You searched for: ���������������������������������������������V���ATV1819���88q3P
<< Previous | Displaying results 26-50 of 56 for "���������������������������������������������V���ATV1819���88q3P" | Next >>
-
German Surrender
Timeline EventMay 7, 1945. On this date, German armed forces surrendered unconditionally to Allied forces in the west.

-
Death Marches
ArticleAs Allied forces approached Nazi camps in the last months of WWII, the SS organized brutal “death marches” (forced evacuations) of concentration camp inmates.

-
Lublin/Majdanek Concentration Camp: Administration
ArticleIn 1940, the Nazis established Lublin (Majdanek) concentration camp in Lublin, Poland. Learn more about camp administration.

-
History of the Jewish Community in Kalisz: 12th Century to World War I
ArticleOne of the oldest cities in Poland, Kalisz played a pivotal role in Polish Jewish history. Learn about the Jewish Community in Kalisz from the 12th Century to WWI.

-
Tower of Sephardic faces: The Jewish community of Monastir, Macedonia
ArticleOn March 11, 1943, over 3,000 of Monastir’s Jews were deported to Treblinka. Learn more about the history of the community and postwar memorialization.

-
1945: Key Dates
ArticleExplore a timeline of key events during 1945 in the history of Nazi Germany, World War II, the Holocaust, and liberation and the aftermath of the Holocaust.

-
The Nuremberg Code
ArticleLeading German physicians and administrators were put on trial for their role during the Holocaust. The resulting Nuremberg Code was a landmark document on medical ethics. Learn more
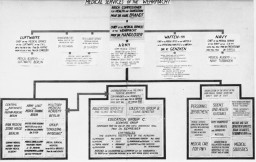
-
Reich Security Main Office (RSHA)
ArticleThe Reich Security Main Office (RSHA), created by Heinrich Himmler, brutally coordinated and perpetrated many aspects of the Holocaust.

-
Soviet and US Troops Meet at Torgau
Timeline EventApril 25, 1945. On this date, Soviet and American troops met at Torgau, Germany.

-
Background: Jurists' Trial Verdict
ArticleThe Justice Case, or Jurists’ Trial, of the Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings tried members of the German justice administration. Browse excerpts from the verdict.

-
Columbia-Haus
ArticleThe Columbia-Haus camp was one of the early camps established by the Nazi regime. It held primarily political detainees. Learn more about the history of the camp.
-
Hodonín U Kunštátu (Hodonín bei Kunstadt) (Roma camp)
ArticleIn March 1942, the Hodonin camp was classified as a camp for Roma. It was a transfer station during deportation to Auschwitz-Birkenau. Learn about the camp and its history.

-
Hajj Amin al-Husayni: Key Dates
ArticleKey dates associated with Hajj Amin al-Husayni, former Mufti of Jerusalem who participated in a pro-Axis coup in Iraq in 1941. Explore further

-
Law, Justice, and the Holocaust
ArticleLearn about the role of the legal profession as the Nazi leadership gradually moved Germany from a democracy to a dictatorship.

-
World War II in Europe
ArticleWorld War II lasted from 1939 to 1945, when the Allies defeated the Axis powers. Learn about key invasions and events during WWII, also known as the Second World War.

-
Earl G. Harrison: Biography
ArticleEarl G. Harrison, Commissioner for Immigration and Naturalization under FDR, is known for a report harshly criticizing the US and British treatment of Jewish DPs.

-
Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings, Case #9, The Einsatzgruppen Case
ArticleThe Einsatzgruppen Case was Case #9 of 12 Subsequent Nuremberg Proceedings against leading German industrialists, military figures, SS perpetrators, and others.

-
The Security Police (SiPo)
ArticleThe Security Police (Sicherheitspolizei, SiPo) was a German police organization created by Heinrich Himmler. Learn about its origin and role in the Holocaust.

-
München-Schwabing
ArticleLearn about the establishment and history of the Dachau subcamp München-Schwabing, and the role of Eleonore Baur (also known as Schwester Pia or Sister Pia).
-
Incitement to Genocide in International Law
ArticleAfter the Holocaust, the IMT charged the first case of “incitement to genocide.” Learn more about the crime and its application in modern genocide law.

-
The Nazi Kripo (Criminal Police)
ArticleThe Nazi Kripo, or Criminal Police, was the detective force of Nazi Germany. During the Nazi regime and WWII, it became a key enforcer of policies based in Nazi ideology.

-
Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B
ArticleIn 1939, the Nazis established the Mannschafts-Stammlager (Stalag) IX B camp in Germany. Learn more about the camp’s history, prisoners, and liberation.
-
Anti-Jewish Legislation in North Africa
ArticleThe Vichy regime introduced race laws to the North African territories in October of 1940. Learn about the impact of the laws on the region’s Jewish people.

-
Japanese American Relocation
ArticleLearn more about the forcible relocation of some 120,000 people of Japanese descent living in the US to “relocation centers.”

-
The Eastern Front: The German War against the Soviet Union
ArticleOften referred to as the “eastern front,” the German-Soviet theater of war was the largest and deadliest of World War II. Learn more about the background and key events.

