swallowing poison, but decided…

-
John Dolibois describes attitude of captured Nazi leaders
Oral HistoryJohn Dolibois immigrated to the United States in 1931 at the age of 13. After graduating from college, Dolibois joined the 16th Armored Division of the US Army. Due to his German language skills, he became involved in military intelligence. He returned to Europe in this capacity toward the end of World War II. Dolibois interrogated German prisoners of war, including leading Nazis, in preparation for the postwar trials of war criminals. He was later appointed US ambassador to Luxembourg, his birthplace.

-
Lucine Horn describes the German occupation of Lublin
Oral HistoryLucine was born to a Jewish family in Lublin. Her father was a court interpreter and her mother was a dentist. War began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Lucine's home was raided by German forces shortly thereafter. Soon after the German occupation of Lublin, Jews there were forced to wear a compulsory badge identifying them as Jews. A ghetto in Lublin was closed off in January 1942. Lucine survived a series of killing campaigns and deportations from the ghetto during March and…

-
Lublin/Majdanek: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events in the history of the Lublin/Majdanek camp in German-occupied Poland.

-
SS and Nazi Policy
ArticleThe SS was the elite guard of the Nazi regime and became a virtual state within a state in Nazi Germany. Learn about its role in carrying out Nazi policies.

-
Death Marches
ArticleAs Allied forces approached Nazi camps in the last months of WWII, the SS organized brutal “death marches” (forced evacuations) of concentration camp inmates.

-
Lublin/Majdanek Concentration Camp: Administration
ArticleIn 1940, the Nazis established Lublin (Majdanek) concentration camp in Lublin, Poland. Learn more about camp administration.

-
Stutthof
ArticleLearn about the Stutthof camp from its establishment until liberation in May 1945, including conditions, forced labor, subcamps, and death marches.

-
Misuse of Holocaust Imagery Today: When Is It Antisemitism?
ArticleLearn more about the modern misuse of images and symbols from the Holocaust and how this distortion can lead to antisemitism.
-
Theresienstadt
ArticleThe Theresienstadt camp/ghetto served multiple purposes during its existence from 1941-45 and had an important propaganda function for the Germans. Learn more.

-
Armed Jewish Resistance: Partisans
ArticleFacing overwhelming odds, Jews throughout occupied Europe attempted armed resistance against the Germans and their Axis partners.

-
Polish Victims
ArticleIn September 1939, the Germans launched a campaign of terror intended to destroy the Polish nation and culture. Learn more about the German occupation of Poland.

-
Polish Jewish Refugees in Lithuania, 1939–40
ArticleLearn more about Polish Jewish refugees that relocated to Lithuania between 1939-1940.

-
Killing Center Revolts
ArticleUnder the most adverse conditions, prisoners initiated revolts in killing centers. Learn more about prisoner uprisings in Treblinka, Sobibor, and Auschwitz.

