<< Previous | Displaying results 4301-4350 of 6769 for "" | Next >>
Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In this entry, Ada describes her experience with SS officers and camp personnel while living in a concentration camp.

Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In later entries, she describes her liberation and life after the war. In this entry, Ada describes her journey from Plaszow to Auschwitz in October 1944.

Ada Abrahamer kept a diary from September 1939 until March 1946, though only the pages from 1944-1946 survived. Ada’s diary documents her experiences as a young Jewish woman in German-occupied Poland. German authorities imprisoned Ada in the Krakow ghetto and several forced labor and concentration camps, including Auschwitz. In later entries, she describes her liberation and life after the war. In this entry from October 1944, Ada describes the selection process at Auschwitz-Birkenau.

Identification papers issued to Erika Tamar stating that she was born in Vienna on June 10, 1934. Erika was one of the 50 children rescued by Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus.

A chart detailing physical characteristics of a Romani (Gypsy) individual, c. 1938. Dr. Robert Ritter and his team created extensive family trees and genealogical charts in order to identify, register, and classify all Romani people living in Nazi Germany. During the Nazi era, Dr. Robert Ritter was a leading authority on the racial classification of people pejoratively labeled “Zigeuner” (“Gypsies”). Ritter’s research was in a field called eugenics, or what the Nazis called “racial…

A genealogical chart of the Franz family, composed of identification photographs taken by the criminal department of the Aschaffenburg Identification Service [Erkennungsdienst]. Bavaria, Germany, 1942. This particular Romani family tree includes notes labeling individuals as "vagrants," "invalids," or "habitual criminals." Racial hygienists would collect genealogical documents or create family trees in order to identify, register, and classify all Romani people living in Nazi Germany. Roma (pejoratively…

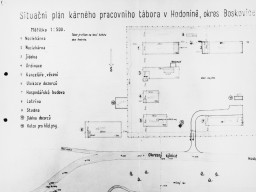
Diagram of the Hodonín u Kunštátu (Hodonin bei Kunstadt) camp in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (Czech Republic). Before it was converted into a Zigeunerlager (“Gypsy camp”) in 1942, it served as a penal labor camp. Translation of key: Scale 1:500 Sleeping quarters Sleeping quarters Mess-hall Infirmary Offices, prison Living quarters for guard staff Economic/Agricultural Building Latrine Well Mess-hall for guard staff Pens for guard dogs
During World War II, people often used false identities and forged identity documents to evade Nazi authorities. False identities were essential for resistance fighters, aid workers, and Jews hoping to pass as non-Jews. Creating high-quality, convincing forgeries required dozens of people to work together clandestinely. It also required sophisticated photography and printing equipment. For Jews passing as non-Jews, acquiring forged documents could mean the difference between life and death. This forged…

During World War II, people often used false identities and forged identity documents to evade Nazi authorities. False identities were essential for resistance fighters, aid workers, and Jews hoping to pass as non-Jews. Creating high-quality, convincing forgeries required dozens of people to work together clandestinely. It also required sophisticated photography and printing equipment. For Jews passing as non-Jews, acquiring forged documents could mean the difference between life and death. During World…

During World War II, people often used false identities and forged identity documents to evade Nazi authorities. False identities were essential for resistance fighters, aid workers, and Jews hoping to pass as non-Jews. Creating high-quality, convincing forgeries required dozens of people to work together clandestinely. It also required sophisticated photography and printing equipment. For Jews passing as non-Jews, acquiring forged documents could mean the difference between life and death. This…

Kurt I. Lewin, who was Jewish, used this card while in hiding in a Ukrainian Greek Catholic monastery in German-occupied Poland (today Ukraine).

Page from Earl G. Harrison's notebook, recording his impressions of Linz, Austria, while on a tour of displaced persons camps in 1945.

A letter from Salek and Eda Kuenstler to Sophia Zendler promising land in exchange for hiding their daughter.

The back of Samuel Soltz's citizenship papers illustrates the vast array of bureaucratic stamps and visas needed to emigrate from Europe in 1940–41. The stamp in the top left, dated August 21, 1940, represents a visa from the Japanese consul to Lithuania, Chiune Sugihara. Sugihara issued thousands of visas to enable Jews to escape.

This document from the American Consul-General in Vienna certifies that the Trost family applied for American visas on September 15, 1938. It states that the family (Josef, Alice, Dorrit, and Erika) were placed on the waiting list for visas with the numbers 47291-47294.

Marriage certificate obtained by Dr. Mohamed Helmy stating that Anna Gutman (Boros) married an Egyptian man in a ceremony held in Helmy’s home. Dr. Helmy also received certification from the Central Islamic Institute in Berlin attesting to Anna’s conversion to Islam, which the marriage certificate reflects. Translation: Marriage certificate On Wednesday June 16, 1943, we have certified the marriage contract between Abdelaziz Helmy Hammad, 36 years old, who was born on May 6th, 1906, in Faqous,…

Antisemitic propaganda of an agricultural worker kicking a stereotypically depicted Jewish man through a fence. It reads "German export: Out of our German country with the slimy Jewish band."

Cartoon depicting Jews, communists, and other enemies of the Nazis hanging on a gallows, 1935

Antisemitic cartoon showing a Jew leading a Soviet official by a leash. It reads "The 'ideal' person for the chosen people: There’s no accounting for taste."

A postcard sent to Ruth Segal (Rys Berkowicz) care of the Jewish Community (JewCom) in Kobe, Japan. Family and friends in German-occupied Warsaw, Poland, sent the postcard on June 20, 1941. It bears stamps both from the Jewish council (Judenrat) in the Warsaw ghetto and from German censors. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

First page of a letter from a US soldier describing "the living dead" and conditions his unit encountered in a subcamp of Dachau in April 1945.

On May 25, 1939, artist Moritz Schoenberger sent this radiogram (a telegram sent by radio) from the ocean liner "St. Louis" during the voyage from Hamburg, Germany, to Havana, Cuba. On this voyage, the "St. Louis" carried over 900 Jewish refugees fleeing Nazi persecution. The telegram reads, in part, "Physically and spiritually recovered and invigorated most confident about reaching Havana Saturday. Money received. Many thanks. Kisses. Papa." Schoenberger's optimism proved unfounded. Cuban authorities…

San Francisco Chronicle newspaper article titled "The Refugee Tragedy." The article was based on an interview with Moses Beckelman of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee, an aid organization. It discussed the overcrowding of Polish and Lithuanian refugees stranded in Shanghai, Kobe (Japan), and Lisbon (Portugal), all stops en route to North and South America. The primary cause of this bottleneck was a lack of transit and entry visas, a result of most countries closing their borders to…

Authorities in Berlin, Germany, sent this notice to Barbara Wohlfahrt, informing her of her husband Gregor's execution on the morning of December 7, 1939. Although he was physically unfit to serve in the armed forces, the Nazis tried Wohlfahrt for his religious opposition to military service. As a Jehovah's Witness, Wohlfahrt believed that military service violated the biblical commandment not to kill. On November 8, 1939, a military court condemned Wohlfahrt to beheading, a sentence carried out one month…

The Dutch government established a camp at Westerbork to intern Jewish refugees who had entered the Netherlands illegally. This sketch of the Westerbork transit camp was made by a Jewish inmate who was able to emigrate to the United States. In early 1942, the German occupation authorities decided to enlarge Westerbork and convert it into a transit camp for Jews. The systematic concentration of Jews from the Netherlands in Westerbork began in July 1942. From Westerbork, Jews were deported to the killing…
German police authorities issued this passport to Erna "Sara" Schlesinger on July 8, 1939, in Berlin. This first page of the passport illustrates the German laws that facilitated the identification of Jews in Germany. From 1938, German regulations required that Jewish women with a first name of "non-Jewish" origin use the middle name "Sara" on all official documents. Jewish men had to add the name "Israel". The letter "J" (standing for "Jude," that is, the word "Jew" in German) was stamped in red on the…

A German passport issued to Alice Mayer on February 24, 1939, in Bingen, Germany. Mayer's daughter, Ellen, is also listed on the passport. Both mother and daughter's names include the middle name "Sara." This middle name became a mandatory addition required by a law of August 17, 1938. Thereafter, all Jewish women in Germany with a first name of "non-Jewish" origin had to add "Sara" as a middle name on all official documents. Jewish men had to add the name "Israel". This enabled German officials to…

Simone Weil earned this diploma, which certified her to teach kindergarten in France, from the School of Social Work in Strasbourg in 1940. Weil assumed a false identity in late 1943 to facilitate her resistance activities as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE). Among the papers documenting Weil's new identity was a forged version of this diploma bearing the name "Simone Werlin".

Simone Weil used this forged diploma and other false papers to document a new identity assumed in late 1943. As Simone Werlin, she could avoid arrest and change residence to facilitate her rescue of Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE). Weil had earned the diploma, which certified her to teach kindergarten in France, from the School of Social Work in Strasbourg in 1940. The director of the school willingly forged this…

Simone Weil kept this blank identification card bearing her picture in case her cover as "Simone Werlin" were blown and she needed to establish a new false identity. Both resistance workers and sympathetic government employees provided her the necessary stamps and signatures. Such forged documents assisted Weil in her work rescuing Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE).

After adopting a new identity in late 1943, Simone Weil falsified her student card from the year 1938-1939 to bear her assumed name, Simone Werlin. The card verified enrollment in the School of Social Work in Strasbourg. Using forged and falsified documents, Weil was able to move to Chateauroux, France, and establish an operation to rescue Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE).

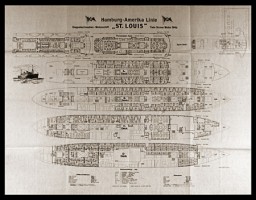
Plan of the two-propeller passenger liner the "St. Louis," showing cabins and room numbers. In 1939, this German ocean liner carried almost 1,000 Jewish refugees seeking temporary refuge in Cuba. It was forced to return to Europe after Cuba and then the United States refused to allow the refugees entry.
Most Polish Jewish refugees stayed in Japan much longer than their 10-day transit visas allowed. Many feared the day when Japanese authorities would no longer extend their stay with permits like the one shown here. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Japanese authorities issued this "Permit for stay in Japan" to Ruth Segal (Rys Berkowicz). After several unsuccessful attempts to obtain visas for the United States, Ruth's father was able to secure a visa for her to go to New Zealand, in the British Commonwealth of Nations. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Family and friends of Ruth Segal (Rys Berkowicz) sent this postcard to her in Kobe, Japan. They sent the postcard from Warsaw, in German-occupied Poland, on June 20, 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Protective document issued to a Jewish woman by the Swedish embassy in Budapest, Hungary, in 1944. Such documents protected the bearer from immediate deportation by the Germans to the Auschwitz killing center in occupied Poland. The "W" in the lower left corner indicates that Raoul Wallenberg initialed the document.

A second RCA Radiogram telegram from Rabbi Grodzenski, Chief Rabbi of Vilna, to the Central Relief Committee in New York. He requests aid for refugees who have gathered in Vilna. The telegram says that more than 1,600 yeshiva students and their families from over 10 cities throughout Poland have fled to Vilna, where they remain in terrible living conditions. November 5, 1939. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Many refugees had difficulties replacing lost or invalidated personal identification documents. The certificate of Polish citizenship shown here was valid in place of a passport. A Polish Jewish refugee used this certificate to travel legally from Lithuania, through the Soviet Union, to Japan. It contains the Curacao notation needed to obtain Soviet and Japanese visas. The bearer of this certificate aimed to reach Palestine, but ended up spending most of the war in Calcutta, India, part of the British…

Setty and Moritz Sondheimer and their two children fled Nazi Germany for Kovno, Lithuania, in 1934. There, Moritz opened a small factory manufacturing buttons and combs. This image shows page 2, containing an identification photograph, of a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer by the German Consulate in Kovno on January 29, 1938. With aid from Japanese diplomat Chiune Sugihara in obtaining Japanese transit visas, Setty and her family emigrated from Kovno in February 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition…

Page 5 of a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer by the German Consulate in Kovno on January 29, 1938. This page contains three visas: (1) visa for Kovno valid from August 27, 1940, until December 31, 1940 (2) a second visa for Kovno valid until June 30, 1941, and (3) first visa for Yokohama, Japan, valid from June 7, 1941, until June 30, 1942. Unable to emigrate from Japan, Setty remained there until she was able to emigrate to the United States in 1947. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and…

Transit visa in a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer, a German citizen. This visa, issued on August 6, 1940, enabled her to travel through Japan en route to Surinam, Curacao, or other Dutch colonies in the Americas. These plans were disrupted when travel across the Pacific Ocean was forbidden following U.S. entry into World War II. Setty remained in Japan until she was able to emigrate to the United States in 1947. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

The Soviet travel agency Intourist issued this type of luggage tag, showing a route map, to passengers on the Trans-Siberian Express. Some Jewish refugees traveled on the Trans-Siberian Express as they fled eastward. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

A Jewish refugee purchased this postcard of the Lenin Library during a stopover in Moscow. Soviet Union, 1940-1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

A train ticket for travel on the Trans-Siberian Railroad. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Voucher for travel on the Trans-Siberian Railroad purchased at the "Intourist Travel Company of the USSR" in England for Joseph and Ruth Schaffer. Thousands of Jewish refugees fled Nazi Europe on the Trans-Siberian Railroad through the Soviet Union to Japan with the help of Japanese visas provided by Japanese diplomat Chiune Sugihara. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Soviet authorities issued this receipt, in Russian, to Moshe Zupnik for the rubles they confiscated from him before he left the Soviet Union. Soviet authorities routinely confiscated most rubles and other valuables from Jewish refugees before they boarded steamers bound for Japan and left the Soviet Union. Vladivostok, Soviet Union, January 22, 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

A page in a passport belonging to Setty Sondheimer containing stamps from Ecuador. These stamps are marked in red with the word "Anulado," the Spanish word for "canceled." The stamps were canceled when Setty's visa for Ecuador expired because she was unable to travel across the Pacific due to fighting in that theater. Setty remained in Japan for the duration of the war and emigrated to the United States in 1947. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Proclamation issued on February 18, 1943, by the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy authorities establishing, for reasons of "military necessity," a "designated area" for "stateless refugees" in the Hongkew area of the International Settlement. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Polish-language newspaper for refugees in Shanghai: Wiadomosci, "News for War Refugees in Shanghai." [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

Announcement dropped by American planes on Shanghai near the end of the war. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.