![A transport of Jewish prisoners marches through the snow from the Bauschovitz train station to Theresienstadt. [LCID: 69720]](https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/images/large/781755a6-1ba5-4d8e-8b2b-9f25bdf3687f.jpg)
Browse an alphabetical list of documents from the Holocaust and World War II. These typed, handwritten, and artistic records are evidence of human experiences before, during, and after the Holocaust and war.
<< Previous | Displaying results 1-25 of 93 for "Document" | Next >>
A chart detailing physical characteristics of a Romani (Gypsy) individual, c. 1938. Dr. Robert Ritter and his team created extensive family trees and genealogical charts in order to identify, register, and classify all Romani people living in Nazi Germany. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial hygiene.”…

A genealogical chart of the Franz family, composed of identification photographs taken by the criminal department of the Aschaffenburg Identification Service [Erkennungsdienst]. Bavaria, Germany, 1942. This particular Romani family tree includes notes labeling individuals as "vagrants," "invalids," or "habitual criminals."Racial hygienists would collect genealogical documents or create family trees in order to identify, register, and classify all Romani people living in Nazi Germany. Roma (pejoratively…

A notice sent by the American Consulate General in Berlin to Arthur Lewy and family, instructing them to report to the consulate on July 26, 1939, with all the required documents, in order to receive their American visas.German Jews attempting to immigrate to the United States in the late 1930s faced overwhelming bureaucratic hurdles. It was difficult to get the necessary papers to leave Germany, and US immigration visas were difficult to obtain. The process could take years.

Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In this entry, Ada describes her experience with SS officers and camp personnel while living in a concentration camp.

Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In later entries, she describes her liberation and life after the war. In this entry, Ada describes her journey from Plaszow to Auschwitz in October 1944.

Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In later entries, she describes her liberation and life after the war. In this entry from August 1944, Ada describes finding love while being imprisoned in Plaszow concentration…

Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In later entries, she describes her liberation and life after the war. In this entry from October 1944, Ada describes the selection process at Auschwitz-Birkenau.

A newspaper advertisement for the Damenklub Violetta, a Berlin club frequented by lesbians, 1928. Before the Nazis came to power in 1933, lesbian communities and networks flourished in Germany.

Announcement dropped by American planes on Shanghai near the end of the war. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

This cartoon, “The Modern Mercury” by Jerry Doyle, appeared in The Philadelphia Record, December 7, 1935. The faded large figure in the background bears the label “Olympics ideals of sportsmanship and international good will.” The image of Hitler in the foreground bears the words “1936 Olympics,” “Intolerance and discrimination,” and “Nazism.”

Antisemitic cartoon showing a Jew leading a Soviet official by a leash. It reads "The 'ideal' person for the chosen people: There’s no accounting for taste."

Antisemitic propaganda of an agricultural worker kicking a stereotypically depicted Jewish man through a fence. It reads "German export: Out of our German country with the slimy Jewish band."

This card verified that Staff Sergeant Richard Schifter had permission to enter European buildings to collect intelligence on behalf of the US Army. Dated September 9, 1944. Born in Vienna, Schifter left Austria after Nazi Germany annexed the country in 1938. After joining the US Army, he was assigned to Camp Ritchie, where many German refugees trained in counterintelligence. Schifter later served as the assistant secretary of state for Human Rights and Humanitarian Affairs and as a special assistant to…

Cartoon depicting Jews, communists, and other enemies of the Nazis hanging on a gallows, 1935

On December 17, 1941, the Romanian government issued a decree requiring a census of all those with "Jewish blood.” All persons having one or two Jewish parents or two Jewish grandparents were ordered to register at the Central Jewish Office. This is a census certificate issued by that office in 1942.

On December 17, 1941, the Romanian government issued a decree requiring a census of all those with “Jewish blood.” All persons having one or two Jewish parents or two Jewish grandparents were ordered to register at the Central Jewish Office. This is a census certificate issued by that office in 1942.

A certificate of "Aryan" descent, issued to Joseph Schäfer of Mühlheim, Germany. To prove one's "Aryan" racial status in Nazi Germany, an individual had to trace their ancestry back to 1800. Signed by an official justice of the peace, this certificate attests to Schäfer's parentage and baptism. Dated January 14, 1936.

Many refugees had difficulties replacing lost or invalidated personal identification documents. The certificate of Polish citizenship shown here was valid in place of a passport. A Polish Jewish refugee used this certificate to travel legally from Lithuania, through the Soviet Union, to Japan. It contains the Curacao notation needed to obtain Soviet and Japanese visas. The bearer of this certificate aimed to reach Palestine, but ended up spending most of the war in Calcutta, India, part of the British…

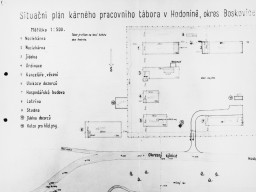
Diagram of the Hodonín u Kunštátu (Hodonin bei Kunstadt) camp in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (Czech Republic). Before it was converted into a Zigeunerlager (“Gypsy camp”) in 1942, it served as a penal labor camp. Translation of key:Scale 1:500Sleeping quartersSleeping quartersMess-hallInfirmaryOffices, prisonLiving quarters for guard staffEconomic/Agricultural BuildingLatrineWellMess-hall for guard staffPens for guard dogs
During the interwar period Dr. Susanne Engelmann served as the principal of a large public high school for girls in Berlin. This letter notified her of her dismissal, as a "non-Aryan," from her teaching position. The dismissal was in compliance with the Civil Service Law of April 7, 1933.On April 7, the German government issued the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service (Gesetz zur Wiederherstellung des Berufsbeamtentums), which excluded Jews and political opponents from all civil…

A letter written by the Berlin transit authority (Berliner Verkehrs Aktiengesellschaft) to Viktor Stern, informing him of his dismissal from his post with their agency as of September 20, 1933. This action was taken to comply with provisions of the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service.On April 7, the German government issued the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service (Gesetz zur Wiederherstellung des Berufsbeamtentums), which excluded Jews and political opponents…

One page of a document belonging to Chief Prosecutor Benjamin Ferencz listing the defendants in the Einsatzgruppen Case along with their position and crimes, line of defense, counts against them, and sentence.

Simone Weil kept this blank identification card bearing her picture in case her cover as "Simone Werlin" were blown and she needed to establish a new false identity. Both resistance workers and sympathetic government employees provided her the necessary stamps and signatures. Such forged documents assisted Weil in her work rescuing Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE).

First page of a letter from a US soldier describing "the living dead" and conditions his unit encountered in a subcamp of Dachau in April 1945.

Kurt I. Lewin, who was Jewish, used this card while in hiding in a Ukrainian Greek Catholic monastery in German-occupied Poland (today Ukraine).

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.