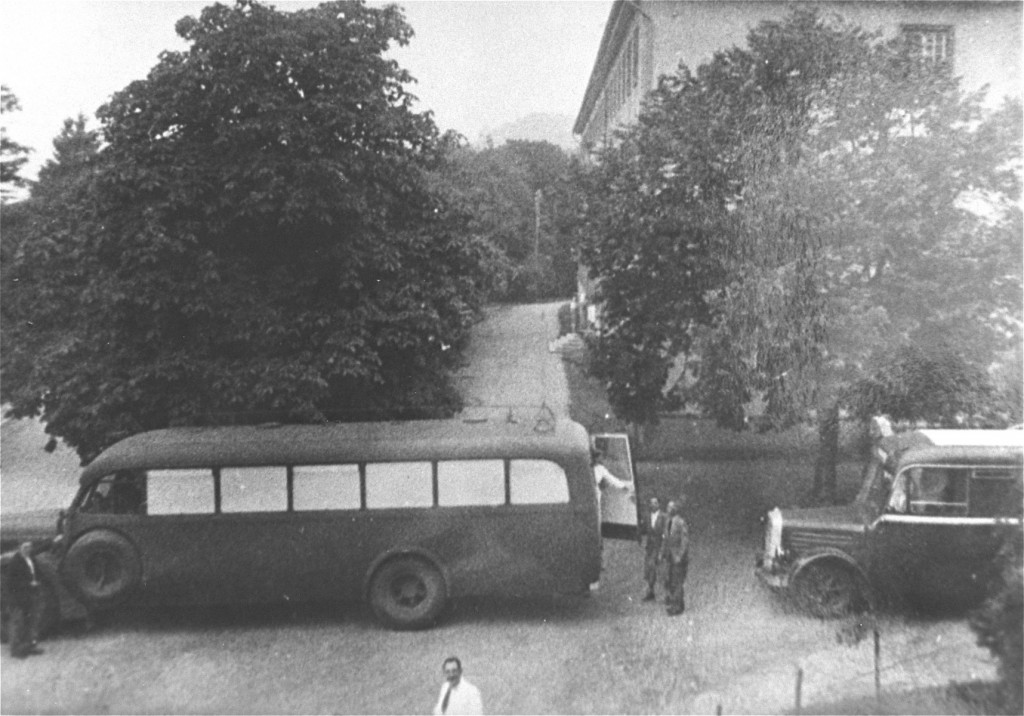Nazi Gas Chambers
During World War II, the Nazis used poisonous gas to murder millions of people in gas chambers. Mass gassings were one of the Nazis’ main methods of mass murder. They murdered Jews, people with disabilities, Roma, Soviet prisoners of war, and others in this way. In the Nazi gas chambers, victims suffered inhumane, terrifying, and often painful deaths.
Key Facts
-
1
There is undeniable proof of the existence of Nazi gas chambers and the Nazis’ use of poisonous gas to murder millions of Jews and other people.
-
2
Nazi German authorities created about fifty distinct gas chambers. Some Nazi gas chambers were installed in the cargo areas of large vans. Others were built in existing rooms or in new, specially constructed buildings.
-
3
The type of poisonous gasses that the Nazis used for mass murder included chemically pure carbon monoxide in canisters; carbon monoxide gas produced by engines; and hydrogen cyanide released from Zyklon B pellets.
During World War II (1939–1945), Nazi Germany used poisonous gas to murder people en masse in gas chambers. The Nazis murdered Jews, people with disabilities, Roma, Soviet prisoners of war, and others using poisonous gas. The first Nazi mass gassing took place in fall 1939, shortly after the start of World War II. The last mass gassings took place in late April 1945, when Nazi Germany’s total defeat was imminent.
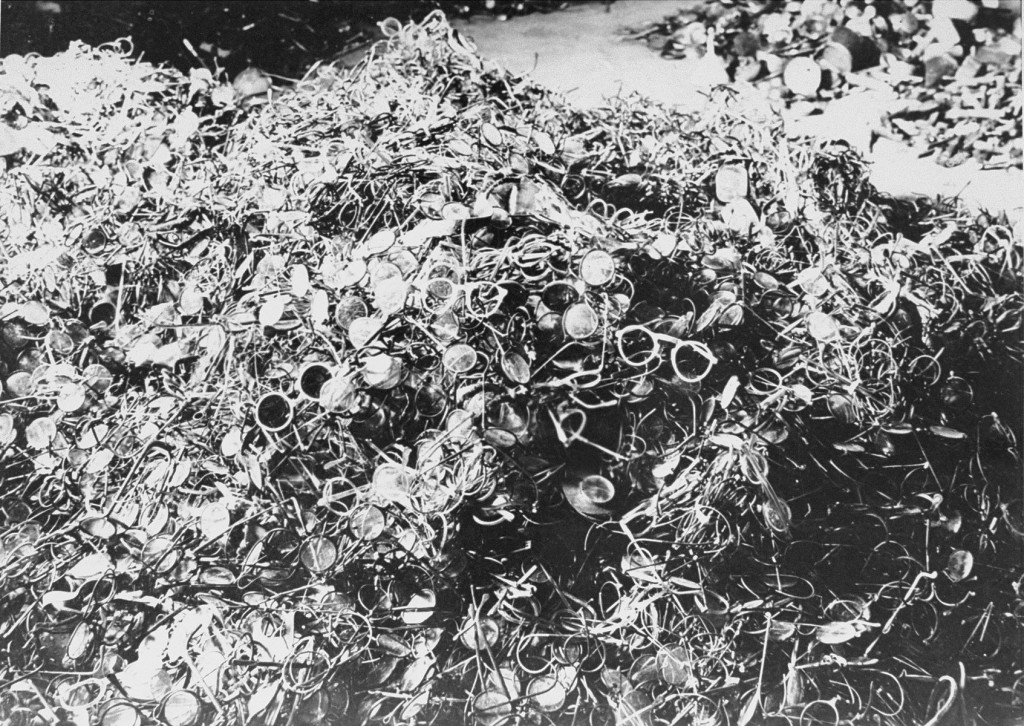
In popular culture, gas chambers are considered synonymous with the Holocaust and the mass murder of Europe’s Jews. Of the six million Jews murdered by the Nazis and their helpers in the Holocaust, between 2.3 and 3 million were murdered using poisonous gas. However, the Nazis and their helpers also murdered millions of Jewish people using other means, including mass shooting operations and deliberate deprivation.
In the decades after the Holocaust, people engaging in Holocaust denial and distortion often lie or misrepresent the truth about Nazi gas chambers. They do so despite the fact that there is a large body of verified, undeniable proof about the existence, purpose, and use of Nazi gas chambers. This evidence exists even though the Nazis attempted to destroy paperwork, demolish buildings, and burn the bodies of their victims. Sources of information on Nazi gas chambers include:
- documents created by the Nazis as part of the construction, maintenance, and use of gas chambers;
- wartime intelligence reports about Nazi gassing operations based on firsthand information;
- a small number of surviving gas chamber buildings and rooms;
- sworn testimonies from perpetrators describing mass gassings of Jews and others;
- descriptions of gas chambers provided after the war by eyewitnesses;
- drawings and models of gas chambers created during and after the war;
- reports created by postwar investigative bodies and courts;
- a small number of wartime photographs; and
- postwar archaeological studies.
Combined, this evidence is incontrovertible proof of the existence and purpose of Nazi gas chambers.
What is a gas chamber? How did Nazi gas chambers work?
Gas chambers are enclosed, tightly sealed spaces where people are killed by asphyxiation as a result of deliberate exposure to poisonous gas.
The Nazis created about fifty distinct gas chambers to murder people, primarily Jews and people with disabilities. The Nazis installed gas chambers in the cargo areas of large vans; in existing rooms and buildings; and in specially constructed new buildings. The Nazis often tried to disguise the gas chambers, usually by labeling them as bathing rooms. They sometimes even installed fake shower heads in the gas chambers. The Nazis did this to trick the victims and hide the truth from them as long as possible.
In the Nazi gas chambers, victims suffered an inhumane, terrifying, and often painful death. In some gas chambers, Nazis murdered victims using hydrogen cyanide gas released from Zyklon B pellets. In other gas chambers, they used chemically pure carbon monoxide or carbon monoxide produced by engines. Exposure to high concentrations of these gasses deprived the victims of oxygen, causing asphyxiation.
In most cases, poisonous gas killed victims in the gas chambers in a matter of minutes, though in some cases death took longer. This was not a humane or peaceful death. Witness accounts indicate that conditions in the gas chambers were terrifying.
First Nazi Experiments with Poisonous Gas, 1939–1940
The Nazis began experimenting with poisonous gas as a method of mass murder shortly after the German invasion of Poland in September 1939. They conducted these first experiments in the fall of 1939, as part of their plan to murder people with disabilities.
The first experiments were conducted in October 1939 by Dr. August Becker. Becker was a chemist from the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). His experiments took place in a makeshift gas chamber at Fort VII in Poznań in German-occupied Poland.
Chemist Albert Widmann from the Criminal Technical Institute of the Security Police (Kriminaltechnisches Institut der Sicherheitspolizei, KTI) was also involved in developing gassing procedures in the fall and winter of 1939–1940. In that period, Widmann and Becker and a number of other Nazi officials conducted a gassing demonstration using pure carbon monoxide gas in Brandenburg, Germany. The method they tested was then used to murder people with disabilities in the Nazi Euthanasia Program.
Sonderkommando Lange’s Gas Van, 1939–1941
Starting in the fall of 1939 and into 1941, a special killing unit called Sonderkommando Lange (literally, “special commando Lange”) used poisonous gas to murder people with disabilities in the Warthegau region of German-occupied Poland. Under the leadership of SS officer Herbert Lange, this unit traveled from site to site murdering patients from Polish psychiatric facilities and other institutions in a gas van. Unlike later models, which used carbon monoxide from the vehicle’s exhaust, Lange’s gas van used chemically pure carbon monoxide from canisters to murder victims. By fall 1941, the Sonderkommando Lange had murdered more than 7,500 people with disabilities.
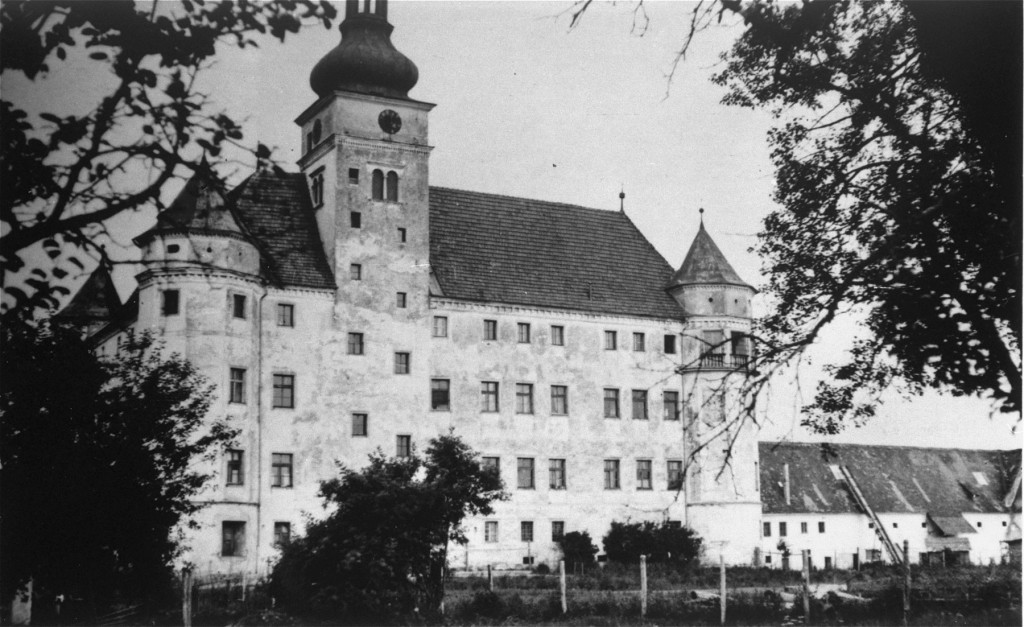
Gas Chambers at T4 Killing Centers
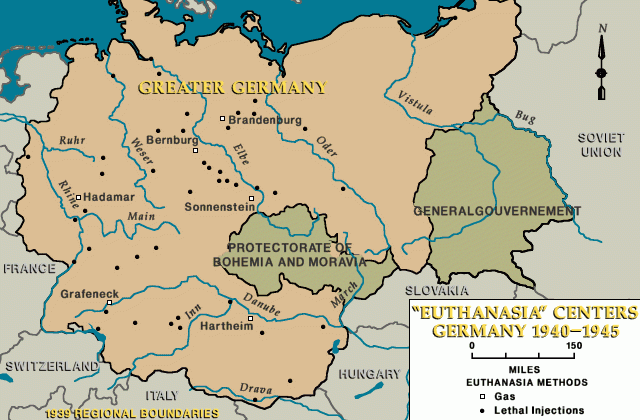
Beginning in January 1940, Nazi German authorities began to murder people with disabilities in gas chambers they built at killing centers. This was part of the Euthanasia Program, also called “Operation T4” (Aktion T4). Operation T4 was the Nazi program to murder Germans with disabilities living in institutional care facilities within Nazi Germany. The T4 administrators used pure, chemically created carbon monoxide gas to asphyxiate patients.
Nazi German authorities created gas chambers at six T4 killing centers:
- Grafeneck;
- Brandenburg;
- Hartheim;
- Sonnenstein;
- Bernburg; and
- Hadamar.
The Euthanasia Program was officially halted in August 1941. By this time, Nazi authorities had murdered about 70,000 people with disabilities in the gas chambers of the T4 killing centers. However, they later continued to murder people with disabilities by other means, including drug overdoses, lethal injection, and starvation. Eventually, the Nazi authorities dismantled the gas chambers at the T4 killing centers.
Aktion 14f13: Gassing Concentration Camp Prisoners in T4 Killing Centers, 1941–1944
Beginning in spring 1941, under the auspices of a secret killing operation called Aktion 14f13, the Nazis murdered thousands of concentration camp prisoners using poisonous gas. As part of Aktion 14f13, T4 doctors selected prisoners who were ill, exhausted, or weak to be murdered in the gas chambers of three T4 killing centers (Hartheim, Bernburg, and Sonnenstein). They also seem to have targeted specific groups of prisoners, including Jews, for murder. These killings began in spring 1941 and lasted until December 1944.
New Experiments with Poisonous Gas in 1941
The Nazis’ use of poisonous gas for mass murder took on its most extreme form in the genocide of Europe’s Jews.
Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, the Nazis began to massacre Jews. Initially, they did so primarily in mass shooting operations. But a number of Nazi authorities soon began experimenting with how to most efficiently use poisonous gas to murder Jews and other victims. In late summer and fall 1941, Nazi authorities conducted experiments to murder people using exhaust gas from car engines (in Minsk and Mogilev in German-occupied Belarus); exhaust from stationary engines (in the Lublin district of the General Government in German-occupied Poland); and Zyklon B at the Auschwitz concentration camp.
Combined, these tests led to the development of gas vans and killing centers that the Nazis would use to murder millions of Jews and others. By the end of 1941, Nazi authorities were using poisonous gas to murder Jews en masse.
Creation of New Gas Vans to Murder Jews and Others
In 1941, Nazi authorities with the Reich Security Main Office created and tested new types of gas vans. These vans were set up to funnel the engine’s exhaust into a specially built, sealed cargo compartment. Nazi officials tested the first of these vans at the Sachsenhausen concentration camp in fall 1941.
By December 1941, the Einsatzgruppen and other SS and police units began to use the RSHA gas vans to murder Jews and others, including people with disabilities and partisans (resistance fighters). In spring 1942, German SS and police authorities murdered about 5,000 Jews in one of the RSHA gas vans in German-occupied Serbia. And, German authorities deployed gas vans to murder Jews at the Maly Trostenets killing site near Minsk in German-occupied Soviet Belarus. They also used them in many other locations.
The gas vans did not always function as planned and presented a number of logistical problems. Therefore, German killing units continued to carry out mass shooting operations in addition to murdering people in gas vans.
Gas Chambers at Killing Centers (also called “Death Camps”)
As part of the “Final Solution to the Jewish Question”—the Nazi plan to murder Europe’s Jews—the Nazi German authorities created killing centers in late 1941 and 1942. These were camps where the Nazis murdered Jewish people in gas chambers. The Nazi killing centers are also sometimes called “extermination camps” or “death camps.”
The Nazis created five killing centers to murder Jews:
- Chełmno (Kulmhof);
- Belzec;
- Sobibor;
- Treblinka; and
- Auschwitz-Birkenau.
From December 1941 to late 1944, Nazi mass gassings of Jewish people in killing centers took place at a shocking pace and scale. The first mass gassing of Jews at a Nazi killing center occurred at Chełmno (Kulmhof) on December 8, 1941. Within a year, Nazi authorities murdered more than 1.3 million Jewish people in gas chambers. This pace continued throughout 1943 and the first half of 1944. The last mass gassing at a killing center took place at Auschwitz-Birkenau in October/November 1944. At the killing centers, an unknown number of Jews were also murdered through deprivation, disease, torture, and shootings.
Gas Chambers at Concentration Camps
Murder with poisonous gas continued into the last days of World War II at gas chambers located at concentration camps.
There were gas chambers at some Nazi concentration camps, including Lublin/Majdanek, Mauthausen, Ravensbrück, Sachsenhausen, Neuengamme, and Stutthof. In most cases, prisoners at concentration camps were murdered using Zyklon B gas. Gassing at concentration camps occurred on a much smaller scale than at the killing centers. In most cases, they were primarily used to murder ill or weak prisoners. The victims of each of these gas chambers numbered in the hundreds or thousands. Additionally, authorities at the Natzweiler-Struthof concentration camp created a gas chamber as part of medical and scientific experimentation. There was also a gas chamber at Dachau that scholars believe was never used to kill people.

Attempts to Destroy the Evidence of Nazi Gas Chambers
In the last years of World War II, Nazi German authorities destroyed or dismantled most of the gas chambers they had created. This was part of their efforts to hide evidence of their crimes. They blew up and demolished gas chambers at the killing centers, usually leveling them to the ground.
But the Nazis did not manage to destroy all of the gas chambers that they had created. Notably, the Soviet army discovered a gas chamber building virtually intact when they captured the Lublin/Majdanek concentration camp in July 1944. Film footage of the Soviet liberation of the Majdanek camp provided visual evidence of Nazi gas chambers.
Number of Victims of Nazi Gas Chambers
In total, the Nazis murdered millions of people in gas chambers. The victims included:
- Jews: Of the six million Jews murdered by the Nazis and their helpers in the Holocaust, between 2.3 and 3 million were murdered using poisonous gas.
- People with disabilities: Of the 250,000–300,000 people with disabilities murdered by the Nazis, about 100,000 were murdered using poisonous gas. This includes about 70,000 people killed in the gas chambers of the six “euthanasia” T4 killing centers; about 7,500 people murdered by Sonderkommando Lange; and thousands of others murdered in gas vans in German-occupied eastern Europe.
- Roma (derogatorily called “Gypsies”): The Nazis murdered thousands of Roma in gas chambers at killing centers and in gas vans. The exact number of Roma murdered with poisonous gas is unknown.
- Soviet prisoners of war: The Nazis murdered thousands of Soviet POWS in gas chambers at killing centers and concentration camps. The exact number is unknown. However, most of the 3.3 million Soviet POWs killed by the Nazis were murdered by other means, including shooting and deliberate deprivation.
- Others: Nazi German authorities murdered an unknown number of ethnic Poles (especially Polish intelligentsia), concentration camp prisoners, partisans (resistance fighters), and others in gas chambers.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nazi Gas Chambers
What type of gas did the Nazis use to murder people?
The Nazis used several different types of gas to murder people. This included:
- chemically pure carbon monoxide gas;
- carbon monoxide gas produced by the engines of large vans or by stationary engines; and
- hydrogen cyanide gas produced by Zyklon B pellets.
What is Zyklon B?
The Nazis used Zyklon B to murder Jews in the gas chambers of the Auschwitz-Birkenau killing center. The Nazis also used Zyklon B to murder prisoners at other sites, including the Lublin/Majdanek concentration camp.
Zyklon B is the brand name of a pesticide and disinfectant distributed by the Degesch company (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Schädlingsbekämpfung mbH), a subsidiary of the German chemical company Degussa. Zyklon B is produced as pellets infused with hydrogen cyanide, a poisonous gas. When these pellets are exposed to air, the hydrogen cyanide is released. Before World War II, Zyklon B was commonly used for fumigation (killing bugs and pests). It was also an effective disinfectant. In addition to using Zyklon B to kill people, the Nazis also used it for these purposes.

Why did the Nazis use poisonous gas to murder Jews?
Nazi authorities believed that mass gassing had several advantages over mass shooting operations. Namely, mass gassings were less public and thus easier to keep secret. They argued that it was more “humane” for the perpetrators. And, they considered it less resource-intensive because it did not require munitions needed for the German war effort. However, mass gassings also posed logistical problems for the Nazis, especially in the occupied Soviet territories. This is why the Nazis continued to murder Jews in both mass shootings and by asphyxiation in gas chambers.
Did the Nazis pretend gas chambers were showers?
Yes, many (but not all) Nazi gas chambers were disguised to look like showers. In some cases, these gas chambers even had fake shower heads. The Nazis sometimes labeled the outside of the building as bathhouses or showers. They did this in order to deceive victims about their fate.
How many Nazi gas chambers were there?
Nazi Germany created about fifty distinct gas chambers. This statistic includes stationary gas chambers, meaning gas chambers created in rooms or buildings. It also includes mobile gas chambers located in the cargo area of gas vans. Not all of these gas chambers were in operation at the same time. And some Nazi gas chambers were test sites or improvised spaces that were only used on one or two occasions.
Did all Nazi camps have gas chambers?
No. Not all Nazi camps had gas chambers. Nazi Germany created tens of thousands of camps, and most did not have gas chambers.
Were Nazi gas chambers real?
Yes, Nazi gas chambers were real. In the decades after the Holocaust, people engaging in Holocaust denial and distortion often repeat misleading claims and outright lies in an attempt to sow doubt about Nazi crimes. In fact, there is a large body of verified, undeniable evidence about Nazi gas chambers. Sources of information on Nazi gas chambers include extant gas chambers at former Nazi camps; documents created by the Nazis; wartime intelligence reports; written and oral testimonies by perpetrators, witnesses, and victims after the war; reports from postwar investigations; a small number of wartime photographs; and postwar archaeological studies. Combined, this evidence is incontrovertible proof of the existence and purpose of Nazi gas chambers.
Footnotes
-
Footnote reference1.
This statistic counts gas chamber buildings that contained multiple smaller gas chamber rooms as one gas chamber. For example, at the Treblinka killing center, the second gas chamber building had ten gas chamber rooms. Here, this is counted as one gas chamber. Counting each gas chamber room separately, the total number of Nazi gas chambers is more than 80.
-
Footnote reference2.
This statistic counts gas chamber buildings that contained multiple smaller gas chamber rooms as one gas chamber. For example, at the Treblinka killing center, the second gas chamber building had ten gas chamber rooms. Here, this is counted as one gas chamber. Counting each gas chamber room separately, the total number of Nazi gas chambers is more than 80.