<< Previous | Displaying results 3301-3350 of 6769 for "" | Next >>
Children's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking experiences of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Chaim Kozienicki.

Young people's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking experiences of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Jakub Lapides.

Young people's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking experiences of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Lolek Lubinski

Children's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking events of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Sara Rachela Plagier.

Children's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking events of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Jutta Szmirgeld.

Children's diaries bear witness to some of the most heartbreaking events of the Holocaust. Learn about the diary and experiences of Israel Unikowski.
Learn about the Freiburg subcamp of Flossenbürg, including its establishment, prisoner population, and conditions there.
Explore a timeline of key events in the history of the Lublin/Majdanek camp in German-occupied Poland.

Learn about areas of research related to the number of deaths at the Lublin/Majdanek concentration camp system.

Learn about the North African military campaigns of World War II which took place between September 13, 1940, and May 13, 1943.

Learn more about the Western Desert campaign during World War II in Egypt and Libya between 1940-1943.

Operation Torch was the Allied invasion of French Morocco and Algeria during the North African Campaign of World War II. Learn more.
Learn more about the 1943 Tunisia campaign, a four-month long struggle between Allied and Axis powers in North Africa during World War II.

"Learn more about Stanisławów during World War II. This article is an excerpt from Nechama Tec’s Resilience and Courage: Women, Men, and the Holocaust (2003). "
World War II was the largest and most destructive conflict in history. Learn about key WWII dates in this timeline of events, including when WW2 started and ended.

Racism, including racial antisemitism (prejudice against or hatred of Jews based on false biological theories), was an integral part of Nazism. Learn more
Moses Beckelman was an American social worker who joined the JDC in 1939. Learn more about his efforts to help refugees fleeing Nazism during the war.

Stephen Wise (1874–1949) was a prominent Jewish leader in the United States between 1933-1945. Learn more about his work during the Holocaust.

Germany started World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, by invading Poland. War would continue until 1945. Learn more about key events in the history of WWII.

Antisemitism: hostility toward or hatred of Jews as a religious or ethnic group, often accompanied by social, economic, or political discrimination. Appellplatz: German word for roll call square where prisoners were forced to assemble. Aryan: Term used in Nazi Germany to refer to non-Jewish and non-Roma (Gypsy) Caucasians. Northern Europeans with especially "Nordic" features such as blonde hair and blue eyes were considered by so-called race scientists to be the most superior of Aryans, members of a…
The experiences of World War I and its aftermath would profoundly shape the attitudes and actions of leaders and ordinary people during the Holocaust.

The Weimar Republic was a liberal democratic republic founded in Germany in the aftermath of WWI. Learn about the era’s political and economic crises and social trends.

Adolf Hitler, leader of the Nazi Party, aimed to eliminate Europe's Jews and other perceived enemies of Nazi Germany. Learn more.

Before the Nazi rise to power, Jews represented less than 1% of Germany's population. Learn more about Jewish communities in Germany before the Holocaust.

Nazi propaganda had a key role in the persecution of Jews. Learn more about how Hitler and the Nazi Party used propaganda to facilitate war and genocide.

The Nazis frequently used propaganda to disguise their political aims and deceive the German and international public. Learn more.

Shortly after taking power in January 1933, Adolf Hitler and the Nazis took control of German newspapers, detailing how the news was to be reported.

The April 1, 1933, boycott of Jewish-owned businesses marked the beginning of a nationwide campaign by the Nazi Party against the entire German Jewish population.

Nazi ideology aimed to promote the myth of an ideal national community and label those who were to be excluded from it as enemies. Propaganda was essential in promoting such myths.

Learn about the provisions and impact of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, including the "War Guilt Clause" which held Germany responsible for starting World War I.
Anne Frank is among the most well-known of the six million Jews who died in the Holocaust. Discover who Anne Frank was and what happened to her.

The Diary of Anne Frank is often the first exposure readers have to the history of the Holocaust. Learn about Anne's diary, including excerpts and images.

Börgermoor was part of the Nazi regime’s early system of concentration camps. It was located in the Emsland region of Prussia.
Ghettos separating Jews from the rest of the population were part of the Nazi plan to destroy Europe's Jews. Read about ghettoization during the Holocaust.

Adolf Hitler established himself as absolute Führer, or leader, of the Nazi Party by 1921. Learn more about Hitler in the years 1919-1924.

Under Adolf Hitler, the Nazi regime was responsible for the mass murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other victims. Learn about Hitler in the years 1924-1930.

Under Adolf Hitler's leadership, the Nazi regime was responsible for the mass murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other victims. Learn about Hitler in the years 1930-1933.

The German invasion of Poland in the fall of 1939 triggered WWII. Learn more about key dates and events, causes, and related Holocaust history.

Survivors of the Holocaust faced huge obstacles in rebuilding their lives. Learn about the challenges they faced in the aftermath of the Holocaust.

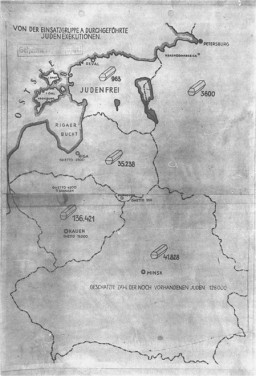
Einsatzgruppen, often called “mobile killing units,” are best known for their role in the murder of Jews in mass shooting operations during the Holocaust.
The liberation of concentration camps toward the end of the Holocaust revealed unspeakable conditions. Learn about liberators and what they confronted.

Germany started World War II in Europe on September 1, 1939, by invading Poland. War would continue until 1945. Learn more about WWII and genocide in Europe.

The search for refuge frames both the years before the Holocaust and its aftermath. Learn about obstacles refugees faced when searching for safe havens.

The Third Reich began with the Nazi rise to power in 1933 and ended with the German surrender in 1945. Learn more about Nazi Germany during World War II.

Children were especially vulnerable to Nazi persecution. Learn more about the fates of Jewish and non-Jewish children.

Nazi Germany and its allies established over 44,000 concentration camps and incarceration sites during the Holocaust. Read about the Nazi camp system.

The term Final Solution to the Jewish Question was a euphemism used by Nazi Germany’s leaders. It referred to the mass murder of Europe’s Jews.

The United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941, following the attack on Pearl Harbor. Learn more about World War II in the Pacific.

As Allied forces approached Nazi camps in the last months of WWII, the SS organized brutal “death marches” (forced evacuations) of concentration camp inmates.

Thousands of Nazi criminals were never arrested. Learn more about the postwar efforts to bring Nazi perpetrators to justice.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.