<< Previous | Displaying results 251-275 of 981 for "" | Next >>
-
Refuge in Latin America
ArticleBetween 1933-1945, Latin American governments officially permitted approx. 84,000 Jewish refugees. Learn more about Latin America refugee policy.

-
President Obama's Remarks at Buchenwald
ArticlePresident Barack Obama visited Buchenwald concentration camp in Germany on June 5, 2009. In a speech at the site, he repudiated Holocaust denial. Browse transcript.

-
Julien Bryan
ArticleUS filmmaker and photographer Julien Bryan was one of the few western photographers left in Warsaw upon the German invasion of Poland in September 1939.

-
Siege (1940)
ArticleJulien Bryan’s ten-minute film Siege, first non-Nazi produced footage of the start of WWII, records horror and chaos in Warsaw following the German invasion.

-
Incitement to Genocide in International Law
ArticleAfter the Holocaust, the IMT charged the first case of “incitement to genocide.” Learn more about the crime and its application in modern genocide law.

-
Oradour-sur-Glane
ArticleIn 1944, Waffen-SS troops massacred residents of Oradour-sur-Glane, a small village in France. Learn about the German occupation and destruction of the village.

-
Beer Hall Putsch (Munich Putsch)
ArticleOn November 8–9, 1923, Hitler and the Nazi Party led an attempt to overthrow the German government. This attempted coup came to be called the Beer Hall Putsch.

-
Yugoslavia
ArticleLearn more about the history of Yugoslavia before World War II and the Axis invasion of 1941.

-
Law, Justice, and the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the role of the legal profession as the Nazi leadership gradually moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship.

-
Reichstag Fire Decree
ArticleThe Reichstag Fire Decree of February 1933 restricted individual freedoms, and allowed Hitler's government to overrule state and local laws and overthrow state and local governments.

-
Arrests without Warrant or Judicial Review
ArticleAllowing arrests without a warrant or judicial review was a key step in the process by which the Nazi regime moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship

-
The Enabling Act
ArticleThe Enabling Act of March 1933 allowed the Reich government to issue laws without the consent of Germany’s parliament. It laid the foundation for the Nazification of German society.

-
Law for the Imposition and Implementation of the Death Penalty
ArticleLearn more about the Law for the Imposition and Implementation of the Death Penalty, which the Nazis enacted after the Reichstag Fire Decree in 1933.

-
Law against the Founding of New Parties
ArticleThe Law against the Founding of New Parties proclaimed the Nazi Party as the only political party in Germany, which became a one-party dictatorship led by the Nazis.

-
Oaths of Loyalty for All State Officials
ArticleThe Oath of Loyalty for All State Officials started to change in 1934. Learn more about the oath and Germany’s journey from democracy to a Nazi dictatorship.

-
Glossary of Terms and Individuals in the Nazi Judicial System
ArticleLearn more about the Holocaust Encyclopedia’s key terms and individuals in the Nazi judicial system.
-
Antisemitic Legislation 1933–1939
ArticleHundreds of laws, decrees, guidelines, and regulations increasingly restricted the civil and human rights of Jews in Germany from 1933-39. Learn more.

-
Supreme Court Decision on the Nuremberg Race Laws
ArticleLearn more about the 1936 German Supreme Court decision on the Nuremberg Race Laws.

-
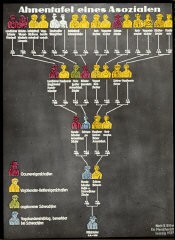
Decree against Public Enemies
ArticleThe Decree against Public Enemies was a key step in the process by which the Nazi leadership moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship.
-
Katzenberger Case, March 13, 1942
ArticleThe Nuremberg Special Court ruled on the Katzenberger Race Defilement Case in 1942. Learn more about the outcome and impact of the case.
-
First Letter to All Judges
ArticleLearn how the "First Letter to all Judges" increased the pressure on German judges to give verdicts and sentences according to Nazi principles and ideology.

-
Background: Jurists' Trial Verdict
ArticleThe Justice Case, or Jurists’ Trial, of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings tried members of the German justice administration. Browse excerpts from the verdict.

-
Ardeatine Caves Massacre
ArticleNow a national memorial site, the Ardeatine Caves outside Rome were the site of a German reprisal for a bombing by Italian resistance operatives in March 1944.
-
The Kielce Pogrom: A Blood Libel Massacre of Holocaust Survivors
ArticleThe Kielce pogrom was a violent massacre in the town of Kielce, Poland in 1946. Learn more about the events that led up to the attack and the aftermath.

-
Introduction to the Definition of Genocide
ArticleExplore an outline of the main definitional elements of the crime of genocide and how significant aspects of the law have developed through recent cases.

