<< Previous | Displaying results 2451-2500 of 6769 for "" | Next >>
Miriam Peleg (1913–1996) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Born Maria Hochberg, Miriam was from a Polish-Jewish family. She grew up in a small town about 70 miles east of Kraków. As early as the summer of 1940, Miriam obtained…

Władysław Bartoszewski (1922–2015) was a co-founder and member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. After World War II broke out in 1939, Władysław worked as a janitor at a Polish Red Cross clinic. In the fall of 1940, Władysław was caught…

Gary (Gerhard) was born in Berlin, Germany, in 1924. His father owned a men’s clothing store. As a child, Gary faced antisemitism from his peers. His family’s store was boycotted several times, and ultimately destroyed in 1938 during Kristallnacht. As the city prepared for tourists to arrive in Berlin for the 1936 Olympics, Gary noticed anti-Jewish signs vanish from storefronts. In 1939, Gary and his parents escaped Germany after securing passage to Shanghai, China. His father died of illness in…

Peter was six years old when his mother enrolled him in a special Hitler boarding school for future Nazi Party officials in 1935. He studied traditional academic subjects, but was constantly exposed to Nazi ideas and prepared for a military life. Peter was also a member of the Hitler Youth. He came to believe in Hitler as the savior of Germany. Peter would later describe his indoctrination as a subtle process. It took two years after the war had ended for Peter to come to terms with the atrocities that the…

In 1936, John Woodruff was one of 18 African Americans on the US Olympic team competing in Berlin. He won the gold medal for the men's 800-meter race. In this clip he describes his feelings upon winning the medal. Interview date: May 15, 1996

Olympic athlete John Woodruff describes his tactics for winning the 800-meter race

In 1936, John Woodruff was one of 18 African Americans on the US Olympic team competing in Berlin. He won the gold medal for the men's 800-meter race. In this clip from an interview on May 15, 1996, Woodruff describes his personal experiences of racial discrimination during and after the Olympic Games of 1936.

Joseph Leo Diamantstein was born in Heidelberg, Germany, on December 1, 1924, to Jewish parents. He was the youngest of four children. His family experienced antisemitism in Frankfurt, and ultimately decided to leave Germany. Beginning in 1933, the Hitler Youth and the League of German Girls had an important role to play in the new Nazi regime. Through these organizations, the Nazi regime planned to indoctrinate young people with Nazi ideology. This was part of the process of Nazifying German…

Herbert Oppenheimer was born on January 4, 1926, in Berlin, Germany. He lived with foster parents, who were Seventh-Day Adventists. While living with his foster parents, he had to join Hitler Youth along with everyone else in his class at school. During this time, he learned that he was Jewish. The school consequently expelled him from the Hitler Youth. All prospective members of the Hitler Youth had to be "Aryans." He had to leave his foster parents in April 1939, and lived in an orphanage run by the…

Guy Stern was born on January 14, 1922, in Hildesheim, Germany, into a Jewish family. As a child, he attended a German school, where he had many non-Jewish friends. Beginning in 1933, the Hitler Youth and the League of German Girls had an important role to play in the new Nazi regime. Through these organizations, the Nazi regime planned to indoctrinate young people with Nazi ideology. This was part of the process of Nazifying German society. The aim of this process was to dismantle existing social…

Agnes Allison (née Agnes Suzannah Halàsz) was born on October 28, 1926, in Budapest, Hungary, to Ilona Gero and Robert Halász. She had a younger sister, Judy. Agnes attended a private German school established for the children of diplomats. There was a Hitler Youth movement at the school. Agnes and her family were forced out of their home following the German occupation of Hungary. She went into hiding in December 1944. Beginning in 1933, the Hitler Youth and the League of German Girls had an…

Leon Bass was born in Philadelphia, PA in 1925. He joined the US Army in 1943 and served as a member of the all-Black 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion attached to General Patton's Third Army. Leon's unit was involved in the Battle of the Bulge as well as the liberation of Buchenwald. After the war, Leon went on to receive his doctorate, teach, and speak about the Holocaust and racism. In this interview, Leon describes the his frustration with the discord between the United State's condemnation of Nazi…

Leon Bass was born in Philadelphia, PA in 1925. He joined the US Army in 1943 and served as a member of the all-Black 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion attached to General Patton's Third Army. Leon's unit was involved in the Battle of the Bulge as well as the liberation of Buchenwald. After the war, Leon went on to receive his doctorate, teach, and speak about the Holocaust and racism. In this interview, Leon describes his first experiences with the realities of war and death. He reflects upon his…

Leon Bass was born in Philadelphia, PA in 1925. He joined the US Army in 1943 and served as a member of the all-Black 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion attached to General Patton's Third Army. Leon's unit was involved in the Battle of the Bulge as well as the liberation of Buchenwald. After the war, Leon went on to receive his doctorate, teach, and speak about the Holocaust and racism. In this interview, Leon describes the racism and segregation he faced in the United States during the 1940s and how it…

Leon Bass was born in Philadelphia, PA in 1925. He joined the US Army in 1943 and served as a member of the all-Black 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion attached to General Patton's Third Army. Leon's unit was involved in the Battle of the Bulge as well as the liberation of Buchenwald. After the war, Leon went on to receive his doctorate, teach, and speak about the Holocaust and racism. In this interview, Leon describes what he knew about Nazi concentration camps and the Holocaust during and after…

Leon Bass was born in Philadelphia, PA in 1925. He joined the US Army in 1943 and served as a member of the all-Black 183rd Engineer Combat Battalion attached to General Patton's Third Army. Leon's unit was involved in the Battle of the Bulge as well as the liberation of Buchenwald. After the war, Leon went on to receive his doctorate, teach, and speak about the Holocaust and racism. In this interview, Leon discusses his unit's movements during the Battle of the Bulge. He describes their path from…

Nesse's family had a dairy business. The Germans occupied Lithuania in 1941 and established a ghetto in Siauliai. Nesse lived in the ghetto until 1943 when she was old enough to work. In 1944 Nesse, her mother, and a brother were deported to the Stutthof camp near Danzig. Nesse worked in several Stutthof subcamps until January 1945, when the inmates were put on a death march. She was liberated by the Soviets in March. Nesse, her mother, and two brothers survived, and she arrived in the United States in…

Vladka belonged to the Zukunft youth movement of the Bund (the Jewish Socialist party). She was active in the Warsaw ghetto underground as a member of the Jewish Fighting Organization (ZOB). In December 1942, she was smuggled out to the Aryan, Polish side of Warsaw to try to obtain arms and to find hiding places for children and adults. She became an active courier for the Jewish underground and for Jews in camps, forests, and other ghettos.

Sally Pitluk was born to Jewish parents in Płońsk, Poland in 1922. A few days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, Płońsk was occupied. Sally and her family lived in a ghetto from 1940-1942. In October of 1942, Sally was transported to Auschwitz, where she was tattooed and moved into the subcamp Budy for forced labor. She stayed in the Auschwitz camp complex until the beginning of 1945 when she and other prisoners were death marched to several different camps. She was liberated in 1945 and…
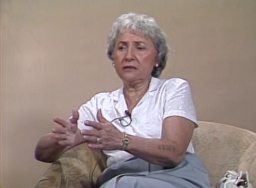
Sally Pitluk was born to Jewish parents in Płońsk, Poland in 1922. A few days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, Płońsk was occupied. Sally and her family lived in a ghetto from 1940-1942. In October of 1942, Sally was transported to Auschwitz, where she was tattooed and moved into the subcamp Budy for forced labor. She stayed in the Auschwitz camp complex until the beginning of 1945 when she and other prisoners were death marched to several different camps. She was liberated in 1945 and…

Burned bodies of former prisoners of Rottleberode, a subcamp of Dora-Mittelbau, lie near the entrance to a barn that had been set on fire by SS troops while the prisoners were on a death march. Gardelegen, Germany, April 18, 1945.

Three German mayors view the corpse of a prisoner burned alive in a barn by the SS while on a death march from Rottleberode, a subcamp of Dora-Mittelbau. Gardelegen, Germany, April 18, 1945.

German civilians from Schwarzenfeld dig graves for the reburial of 140 Hungarian, Russian, and Polish Jews exhumed from a mass grave near the town. The victims died while on an evacuation transport from the Flossenbürg concentration camp. Schwarzenfeld, Germany, April 25, 1945. Following the discovery of death march victims, US Army officers forced local Germans to view the scene of the crime and ordered the townspeople to give the victims a proper burial.

US troops and German civilians from Neunburg vorm Wald attend a funeral service for Polish, Hungarian, and Russian Jews found in the forest near their town. The victims were shot by the SS while on a death march from Flossenbürg. Neunburg, Germany, April 29, 1945. Following the discovery of death march victims, US Army officers forced local Germans to view the scene of the crime and ordered the townspeople to give the victims a proper burial.

SS troops unload artillery at a river crossing on the way to the front. Soviet Union, October 1941.

German infantry during the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941.

German officers review their orders during the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941.

This photograph shows German vehicles that have been loaded on trains headed toward the eastern front to reinforce German forces during the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941. A German soldier poses in the front car.

A column of refugees in the Soviet Union, following the German invasion of Soviet territory on June 22, 1941. Soviet Union, between 1941 and 1944.

Soviet refugees sit around a fire in a makeshift camp, following the German invasion of Soviet territory on June 22, 1941. Soviet Union, between 1941 and 1944.

False identification papers used by Adolf Eichmann while he was living in Argentina under the assumed name Ricardo Klement.


SS Lieutenant Klaus Barbie in Nazi uniform. Barbie, responsible for atrocities against Jews and resistance activists in France, was known as the "Butcher of Lyon." Germany, date uncertain.

Simon Wiesenthal, Holocaust survivor and an investigator of Nazi war criminals, tours a synagogue for refugee Jews in central Europe. Place uncertain, 1946.

Nazi physician Carl Clauberg (at left), who performed medical experiments on prisoners in Block 10 of the Auschwitz camp. Poland, between 1941 and 1944.
Photograph of seven-year-old Jacqueline Morgenstern in Paris, France, 1940. Jacqueline was later a victim of tuberculosis medical experiments at the Neuengamme concentration camp. The SS took 20 of the children who had been victims of medical experiments at Neuengamme to a school building in Hamburg. Situated on Bullenhuser Damm, this location was a subcamp of Neuengamme. Jacqueline and the other children in the group (10 boys and 10 girls, all Jewish) were killed there.

Eduard, Elisabeth, and Alexander Hornemann. The boys, victims of tuberculosis medical experiments at Neuengamme concentration camp, were murdered shortly before liberation. Elisabeth died of typhus in Auschwitz. The Netherlands, prewar.

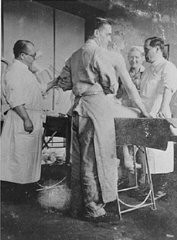
A victim of a Nazi medical experiment is immersed in icy water at the Dachau concentration camp. SS doctor Sigmund Rascher oversees the experiment. Germany, 1942.

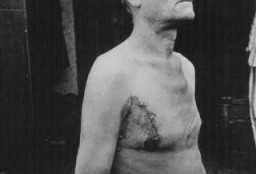
A Soviet prisoner of war, victim of a tuberculosis medical experiment at Neuengamme concentration camp. Germany, late 1944.
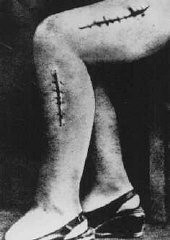
A war crimes investigation photo of the disfigured leg of a survivor from Ravensbrück, Polish political prisoner Helena Hegier (Rafalska), who was subjected to medical experiments in 1942. This photograph was entered as evidence for the prosecution at the Medical Trial in Nuremberg. The disfiguring scars resulted from incisions made by medical personnel that were purposely infected with bacteria, dirt, and slivers of glass.
Soviet soldiers inspect a box containing poison used in medical experiments. Auschwitz, Poland, after January 27, 1945.

United Nations personnel vaccinate an 11-year-old concentration camp survivor who was a victim of medical experiments at the Auschwitz camp. Photograph taken in the Bergen-Belsen displaced persons camp, Germany, May 1946.

Josef Mengele, German physician and SS captain. He was the most prominent of a group of Nazi doctors who conducted medical experiments that often caused great harm or death to the prisoners. In November 1943 Mengele became "Chief Camp Physician" of Auschwitz II (Birkenau). Many of those subjected to Mengele's experiments died as a result or were murdered in order to facilitate post-mortem examination.

Nazi physician Carl Clauberg, who performed medical experiments on prisoners in Block 10 of the Auschwitz camp. Place and date uncertain.

Friedrich Hoffman, holding a stack of death records, testifies about the murder of 324 Catholic priests who were exposed to malaria during Nazi medical experiments at the Dachau concentration camp. Dachau, Germany, November 22, 1945.

Four Polish women arrive at the Nuremberg train station to serve as prosecution witnesses at the Doctors Trial. From left to right are Jadwiga Dzido, Maria Broel-Plater, Maria Kusmierczuk, and Wladislawa Karolewska. December 15, 1946.

Wladislava Karolewska, a victim of medical experiments at the Ravensbrück camp, was one of four Polish women who appeared as prosecution witnesses at the Doctors Trial. Nuremberg, Germany, December 22, 1946.

Concentration camp survivor Jadwiga Dzido shows her scarred leg to the Nuremberg court, while an expert medical witness explains the nature of the procedures inflicted on her in the Ravensbrück concentration camp on November 22, 1942. The experiments, including injections of highly potent bacteria, were performed by defendants Herta Oberheuser and Fritz Ernst Fischer. December 20, 1946.

Waldemar Hoven, head SS doctor at the Buchenwald concentration camp, testifies in his own defense at the Doctors Trial. Hoven conducted medical experiments on prisoners. Nuremberg, Germany, June 23, 1947.

Herta Oberheuser was a physician at the Ravensbrück concentration camp. This photograph shows her being sentenced at the Doctors Trial in Nuremberg. Oberheuser was found guilty of performing medical experiments on camp inmates and was sentenced to 20 years in prison. Nuremberg, Germany, August 20, 1947.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.