You searched for: 存币生息系统定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建存币生息系统定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建7ZcKfeL1Bf
<< Previous | Displaying results 201-225 of 245 for "存币生息系统定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建存币生息系统定制开发【TG���������@EK7676】平台包网搭建7ZcKfeL1Bf" | Next >>
-
Jewish Badge: During the Nazi Era
ArticleNazi officials implemented the Jewish badge as a key element in their plan to persecute and eventually destroy the Jewish population of Europe. Learn more

-
The Vélodrome d'Hiver (Vél d'Hiv) Roundup
ArticleThe Vélodrome d'Hiver (or Vél d'Hiv) roundup was the largest French deportation of Jews during the Holocaust. It took place in Paris on July 16–17, 1942.

-
Eleanor Roosevelt
ArticleEleanor Roosevelt, longest serving First Lady in US history, used her social and political influence to intervene on behalf of refugees before and during WWII.

-
Earl G. Harrison: Biography
ArticleEarl G. Harrison, Commissioner for Immigration and Naturalization under FDR, is known for a report harshly criticizing the US and British treatment of Jewish DPs.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #9, The Einsatzgruppen Case
ArticleThe Einsatzgruppen Case was Case #9 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
US Troops Capture Ludendorff Railroad Bridge at Remagen
Timeline EventMarch 7, 1945. On this date, the US 9th Armored Division captured the Ludendorff Railroad Bridge at Remagen, between Koblenz and Bonn, Germany.

-
The 45th Infantry Division during World War II
ArticleThe 45th Infantry Division participated in major WWII campaigns and is recognized for liberating the Dachau concentration camp in 1945.
-
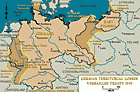
Treaty of Versailles
ArticleLearn about the provisions and impact of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, including the "War Guilt Clause" which held Germany responsible for starting World War I.
-
Timeline of the German Military and the Nazi Regime
ArticleKey dates illustrating the relationship between Germany’s professional military elite and the Nazi state, and the German military’s role in the Holocaust.

-
The United States and the Nazi Threat: 1933–37
ArticleLearn about responses in the United States to reports about Nazi anti-Jewish policies and violence against Jews from 1933–37.

-
Selma (Wijnberg) Engel describes forced labor sorting the clothing and possessions of people deported to Sobibor
Oral HistorySelma was the youngest of four children born to Jewish parents. When she was 7, Selma and her family moved to the town of Zwolle where her parents ran a small hotel. When the Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940, they confiscated the hotel. The family had to live in a poor Jewish section of the town. Selma went into hiding but was betrayed and then sent to the Westerbork camp. In April 1943 she was deported to Sobibor, where she worked in the clothes sorting area. There, the prisoners tried to pocket…

-
Felix Horn describes antisemitism in Lvov and conditions in the Janowska camp
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Zdziecioł (Zhetel)
ArticleThe Nazis occupied Zdziecioł (Zhetel), Poland in 1941. Learn more about the city and ghetto during World War II.
-
Combating Holocaust Denial: Evidence of the Holocaust presented at Nuremberg
ArticleAt the Nuremberg trials, Allied prosecutors submitted documentation left by the Nazi state itself. This evidence is a lasting refutation of attempts to deny the Holocaust.

-
Freiberg
ArticleLearn about the Freiburg subcamp of Flossenbürg, including its establishment, prisoner population, and conditions there.
-
First Letter to All Judges
ArticleLearn how the "First Letter to all Judges" increased the pressure on German judges to give verdicts and sentences according to Nazi principles and ideology.

-
1943: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1943 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, and the Holocaust.

-
Halle
ArticleHalle an der Saale was a satellite camp of Buchenwald concentration camp. It was established by the Nazis in Saxony, Germany in 1941.
-
Oranienburg
ArticleThe Oranienburg concentration camp was established as one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany on March 21, 1933. Learn more

-
Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B
ArticleIn 1939, the Nazis established the Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B camp in Germany. Learn more about the camp’s history, prisoners, and liberation.
-
Lackenbach (Roma internment and transit camp)
ArticleThe Lackenbach internment and transit camp for Roma, located in what had been eastern Austria, was a departure point for deportations to Lodz and Auschwitz.

-
Charles E. Coughlin
ArticleCharles Coughlin, Catholic priest and populist leader, promoted antisemitic and pro-fascist views. In the 1930s, he was one of the most influential public figures in the US.

-
The Rescue Mission of Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus
ArticleIn the spring of 1939, Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus rescued 50 Jewish children from Vienna, Austria, by bringing them to the United States. Learn about their mission.

-
Madeline Deutsch describes adjusting to social and educational life after the war
Oral HistoryMadeline was born into a middle class family in an area of Czechoslovakia that was annexed by Hungary in 1938-1939. Her father worked out of their home and her mother was a homemaker. Madeline attended high school. In April 1944 her family was forced into a Hungarian ghetto. The family lived in the ghetto for two weeks before being transported to Auschwitz. Madeline and her mother were separated from her father and older brother. Neither her father nor brother survived the war. A week after arriving in…

-
Selma (Wijnberg) Engel describes deportation to Sobibor
Oral HistorySelma was the youngest of four children born to Jewish parents. When she was 7, Selma and her family moved to the town of Zwolle where her parents ran a small hotel. When the Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940, they confiscated the hotel. The family had to live in a poor Jewish section of the town. Selma went into hiding but was betrayed and then sent to the Westerbork camp. In April 1943 she was deported to Sobibor, where she worked in the clothes sorting area. There, the prisoners tried to pocket…

