You searched for: hiding
<< Previous | Displaying results 1-50 of 499 for "hiding" | Next >>
-
Jewish girls in hiding in a convent
PhotoA group of Jewish girls hiding, under assumed identities, in a convent. Ruiselede, Belgium, 1943-44.

-
Augusta Feldhorn in hiding
PhotoAugusta Feldhorn stands next to a nun while in hiding. Augusta, a Jewish child, was in hiding under an assumed Christian identity. Belgium. 1942-1945.

-
Hiding in disguise as a priest
PhotoAn Italian Jew who survived the war by disguising himself as a priest and living in the Vatican from October 1943 to June 1944. A number of Jews were able to seek refuge in religious houses throughout Rome, including in the Vatican. Rome, Italy, 1943-1944.

-
Identity Card Used in Hiding
Timeline EventAugust 3, 1943. On this date, Kurt I. Lewin was issued a forged ID card for "Roman-Paul Mytka." He used that identity to survive the war.

-
Hiding under a different religion
PhotoSome Jewish children survived the Holocaust because they were protected by people and institutions of other faiths. Children quickly learned to master the prayers and rituals of their "adopted" religion in order to keep their Jewish identity hidden from even their closest friends. This photograph shows two hidden Jewish children, Beatrix Westheimer and her cousin Henri Hurwitz, with Catholic priest Adelin Vaes, on the occasion of Beatrix's First Communion. Ottignies, Belgium, May 1943.

-
Dawid Tennenbaum in hiding
PhotoIn 1942, eleven-year-old Dawid Tennenbaum went into hiding with his mother, settling in the Lvov region as Christians. Dawid disguised himself as a girl and as mentally disabled. This exempted him from attending school and prevented his being exposed.

-
Dress Worn by a Child in Hiding
ArtifactA child's dress embroidered with red and blue flowers with small green leaves. This dress was hand embroidered by Lola Kaufman's mother in the Czortkow ghetto. Lola (born Lea Rein) wore this dress when she went into hiding. Lola was hidden first under a bed in the house of the woman who used to deliver milk to the family, then in a dugout under a cellar of a barn where she joined three other Jews in hiding. In March 1944, the Soviets liberated the area. The hidden Jews left their hideout in the middle of…

-
Child's Sweater Worn in Hiding
ArtifactDuring the 1943 liquidation of the Lvov ghetto, dozens of Jews fled into the city sewers to escape death. Eight-year-old Krystyna Chiger (later Kristine Keren) hid with her family and 16 others beneath the city's streets for 14 months, during which she wore this sweater.

-
Selma Schwarzwald in hiding as a Polish Catholic
PhotoSelma Schwarzwald poses outside while wearing her first communion dress. Selma lived in hiding as a Polish Catholic during the war. Busko-Zdroj, Poland, 1945.

-
Letter Asking for Help to Hide Daughter
Timeline EventFebruary 1, 1943. On this date, Selek and Eda Kuenstler wrote to Sophia Zendler and begged her to hide their child.

-
Drawing of shoes by a Jewish teenager in hiding
ArtifactJewish teenager Ava Hegedish drew this poignant picture of her mother's well-worn shoes while in hiding. It was drawn while Ava was in hiding at a farm near Belgrade, Yugoslavia (now Serbia), between 1941 and 1944. Once Nazi Germany and its Axis partners partitioned Yugoslavia and Belgrade fell under German control, Ava’s father thought the family’s best chance of survival was to separate and go into hiding. Ava ended up at a farm with some extended-family Serbian relatives. Because she…

-
Sam Spiegel describes hiding in woods before liberation
Oral HistoryIn 1942, Sam was forced into a ghetto in his hometown and assigned to work in a munitions factory. In 1944 he was transported to Auschwitz and then forced to work in a train factory. He survived eight days on a death march after the evacuation of Auschwitz by the Nazis. He was liberated by Soviet units in January 1945. He lived in a displaced persons camp in Germany where worked for the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration. In 1947, he immigrated to the United States.

-
Yugoslav Jews in hiding
PhotoMr. Mandil and his son Gavra, Yugoslav Jews, while in hiding. The Mandil family escaped to Albania in 1942. After the German occupation in 1943, Mandil's Albanian apprentice hid the family, all of whom survived. Albania, between 1942 and 1945.
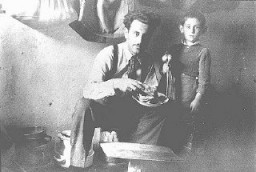
-
Jerry von Halle describes hiding in Amsterdam
Oral HistoryIn 1933 Jerry's family moved from Hamburg to Amsterdam. The Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940. In 1941, Jerry's brother perished in Mauthausen. Jerry and his parents went into hiding first in Amsterdam and then in a farmhouse in the south. The Gestapo (German Secret State Police) arrested Jerry's father in 1942, but Jerry and his mother managed to return to their first hiding place. They were liberated in Amsterdam by Canadian and Jewish Brigade troops.

-
Anita Magnus Frank describes hiding in the Netherlands
Oral HistoryWhen the war began, Anita and her family lived in Breda, the Netherlands. With the 1940 German occupation, they went into hiding and took on new names that shielded their Jewish identity. Anita and her brother first were hidden in a non-Jewish neighbor's home, and later by a Quaker family near Utrecht. Anita, her parents, brother, and two sisters survived the war.

-
Hetty d'Ancona Deleeuwe describes difficulties of going into hiding
Oral HistoryThe Germans invaded the Netherlands in May 1940. After a year or so, Hetty and other Jewish children could no longer attend regular schools. The Germans took over her father's business in 1942. Hetty's father tried to prove that the family was Sephardic, and they were thus exempted from a roundup in 1943. Hetty's father decided that the family should leave Amsterdam, and Hetty was hidden with a family in the southern Netherlands. She and both her parents survived.

-
Felix Horn describes a hiding place in Warsaw
Oral HistoryFelix was born to an assimilated Jewish family in Lublin, Poland. His father was a locksmith and his mother was a singer. Following the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, Felix fled east to Rovno and then to Soviet-occupied Lvov, where he was accepted at a medical school. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Felix was taken to a labor camp. He escaped and returned to Lublin, and found that his family had been forced into the ghetto established there. After the…

-
Fred Deutsch describes conditions in hiding place in forest
Oral HistoryFred was born in Czechoslovakia in a town near the Polish border. Fred and his family were forced by the Germans to relocate east to a town bordering Slovakia. At the end of 1942, they escaped from the town and went into hiding. The family hid in bunkers in the forest until the end of the war. They moved every few weeks to avoid detection by the Germans or Slovak authorities. While the family was in hiding, Fred's grandfather made arrangements for Fred to attend school under an assumed name and religion. A…

-
Fred Deutsch describes some of the risks involved in hiding
Oral HistoryFred was born in Czechoslovakia in a town near the Polish border. Fred and his family were forced by the Germans to relocate east to a town bordering Slovakia. At the end of 1942, they escaped from the town and went into hiding. The family hid in bunkers in the forest until the end of the war. They moved every few weeks to avoid detection by the Germans or Slovak authorities. While the family was in hiding, Fred's grandfather made arrangements for Fred to attend school under an assumed name and religion. A…

-
House in Amsterdam with a specially constructed hiding place
PhotoThe house in Amsterdam where Tina Strobos hid over 100 Jews in a specially constructed hiding place. Her house was raided eight times, but the Jews were never discovered. Netherlands, date uncertain.

-
Beads used by a Dutch Jewish girl in hiding
ArtifactThese tiny black, white, gold, and clear glass beads were used by Rachel “Chelly” de Groot from November 1942 to April 1944 and recovered by her brother Louis after the war. Chelly used the beads to make handicrafts. On November 16, 1942, Chelly, then 15, Louis, 13, and their parents Meijer and Sophia left Arnhem and went into hiding after the Dutch police warned them of a raid. Meijer and Sophia hid in Amsterdam while Chelly and Louis moved around to different locations. In summer or fall 1943,…

-
Selma Engel diary entry about life in hiding
ArtifactDiaries reveal some of the most intimate, heart-wrenching accounts of the Holocaust. They record in real time the feelings of loss, fear, and, sometimes, hope of those facing extraordinary peril. Selma Wijnberg and Chaim Engel met and fell in love in the Sobibor killing center. After the young couple made a daring escape during the camp uprising and fled into hiding, Selma began a diary to record their experiences. The diary was written in 1943-1944 while Selma was in hiding in German-occupied…

-
Suse Gruenbaum Schwarz describes preparation for and hiding during a Nazi raid
Oral HistorySuse's family moved to the Netherlands in 1933. After invading the Netherlands in 1940, the Germans imposed anti-Jewish measures. From 1942, Suse could not attend school. The family went into hiding in 1943, Suse and her mother on one farm and her father on another. Later, her father and another couple came to hide with Suse. They were liberated in 1945. Suse arrived in the United States in 1947.

-
Carla Heijmans Lessing describes the fear her family felt while in hiding
Oral HistoryAfter invading the Netherlands in 1940, the Germans imposed anti-Jewish measures. With the aid of a Catholic priest who helped Jews find hiding places, Carla, her mother, and her brother went into hiding in August 1942 to avoid deportation to work camps. They had to leave the hiding place after three months and with the priest's help found shelter in Delft with a Catholic family which had seven children. They remained in hiding there for 30 months, until liberation in May 1945.

-
Jerry von Halle describes hunger while in hiding in Amsterdam
Oral HistoryIn 1933 Jerry's family moved from Hamburg to Amsterdam. The Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940. In 1941, Jerry's brother perished in Mauthausen. Jerry and his parents went into hiding first in Amsterdam and then in a farmhouse in the south. The Gestapo (German Secret State Police) arrested Jerry's father in 1942, but Jerry and his mother managed to return to their first hiding place. They were liberated in Amsterdam by Canadian and Jewish Brigade troops.

-
Sophie Turner-Zaretsky describes living conditions while in hiding in Poland
Oral HistorySophie was born Selma Schwarzwald to parents Daniel and Laura in the industrial city of Lvov, two years before Germany invaded Poland. Daniel was a successful businessman who exported timber and Laura had studied economics. The Germans occupied Lvov in 1941. After her father's disappearance on her fifth birthday in 1941, Sophie and her mother procured false names and papers and moved to a small town called Busko-Zdroj. They became practicing Catholics to hide their identities. Sophie gradually forgot that…

-
Sarah (Sheila) Peretz Etons describes her experiences as a child in hiding
Oral HistoryGermany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. After the German occupation, Sarah (then just three years old) and her mother were forced into a ghetto. One day, a Polish Catholic policeman warned them that the ghetto was about to be liquidated. He sheltered Sarah and her mother first in his house, then in a potato storage bunker, and then in a chicken coop on his property. Sarah hid there for more than two years, until the area was liberated by Soviet forces. After the war, Sarah emigrated from…

-
Barbara Ledermann Rodbell describes using false papers and living in hiding
Oral HistoryDescribes using false papers and living in hiding

-
Salek and Eda Kuenstler's letter to Sophia Zendler about hiding their daughter
DocumentA letter from Salek and Eda Kuenstler to Sophia Zendler promising land in exchange for hiding their daughter.

-
Portrait of Tsewie Herschel taken while he was living in hiding
PhotoPortrait of Tsewie Herschel seated in a chair, taken while he was living in hiding. Oosterbeek, the Netherlands, 1943–1944. Tsewie never knew his parents. Born in December 1942, he was hidden with the de Jong family in April 1943. That July, his parents were deported from the Netherlands to the Sobibór killing center. The de Jongs renamed Tsewie "Henkie," raised him as a Christian, and treated him as their son. Tsewie learned about his origins from his paternal grandmother, who reclaimed him…

-
Tina Strobos describes the hiding place and alarm system in her house
Oral HistoryTina was a medical student when the Germans invaded the Netherlands in May 1940. She and members of her sorority joined the underground, and she hid Jews in her house from the beginning of the war. Tina found hiding places for Jewish children, forged passports, and served as a courier for the underground.

-
Large wooden crate used by Żegota to hide false documents
ArtifactThis large, lidded wooden chest was used by the Council for Aid to Jews (codenamed “Żegota”) to hide false identity documents from Nazi authorities. Żegota was an underground rescue organization of Poles and Jews in German-occupied Poland and operated from December 1942 to January 1945. Supported by the Polish government-in-exile, it coordinated efforts to save Jews in German-occupied Poland from Nazi persecution and murder. One of Żegota’s most impactful clandestine activities was producing and…

-
Member of the Kovno ghetto underground hides supplies in a well
PhotoPhotograph taken by George Kadish: a member of the Kovno ghetto underground hides supplies in a well used as the entrance to a hiding place in the ghetto. Kovno, Lithuania, 1942.

-
Hiding place discovered during Warsaw ghetto uprising
PhotoTwo Jewish men captured by the SS pull a woman from an underground bunker during the suppression of the Warsaw ghetto uprising. Warsaw, Poland, May 8, 1943.

-
Freya (Alice) Lang Rosen recalls experiences while hiding in France
Oral HistoryRecalls experiences while hiding in France

-
Wilek (William) Loew describes the hiding place in which his mother survived an Aktion in Lvov
Oral HistoryWilek was the son of Jewish parents living in the southeastern Polish town of Lvov. His family owned and operated a winery that had been in family hands since 1870. Wilek's father died of a heart attack in 1929. Wilek entered secondary school in 1939. Soon after he began school, World War II began with the German invasion of Poland. Lvov was in the part of eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. Although the Soviets took over Wilek's home and the family business, Wilek was able to continue his…

-
Liny Pajgin Yollick describes how hiding their Jewish identity saved her family's life in Nice, France
Oral HistoryIn May 1940, the Germans occupied the Netherlands. In 1942, it took Liny, her mother, and her sister six months to escape to southern France. They pretended to be Protestant, obtained visas to travel through Spain and Portugal, and were on one of the last trains to cross into Spain after the Germans took over southern France. They boarded a Portuguese ship bound for Dutch Guiana (Suriname). Liny was placed in a refugee camp, and then worked in the Dutch embassy in Washington D.C. She eventually settled in…

-
Renee Schwalb Fritz describes her experience as a Jewish child hiding in a Catholic convent
Oral HistoryRenee's father left for the United States in 1939. Before Renee and her mother could join him, they had to flee to Belgium to escape the repression of Jews in Austria. The Germans occupied Belgium in 1940. Renee was hidden in a convent for two years, until the Germans became suspicious. The underground took Renee to a Protestant family's farm, and then to an orphanage. After the war she was reunited with her mother, who had survived Auschwitz. Five years later they joined her father in the United States.

-
Forcing Jews out of hiding during the Warsaw ghetto uprising
PhotoJewish homes in flames after the Nazis set residential buildings on fire in an effort to force Jews out of hiding during the Warsaw ghetto uprising. Poland, April 19–May 16, 1943.

-
Metal box used to hide contents of the Oneg Shabbat archives
ArtifactOne of the ten metal boxes in which portions of the Ringelblum Oneg Shabbat archives were hidden and buried in the Warsaw ghetto. The boxes are currently in the possession of the Jewish Historical Institute in Warsaw.

-
Villiam Krausz sits with a doll and a teddy bear shortly before the family went into hiding
PhotoBenjamin Kedar (born Villiam Krausz) sits with a doll and a teddy bear shortly before his family went into hiding. Villiam's parents married in Prague and settled in Nitra, Slovakia. They worked as physicians. They had a daughter, Helen, in 1934, and Villiam in 1938. In 1942 the family relocated to a nearby village until September 1944. At that point, they went into hiding with Slovak peasants to avoid deportation to Auschwitz. Villiam, his sister, and his parents survived the…

-
Eva Brust Cooper describes hiding after her family received protective papers from Raoul Wallenberg
Oral HistoryEva was little affected by the war until 1944, when the Germans occupied Budapest. Eva's father was prominent in the Jewish community, and the family was able to retain their apartment in a Jewish star house (a house designated for Jews). In October Eva's parents secured protective papers from Raoul Wallenberg, but the family decided not to stay in a Swedish safe house. They hid in and near Budapest until the Soviet liberation of Budapest in 1945.

-
Barbara Ledermann Rodbell describes false papers and moving people to hiding places
Oral HistoryIn 1933 Barbara's family moved to Amsterdam, in the Netherlands. They became friends of Anne Frank and her family. The Germans invaded the Netherlands in 1940. Barbara's boyfriend, Manfred, had underground contacts and she got false papers. Her mother, sister, and father were deported to the Westerbork camp and then to Auschwitz. Barbara survived using her false papers and worked for the resistance. She helped take Jews to hiding places and also hid Jews in an apartment rented under her false name.

-
Alisa (Lisa) Nussbaum Derman describes going into hiding in June 1942 during roundups in the Slonim ghetto
Oral HistoryLisa was one of three children born to a religious Jewish family. Following the German occupation of her hometown in 1939, Lisa and her family moved first to Augustow and then to Slonim (in Soviet-occupied eastern Poland). German troops captured Slonim in June 1941, during the invasion of the Soviet Union. In Slonim, the Germans established a ghetto which existed from 1941 to 1942. Lisa eventually escaped from Slonim, and went first to Grodno and then to Vilna, where she joined the resistance movement. She…

-
Abraham Lewent describes hiding during a raid in which his mother and sisters were seized for deportation from Warsaw to Treblinka
Oral HistoryLike other Jews, the Lewents were confined to the Warsaw ghetto. In 1942, as Abraham hid in a crawl space, the Germans seized his mother and sisters in a raid. They perished. He was deployed for forced labor nearby, but escaped to return to his father in the ghetto. In 1943, the two were deported to Majdanek, where Abraham's father died. Abraham later was sent to Skarzysko, Buchenwald, Schlieben, Bisingen, and Dachau. US troops liberated Abraham as the Germans evacuated prisoners.

-
David Levine describes hiding his two-year-old nephew during a roundup of children in the Kovno ghetto
Oral HistoryDavid was born to a middle class Jewish family and attended a Jewish school. In August 1941, after the Germans occupied Kovno, he was forced into the Kovno ghetto, where he shared two rooms with his immediate and extended family. Many members of his extended family were killed during the Great Aktion in Kovno in October 1941. David worked in a forced-labor brigade in the ghetto. In March 1944, he witnessed the Kinder Aktion and was able to save his nephew. During the destruction of the Kovno ghetto, David…

-
Hidden Children: Daily Life
ArticleSome Jewish children survived the Holocaust by hiding or living under disguised identities. Learn more about their experiences while in hiding.

-
Hidden Children: Hardships
ArticleParents, children, and rescuers faced daunting challenges once the decision was made for a child to go into hiding during the Holocaust.

-
Documentation for a false identity
PhotoDocument issued by the Regional Agricultural Mercantile Cooperative in Busko-Zdroj certifying that Bronislawa Tymejko (the false identity of Sophie Schwarzwald's mother, Laura Schwarzwald) was employed by the cooperative, dated November 1942.

-
Hidden Children: Quest for Family
ArticleAfter the Holocaust, many Jewish parents spent months or years searching for the children they had sent into hiding. Learn about the search for surviving relatives.

