You searched for: Warsaw ghetto
<< Previous | Displaying results 301-344 of 344 for "Warsaw ghetto" | Next >>
-
Stutthof
ArticleLearn about the Stutthof camp from its establishment until liberation in May 1945, including conditions, forced labor, subcamps, and death marches.

-
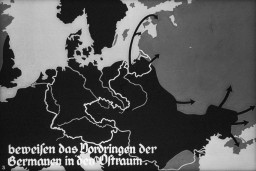
Misuse of Holocaust Imagery Today: When Is It Antisemitism?
ArticleLearn more about the modern misuse of images and symbols from the Holocaust and how this distortion can lead to antisemitism.
-
Polish Jewish Refugees in Lithuania, 1939–40
ArticleLearn more about Polish Jewish refugees that relocated to Lithuania between 1939-1940.

-
Jewish Community of Kalisz: Youth, Culture, Religion
ArticleKalisz had a vibrant Jewish community between WWI and WWII. Learn about its youth movements, schools, cultural life, sports, and religious life.

-
Evidence from the Holocaust at the First Nuremberg Trial
ArticleProsecutors before the IMT based the case against 22 leading Nazi officials primarily on thousands of documents written by the Germans themselves. Learn more.

-
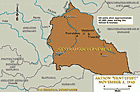
Operation Harvest Festival
Timeline EventNovember 3, 1943. On this date, SS and police units implemented "Operation Harvest Festival" (also known as Aktion Erntefest).
-
Miriam Peleg describes why she joined Żegota
Oral HistoryMiriam Peleg (1913–1996) was a member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. Born Maria Hochberg, Miriam was from a Polish-Jewish family. She grew up in a small town about 70 miles east of Kraków. As early as the summer of 1940, Miriam obtained…

-
Sabina Szwarc
ID CardSabina grew up in a Jewish family in Piotrkow Trybunalski, a small industrial city southeast of Warsaw. Her family lived in a non-Jewish neighborhood. Her father was a businessman and her mother was a teacher. Both Yiddish and Polish were spoken in their home. In 1929 Sabina began public school, and later went on to study at a Jewish secondary school. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Four days later, German troops streamed into Sabina's city. After one month of occupation, her father…
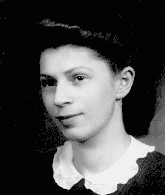
-
Chaim Werzbe
ID CardChaim was raised in a Yiddish-speaking, religious Jewish family in Sokolow Podlaski, a manufacturing town in central Poland with a large Jewish community of about 5,000. The economic activities of most of the townspeople were closely tied to those of nearby Warsaw and surrounding farming communities. As a young man, Chaim liked to play chess and was active in a local Zionist organization. 1933-39: Chaim made a living in the grain business. After settling down, he married a widow who was older than he and…

-
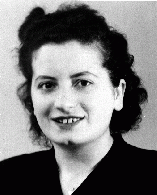
Henia Ring
ID CardThe youngest of two children, Henia was born to a Jewish family in the town of Krzepice. By the early 1930s, the Jewish population of Krzepice comprised more than 40 percent of the town's inhabitants. Henia's father made his living trading cattle in the area. Henia attended a public elementary school. 1933-39: On September 1, 1939, the Germans invaded Poland; a day later, they entered Henia's town. Her family tried to escape to Warsaw but the German forces quickly overtook them and ordered them back to…
-
Elya Rosenblat
ID CardElya, also known as Eli, was the eldest of three sons born to Yiddish-speaking Jewish parents. When Elya was a child his family moved to the industrial city of Radom, located about 60 miles south of Warsaw. After completing school in Radom, Elya apprenticed to become a women's tailor. Eventually, he became licensed as a master tailor. 1933-39: Elya married in 1936 and had a daughter one year later. He and his wife lived on Zeromskiego Street across from Elya's younger brother, Itzik, who was also a…

-
Abraham Lewent describes conditions in Skarzysko camp
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Ludmilla Page describes German industrialist Oskar Schindler
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Abraham Lewent describes deportation to and conditions in Majdanek
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Abraham Lewent describes his father's death at Majdanek
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Ludmilla Page describes sabotage during production of munitions in Oskar Schindler's factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes a celebration of Oskar Schindler's birthday in Bruennlitz toward the end of the war
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes her years in Poland living under a false identity
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
William (Bill) Lowenberg describes forced labor in the Kaufering subcamp of the Dachau concentration camp
Oral HistoryAs a boy, Bill attended school in Burgsteinfurt, a German town near the Dutch border. After the Nazis came to power in Germany in January 1933, Bill experienced increasing antisemitism and was once attacked on his way to Hebrew school by a boy who threw a knife at him. In 1936, he and his family left Germany for the Netherlands, where they had relatives and thought they would be safe. However, after Germany invaded the Netherlands in May 1940, antisemitic legislation--including the order to wear the Jewish…

-
Killing Centers: In Depth
ArticleThe Nazis established killing centers in German-occupied Europe during WWII. They built these killing centers for the mass murder of human beings.

-
Abraham Lewent recalls how, while ill with typhoid, he persuaded the Skarzysko doctor that he was fit to work
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Ludmilla Page describes conditions in Oskar Schindler's munitions factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Abraham Lewent describes the moments following his liberation from a death march from the Dachau camp
Oral HistoryLike many other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
Doris Greenberg describes arrival procedures at Ravensbrück
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded Poland in 1939 and established a ghetto in Warsaw in 1940. After her parents were deported, Doris hid with her sister and other relatives. Doris's sister and an uncle were killed, and she learned that her parents had been killed. Her grandmother committed suicide. Doris was smuggled out of the ghetto and lived as a non-Jewish maid and cook, but was ultimately deported to the Ravensbrück camp. Upon arrival there, Doris and her friend Pepi contemplated swallowing poison, but decided…

-
Channa Morgensztern
ID CardChanna and her husband and five children lived 35 miles east of Warsaw in the small predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn. Channa's husband, Jankel, was employed as a clerk in the town hall. After Channa's children reached school age, she helped her mother run a newspaper kiosk in town. 1933-39: Germany has invaded Poland, and Channa's hopes that Kaluszyn wouldn't be in the line of fire have been shattered. First, a German plane flew over their town and dropped a bomb on people waiting in line outside a…

-
Isachar Herszenhorn (Irving Horn)
ID CardIsachar was born to a Jewish family in the Polish city of Radom, approximately 75 miles south of Warsaw. The city was the center of Poland's leather-tanning industry. Isachar's father worked as a salesman for a nearby tanning factory. His father was a successful salesman and the family lived comfortably. 1933-39: During registration for Isachar's first-grade class in 1934, a Jewish boy was pushed down the stairs. When his mother confronted the principal about the incident, all he said was that the boy had…

-
Rivka Rzondzinski
ID CardThe mother of six children, Rivka lived 35 miles east of Warsaw in the small predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn. The Rzondzinski family was very religious. When Rivka's husband, Fiszel, died in the early 1930s, she and her oldest daughter, Channa, opened a newspaper kiosk near the Kaluszyn railroad station. 1933-39: When Germany invaded Poland several days ago, Rivka's daughter Raizel's husband and her two sons fled eastward to the USSR with other Jewish men. They were afraid that the Germans would…

-
Josel Gerszonowicz
ID CardThe oldest of eight children, Josel was born in Miechow, a small town in south central Poland. His father was a machinist and locksmith. As a boy, Josel spent long days learning Hebrew in the Jewish school and taking general subjects at the public school. He was 13 years old when he left school to work in his father's shop. 1933-39: Josel met his wife, Esther, through a matchmaker, and they settled in nearby Dzialoszyce, a town with a Jewish community of about 7,000, and a beautiful synagogue that had…

-
Chaie Sura Kisielnicki
ID CardChaie Sura was the youngest of three children born to Jewish parents living 35 miles east of Warsaw in the small, predominantly Jewish town of Kaluszyn. Her father owned a wholesale grocery store, a restaurant and a gas station, which were located together on the busy main road. The Kisielnicki family lived in rooms in the same building as their business. 1933-39: When Germany invaded Poland several days ago, Chaie Sura's father and brothers fled eastward towards the USSR with other Jewish men who were…
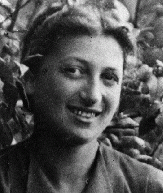
-
Henry J. Kellermann describes the reactions of defendants during the Nuremberg Trial
Oral HistoryHenry received a Doctor of Law (J.D.) degree from the University of Berlin in 1937. Sponsored by the rabbi of the Baltimore Hebrew congregation, Henry immigrated to the United States in the same year. In 1945, the Office of Strategic Services (OSS) assigned him to prepare pre-trial briefs for the International Military Tribunal held in Nuremberg, Germany. He interrogated a number of witnesses and defendants. After the war, he held various diplomatic posts.

-
Tattoos and Numbers: The System of Identifying Prisoners at Auschwitz
ArticleLearn more about how the Nazis identified and tattooed prisoners at the Auschwitz concentration camp complex.

-
Aryan
ArticleAdolf Hitler and the Nazi Party adapted, manipulated, and radicalized the unfounded belief in the existence of an "Aryan race." Learn about the term Aryan.

-
Wilek (William) Loew describes refugees from western Poland after their arrival in Soviet-occupied Lvov
Oral HistoryWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in the southeastern Polish town of Lvov. His family owned and operated a winery that had been in family hands since 1870. Wilek's father died of a heart attack in 1929. Wilek entered secondary school in 1939. Soon after he began school, World War II began with the German invasion of Poland. Lvov was in the part of eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. Although the Soviets took over Wilek's home and the family business, Wilek was able to continue his…

-
Władysław Bartoszewski discusses Żegota
Oral HistoryWładysław Bartoszewski (1922–2015) was a co-founder and member of the Council for Aid to Jews, codenamed “Żegota.” Żegota was a clandestine rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, Żegota coordinated efforts to save Jews from Nazi persecution and murder. It operated from 1942 to 1945. After World War II broke out in 1939, Władysław worked as a janitor at a Polish Red Cross clinic. In the fall of 1940, Władysław was caught…

-
Life After the Holocaust: Regina Gelb
ArticleAfter WWII and the fall of the Nazi regime, Holocaust survivors faced the daunting task of rebuilding their lives. Listen to Regina Gelb's story.

-
Ludmilla Page recalls arriving in Auschwitz instead of Oskar Schindler's munitions factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes leaving Auschwitz and arriving at the Bruennlitz munitions factory in the Sudetenland
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes arrival at the Brünnlitz munitions factory
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
The United States and the Holocaust, 1942–45
ArticleWhy did the United States go to war? What did Americans know about the “Final Solution”? How did Americans respond to news about the Holocaust? Learn more.

-
Flight and Rescue
ArticleExplore the story of over 2,000 Polish Jewish refugees who fled east to escape war-torn Europe. They sought safety in such distant places as China and Japan.

-
Gusen
ArticleIn 1940, the Nazis established Gusen concentration camp. Learn more about camp conditions, forced labor, and liberation.

-
International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg
ArticleThe International Military Tribunal (IMT) opened in Nuremberg within months of Germany’s surrender. Learn about the judges, defendants, charges, and legacies.

-
Franklin Delano Roosevelt
ArticleFranklin D. Roosevelt was 32nd president of the US. Learn about the domestic and international challenges FDR faced as president during World War II.

-

