You searched for: 圣卢西亚谷歌排名【TG飞机:@bapingseo】INS,FACEBOOK竞价粉【TG电报:@bapingseo】谷歌是競價排名嗎【Telegram:@bapingseo】哪里有英雄联盟比赛输赢竞猜韦德初盘怎么看大小球意甲外围网站足球特1特2是什么意思?i8ZX2K/034020.html
<< Previous | Displaying results 801-850 of 854 for "圣卢西亚谷歌排名【TG飞机:@bapingseo】INS,FACEBOOK竞价粉【TG电报:@bapingseo】谷歌是競價排名嗎【Telegram:@bapingseo】哪里有英雄联盟比赛输赢竞猜韦德初盘怎么看大小球意甲外围网站足球特1特2是什么意思?i8ZX2K/034020.html" | Next >>
-
Mlynów: "Life under the German Occupation," According to Yehudit Rudolf
ArticleExplore firsthand testimony about the occupation of Mlynów, the establishment of the ghetto, resistance activities, and the destruction of the ghetto.
-
Treblinka
ArticleTreblinka was one of three killing centers in Operation Reinhard, the SS plan to murder almost two million Jews living in the German-administered territory of occupied Poland.

-
Assessing Guilt
ArticleAfter WWII, prosecutors faced the challenge of assessing the guilt of propagandists whose words, images, and writings had supported Nazi brutality and mass murder.

-
The Security Police (SiPo)
ArticleThe Security Police (Sicherheitspolizei, SiPo) was a German police organization created by Heinrich Himmler. Learn about its origin and role in the Holocaust.

-
Siegfried Halbreich describes arrival at and conditions in the Sachsenhausen camp
Oral HistoryAfter Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Siegfried fled with a friend. They attempted to get papers allowing them to go to France, but were turned over to the Germans. Siegfried was jailed, taken to Berlin, and then transported to the Sachsenhausen camp near Berlin in October 1939. He was among the first Polish Jews imprisoned in Sachsenhausen. Inmates were mistreated and made to carry out forced labor. After two years, Siegfried was deported to the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, where he was…

-
Siegfried Halbreich describes treatment of prisoners in the Sachsenhausen camp
Oral HistoryAfter Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Siegfried fled with a friend. They attempted to get papers allowing them to go to France, but were turned over to the Germans. Siegfried was jailed, taken to Berlin, and then transported to the Sachsenhausen camp near Berlin in October 1939. He was among the first Polish Jews imprisoned in Sachsenhausen. Inmates were mistreated and made to carry out forced labor. After two years, Siegfried was deported to the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, where he was…

-
Charlene Schiff describes her liberation by Soviet troops
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Felix Horn describes postwar emigration with the Brihah movement and adjustment to life after the war
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Lucine Horn describes obtaining false papers to assume the identity of an "Aryan" outside the Warsaw ghetto
Oral HistoryLucine was born to a Jewish family in Lublin. Her father was a court interpreter and her mother was a dentist. War began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Lucine's home was raided by German forces shortly thereafter. Soon after the German occupation of Lublin, Jews there were forced to wear a compulsory badge identifying them as Jews. A ghetto in Lublin was closed off in January 1942. Lucine survived a series of killing campaigns and deportations from the ghetto during March and…

-
Felix Horn describes attempt to flee from the Majdan Tatarski ghetto
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Felix Horn describes antisemitism in Lvov and conditions in the Janowska camp
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Lucine Horn describes conditions in the Lublin ghetto
Oral HistoryLucine was born to a Jewish family in Lublin. Her father was a court interpreter and her mother was a dentist. War began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Lucine's home was raided by German forces shortly thereafter. Soon after the German occupation of Lublin, Jews there were forced to wear a compulsory badge identifying them as Jews. A ghetto in Lublin was closed off in January 1942. Lucine survived a series of killing campaigns and deportations from the ghetto during March and…

-
Ludmilla Page describes conditions in Oskar Schindler's munitions factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Charlene Schiff describes a clandestine school for children in the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Charlene Schiff describes the German invasion of her town, Horochow, in the summer of 1941
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Charlene Schiff describes foraging for food in order to survive in forests after escaping from the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Siegfried Halbreich describes conditions and forced labor in the Gross-Rosen camp
Oral HistoryAfter Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, Siegfried fled with a friend. They attempted to get papers allowing them to go to France, but were turned over to the Germans. Siegfried was jailed, taken to Berlin, and then transported to the Sachsenhausen camp near Berlin in October 1939. He was among the first Polish Jews imprisoned in Sachsenhausen. Inmates were mistreated and made to carry out forced labor. After two years, Siegfried was deported to the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, where he was…

-
Flight and Rescue
ArticleExplore the story of over 2,000 Polish Jewish refugees who fled east to escape war-torn Europe. They sought safety in such distant places as China and Japan.

-
Writing the News
ArticleShortly after taking power in January 1933, Adolf Hitler and the Nazis took control of German newspapers, detailing how the news was to be reported.

-
Euthanasia Program and Aktion T4
ArticleThe Nazi Euthanasia Program, codenamed Aktion "T4," was the systematic murder of institutionalized people with disabilities. Read about Nazi “euthanasia.”

-
The Order Police
ArticleThe Order Police (Ordnungspolizei, Orpo) were Nazi Germany’s uniformed police forces. They became perpetrators of horrific crimes and played a significant role in the Holocaust.

-
Charles E. Coughlin
ArticleCharles Coughlin, Catholic priest and populist leader, promoted antisemitic and pro-fascist views. In the 1930s, he was one of the most influential public figures in the US.

-

-
The Syrets Labor Education Camp
ArticleSyrets was a labor education camp established by the Germans outside of Kyiv. Learn more about Syrets prisoners and their daily life in the camp.
-
What Groups of People did the Nazis Target?
ArticleJews were the primary targets for mass murder by the Nazis and their collaborators. Nazi policies also led to the brutalization and persecution of millions of others.

-
The Krakow (Cracow) Ghetto during the Holocaust
ArticleThe Krakow ghetto in German-occupied Poland held over 15,000 Jews. Learn more about Krakow and the ghetto’s history during the Holocaust and WWII.

-
"Nuremberg: Its Lesson for Today"
FilmThis footage comes from "Nuremberg, Its Lesson for Today" a 1947 documentary film produced by the US military's Documentary Film Unit, Information Services Division. The film, directed by Pare Lorentz and Stuart Schulberg, shows footage from the trial of Nazi war criminals by the International Military Tribunal. It also intermixes historical footage depicting the founding of the Nazi state, the unleashing of World War II, and Nazi crimes against humanity. The sentencing sequence shown here illustrates the…

-
Charlene Schiff describes being caught while trying to smuggle food into the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Charlene Schiff describes forced labor in the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Lucine Horn describes her escape from the Majdan Tatarski ghetto
Oral HistoryLucine was born to a Jewish family in Lublin. Her father was a court interpreter and her mother was a dentist. War began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Lucine's home was raided by German forces shortly thereafter. Soon after the German occupation of Lublin, Jews there were forced to wear a compulsory badge identifying them as Jews. A ghetto in Lublin was closed off in January 1942. Lucine survived a series of killing campaigns and deportations from the ghetto during March and…

-
Ludmilla Page recalls arriving in Auschwitz instead of Oskar Schindler's munitions factory in Brünnlitz
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Ludmilla Page describes leaving Auschwitz and arriving at the Bruennlitz munitions factory in the Sudetenland
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Benjamin (Ben) Meed describes Warsaw after the German occupation in 1939 and first experiencing antisemitism
Oral HistoryBen was one of four children born to a religious Jewish family. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. After the Germans occupied Warsaw, Ben decided to escape to Soviet-occupied eastern Poland. However, he soon decided to return to his family, then in the Warsaw ghetto. Ben was assigned to a work detail outside the ghetto, and helped smuggle people out of the ghetto—including Vladka (Fagele) Peltel, a member of the Jewish Fighting Organization (ZOB), who later became his wife. Later, he went into…

-
Benjamin (Ben) Meed describes the burning of the Warsaw ghetto during the 1943 ghetto uprising
Oral HistoryBen was one of four children born to a religious Jewish family. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. After the Germans occupied Warsaw, Ben decided to escape to Soviet-occupied eastern Poland. However, he soon decided to return to his family, then in the Warsaw ghetto. Ben was assigned to a work detail outside the ghetto, and helped smuggle people out of the ghetto—including Vladka (Fagele) Peltel, a member of the Jewish Fighting Organization (ZOB), who later became his wife. Later, he went into…

-
Ludmilla Page describes arrival at the Brünnlitz munitions factory
Oral HistoryLudmilla was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Kishinev, Romania. She and her mother, a physician, were living in Poland when the Germans invaded on September 1, 1939. They were taken to Krakow. Ludmilla was forced to live in the Krakow ghetto; her mother was sent to the Warsaw ghetto. Ludmilla worked in a factory at the Plaszow labor camp for a businessman who was a friend of the German industrialist Oskar Schindler. In October 1944, Schindler attempted to save some Jewish workers by relocating them…

-
Charlene Schiff describes the Soviet occupation of Horochow after the outbreak of World War II
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Charlene Schiff describes difficulties in gaining entry to the United States in the aftermath of the Holocaust
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
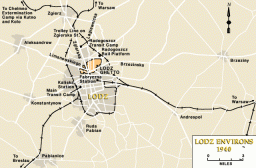
The Lodz Ghetto
Animated MapView an animated map of key events in the history of the Lodz ghetto in occupied Poland, from establishment by the Germans in 1940 until destruction in 1944.
-
John Demjanjuk: Prosecution of A Nazi Collaborator
ArticleJohn Demjanjuk, initially convicted as “Ivan the Terrible,” was tried for war crimes committed as a collaborator of the Nazi regime during the Holocaust.

-
Josef Mengele
ArticleProminent SS physician Josef Mengele, called the "angel of death" by his victims, conducted inhumane medical experiments on prisoners in the Auschwitz camp.

-
The Immigration of Refugee Children to the United States
ArticleMore than one thousand unaccompanied refugee children fleeing Nazi persecution arrived in the United States between 1933 and 1945. Learn more

-
Hajj Amin al-Husayni: Wartime Propagandist
ArticleFormer Mufti of Jerusalem Hajj Amin al-Husayni was an exiled political leader who sought an alliance with the Axis Powers. Learn about his wartime propaganda efforts.

-
President Obama's Remarks at Buchenwald
ArticlePresident Barack Obama visited Buchenwald concentration camp in Germany on June 5, 2009. In a speech at the site, he repudiated Holocaust denial. Browse transcript.

-
Holocaust Denial: Key Dates
ArticleBrowse a timeline listing some key events in the evolution of Holocaust denial and the distortion of the facts of the Holocaust.
-
Charlene Schiff describes conditions in the Horochow ghetto
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Charlene Schiff describes anti-Jewish decrees and anti-Jewish measures after the German invasion of Horochow
Oral HistoryBoth of Charlene's parents were local Jewish community leaders, and the family was active in community life. Charlene's father was a professor of philosophy at the State University of Lvov. World War II began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. Charlene's town was in the part of eastern Poland occupied by the Soviet Union under the German-Soviet Pact of August 1939. Under the Soviet occupation, the family remained in its home and Charlene's father continued to teach. The Germans…

-
Felix Horn describes a hiding place in Warsaw
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Felix Horn describes escaping from the Majdan Tatarski ghetto and seeking shelter
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-

-
Nazi Territorial Aggression: The Anschluss
ArticleThe Anschluss, Germany's annexation of Austria in March 1938, was the Nazi German regime’s first act of territorial aggression and expansion. Learn more.

