<< Previous | Displaying results 6501-6550 of 6720 for "" | Next >>
-
Franklin D. Roosevelt Elected President of the United States
Timeline EventNovember 8, 1932. On this date, Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected as the 32nd President of the United States.

-
Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Timeline EventJune 28, 1914. On this date, Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated in Sarajevo, Yugoslavia, precipitating WWI.

-
Battle of the Somme
Timeline EventJuly 1, 1916. On this date, the most causalities in a single day during World War I occurred at the Battle of Somme.

-
The Armenian Genocide
Timeline EventApril 24, 1915. On this date, Ottoman authorities rounded up 240 Armenian leaders in Constantinople, an event commemorated today by Armenians as the beginning of the genocide.

-
Kristallnacht
Timeline EventNovember 9, 1938. On this date, the Nazi regime coordinated a wave of antisemitic violence in Nazi Germany. This became known as Kristallnacht or the "Night of Broken Glass."

-
Establishment of Dachau Camp
Timeline EventMarch 22, 1933. On this date, the SS established the Dachau concentration camp in Germany.

-
Adolf Hitler Appointed Chancellor
Timeline EventJanuary 30, 1933. On this date, Adolf Hitler was appointed as Chancellor of Germany and the Nazi Party assumed control.

-
Anti-Jewish Boycott
Timeline EventApril 1, 1933. On this date, the Nazi Party and its affiliates organized a nationwide boycott of Jewish-owned businesses in Germany.

-
Book Burning
Timeline EventMay 10, 1933. On this date, books deemed "un-German" are publicly burned throughout Germany.

-
Olympic Games Open in Berlin
Timeline EventAugust 1, 1936. On this date, the Summer Olympics opened in Berlin while the Nazis camouflaged their racist and antisemitic policies.

-
Nuremberg Race Laws
Timeline EventSeptember 15, 1935. On this date, the Nazi government passed the Nuremberg Race Laws, making Jews legally different from their non-Jewish neighbors.

-
Buchenwald Concentration Camp Opens
Timeline EventJuly 15, 1937. On this date, SS authorities opened the Buchenwald concentration camp in Germany.

-
Law Limits Jews in Public Schools
Timeline EventApril 25, 1933. On this date, the German government issued the Law against Overcrowding in Schools and Universities, limiting the amount of Jewish students.

-
Reichstag Fire Decree
Timeline EventFebruary 28, 1933. On this date, President Hindenburg issued the Decree for the Protection of People and the Reich, also known as the Reichstag Fire Decree.

-
First Kindertransport Arrives in Great Britain
Timeline EventDecember 2, 1938. On this date, the first Kindertransport of German Jewish children arrived in Great Britain.

-
Exclusion of Jews from German Economic Life
Timeline EventNovember 12, 1938. On this date, the German government issued the Decree on the Elimination of the Jews from the Economic Life.

-
Law on Alteration of Family and Personal Names
Timeline EventAugust 17, 1938. On this date, the German government issued the Executive Order on the Law on the Alteration of Family and Personal Names.

-
German Jews' Passports Declared Invalid
Timeline EventOctober 5, 1938. On this date, the Reich Ministry of the Interior invalidated all German Jews' passports and required them to have a "J" stamped on them.

-
Antisemitic Exhibition Opens in Munich
Timeline EventNovember 8, 1937. On this date, Josef Goebbels and Julius Streitcher open an antisemitic exhibit named "Der Ewige Jude."

-
American Student Reflects
Timeline EventNovember 11, 1938. On this date, Robert Harlan wrote about what he witnessed during Kristallnacht.

-
Helen Baker Diary Entry
Timeline EventMarch 14, 1938. On this date, Helen Baker documented what she witnessed when Germany annexed Austria. Helen and her husband Ross Baker were Americans living in Vienna.

-
German Annexation of Austria
Timeline EventMarch 11-13, 1938. On this date, German troops invaded and incorporated Austria into the German Reich. This event is known as the Anschluss.

-
Evian Conference
Timeline EventJuly 6-15, 1938. On this date, delegates from 32 countries attended the Evian Conference in France to discuss the growing refugee crisis.

-
Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service
Timeline EventApril 7, 1933. On this date, the German government issued the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service excluding Jews from civil service.

-
Law for the "Prevention of Offspring with Hereditary Diseases"
Timeline EventJuly 14, 1933. On this date, the German government passed the Law for the Prevention of Offspring with Hereditary Diseases.

-
Central Organization of German Jews Formed
Timeline EventSeptember 17, 1933. On this date, a central organization of German Jews was created to signify a unified response against Nazi persecution.

-
Editors Law
Timeline EventOctober 4, 1933. On this date, the German government enacted the Editors Law which forbade "non-Aryans" to work in journalism.

-
Law against "Dangerous Habitual Criminals"
Timeline EventNovember 24, 1933. On this date, the German government issued the Law against the Dangerous Habitual Criminals, allowing indefinite imprisonment.
-
Death of German President von Hindenburg
Timeline EventAugust 2, 1934. On this date, Adolf Hitler became President of Germany after Paul von Hindenburg's death.

-
Hitler Abolishes the Office of President
Timeline EventAugust 19, 1934. On this date, Hitler abolished the office of President and declares himself as Führer, thus becoming the absolute dictator of Germany.

-
Revision of Paragraph 175
Timeline EventJune 28, 1935. On this date, the German government revised Paragraphs 175 and 175a, facilitating the persecution of gay men and men accused of homosexuality.

-
Ban on Jehovah's Witness Organizations
Timeline EventApril 1, 1935. On this date, the German government banned all Jehovah's Witness organizations.

-
Anti-Jewish Laws in Hungary
Timeline EventMay 29, 1938. On this date, Hungary adopted comprehensive anti-Jewish laws, excluding many Jews from professional work.

-
Munich Agreement
Timeline EventSeptember 29-30, 1938. On this date, Germany, Italy, Great Britain, and France signed the Munich agreement, giving Germany the Sudetenland.

-
Jesse Owens Competes in Olympic Games
Timeline EventAugust 3, 1936. On this date, Jesse Owens won a gold medal in the 100-meter dash at the 1936 Olympic Games in Berlin.

-
United States Declares War on Japan
Timeline EventDecember 8, 1941. On this date, Franklin D. Roosevelt asked the US Congress to declare war on Japan following the attack on Pearl Harbor.

-
Warsaw Ghetto Sealed
Timeline EventNovember 15, 1940. On this date, German authorities ordered the Warsaw ghetto to be sealed.

-
Killing Operations Begin at Chelmno
Timeline EventDecember 8, 1941. On this date, killing operations began at the Chelmno killing center.
-
Reichstag Speech
Timeline EventJanuary 30, 1939. On this date, Adolf Hitler declared that the outbreak of war would mean the end of European Jewry.

-
Theresienstadt Camp-Ghetto Established
Timeline EventNovember 24, 1941. On this date, German authorities established the camp-ghetto Theresienstadt in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.

-
Auschwitz Camp Established
Timeline EventMay 20, 1940. On this date, SS authorities established the Auschwitz concentration camp complex.

-
Jewish Badge
Timeline EventSeptember 1, 1941. On this date, Reinhard Heydrich declared that all Jews aged 6 and over in the Third Reich must wear a yellow Star of David.

-
Occupation of Kyiv
Timeline EventSeptember 19, 1941. On this date, German forces entered Kyiv in Soviet Ukraine.

-
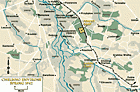
Hidden History: Establishment of the Kovno Ghetto
Timeline EventJuly 10-August 15, 1941. On this date, people confined to the Kovno ghetto created a secret archive to record their experiences.

-
St. Louis Sets Sail
Timeline EventMay 13, 1939. On this date, the German transatlantic liner St. Louis left Hamburg, Germany for Havana, Cuba.

-
Soviet Prisoners of War in Minsk
Timeline EventAugust 15, 1941. On this date, Heinrich Himmler inspected Soviet prisoners of war at a Nazi camp in Minsk, Belarus.

-
Attack on Pearl Harbor
Timeline EventDecember 7, 1941. On this date, Japan attacked the United States Pacific fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii.

-
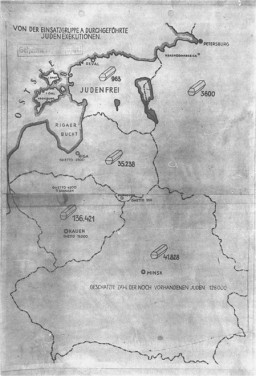
Stahlecker Report
Timeline EventOctober 15, 1941. On this date, Walter Stahlecker submitted a report on the killing of Jewish civilians in the northwestern Soviet Union.
-
Krakow Ghetto Established
Timeline EventMarch 3-20, 1941. During these dates, German authorities announced, established, and sealed the Krakow ghetto.

-
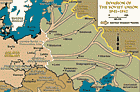
Operation Barbarossa
Timeline EventJune 22, 1941. On this date, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in "Operation Barbarossa," its largest military operation during WWII.