<< Previous | Displaying results 701-750 of 6707 for "" | Next >>
-
Pamphlet outlining the National Socialist Party 25-point Program
ArtifactIn the 25-point program, Nazi Party members publicly declared their intention to segregate Jews from "Aryan" society and to abrogate Jews' political, legal, and civil rights. Germany, 1931.

-
Warsaw district handbill announcing penalties for anyone caught assisting Jews
ArtifactOn September 5, 1942, the SS and Police Leader of the Warsaw District issued this announcement threatening the death penalty for anyone who aided Jews who had left the ghetto without authorization. This poster was put up in the wake of the mass deportation of Jews from the Warsaw ghetto to the Treblinka killing center in summer 1942. SS officials were well aware that thousands of Jews had fled the ghetto to go into hiding and urged people to turn them in. The poster reminds the city's non-Jewish…

-
Postcard sent to Ruth Segal (front)
DocumentA postcard sent to Ruth Segal (Rys Berkowicz) care of the Jewish Community (JewCom) in Kobe, Japan. Family and friends in German-occupied Warsaw, Poland, sent the postcard on June 20, 1941. It bears stamps both from the Jewish council (Judenrat) in the Warsaw ghetto and from German censors. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Aaron A. Eiferman Letter: Page 1
DocumentFirst page of a letter from a US soldier describing "the living dead" and conditions his unit encountered in a subcamp of Dachau in April 1945.

-
Radiogram from Moritz Schoenberger on the "St. Louis"
DocumentOn May 25, 1939, artist Moritz Schoenberger sent this radiogram (a telegram sent by radio) from the ocean liner "St. Louis" during the voyage from Hamburg, Germany, to Havana, Cuba. On this voyage, the "St. Louis" carried over 900 Jewish refugees fleeing Nazi persecution. The telegram reads, in part, "Physically and spiritually recovered and invigorated most confident about reaching Havana Saturday. Money received. Many thanks. Kisses. Papa." Schoenberger's optimism proved unfounded. Cuban authorities…

-
Newspaper article "The Refugee Tragedy"
DocumentSan Francisco Chronicle newspaper article titled "The Refugee Tragedy." The article was based on an interview with Moses Beckelman of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee, an aid organization. It discussed the overcrowding of Polish and Lithuanian refugees stranded in Shanghai, Kobe (Japan), and Lisbon (Portugal), all stops en route to North and South America. The primary cause of this bottleneck was a lack of transit and entry visas, a result of most countries closing their borders to…

-
Notice of Gregor Wohlfahrt's execution
DocumentAuthorities in Berlin, Germany, sent this notice to Barbara Wohlfahrt, informing her of her husband Gregor's execution on the morning of December 7, 1939. Although he was physically unfit to serve in the armed forces, the Nazis tried Wohlfahrt for his religious opposition to military service. As a Jehovah's Witness, Wohlfahrt believed that military service violated the biblical commandment not to kill. On November 8, 1939, a military court condemned Wohlfahrt to beheading, a sentence carried out one month…

-
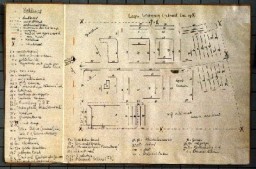
Hand-drawn plan of Westerbork transit camp
DocumentThe Dutch government established a camp at Westerbork to intern Jewish refugees who had entered the Netherlands illegally. This sketch of the Westerbork transit camp was made by a Jewish inmate who was able to emigrate to the United States. In early 1942, the German occupation authorities decided to enlarge Westerbork and convert it into a transit camp for Jews. The systematic concentration of Jews from the Netherlands in Westerbork began in July 1942. From Westerbork, Jews were deported to the killing…
-
German passport Issued to Erna "Sara" Schlesinger (inside)
DocumentGerman police authorities issued this passport to Erna "Sara" Schlesinger on July 8, 1939, in Berlin. This first page of the passport illustrates the German laws that facilitated the identification of Jews in Germany. From 1938, German regulations required that Jewish women with a first name of "non-Jewish" origin use the middle name "Sara" on all official documents. Jewish men had to add the name "Israel". The letter "J" (standing for "Jude," that is, the word "Jew" in German) was stamped in red on the…

-
German passport issued to Alice "Sara" Mayer (inside)
DocumentA German passport issued to Alice Mayer on February 24, 1939, in Bingen, Germany. Mayer's daughter, Ellen, is also listed on the passport. Both mother and daughter's names include the middle name "Sara." This middle name became a mandatory addition required by a law of August 17, 1938. Thereafter, all Jewish women in Germany with a first name of "non-Jewish" origin had to add "Sara" as a middle name on all official documents. Jewish men had to add the name "Israel". This enabled German officials to…

-
Simone Weil's kindergarten teacher certification
DocumentSimone Weil earned this diploma, which certified her to teach kindergarten in France, from the School of Social Work in Strasbourg in 1940. Weil assumed a false identity in late 1943 to facilitate her resistance activities as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE). Among the papers documenting Weil's new identity was a forged version of this diploma bearing the name "Simone Werlin".

-
Teacher certification forged for Simone Weil
DocumentSimone Weil used this forged diploma and other false papers to document a new identity assumed in late 1943. As Simone Werlin, she could avoid arrest and change residence to facilitate her rescue of Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE). Weil had earned the diploma, which certified her to teach kindergarten in France, from the School of Social Work in Strasbourg in 1940. The director of the school willingly forged this…

-
Documentation for a false identity: Simone Weil
DocumentSimone Weil kept this blank identification card bearing her picture in case her cover as "Simone Werlin" were blown and she needed to establish a new false identity. Both resistance workers and sympathetic government employees provided her the necessary stamps and signatures. Such forged documents assisted Weil in her work rescuing Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE).

-
Simone Weil's falsified student card
DocumentAfter adopting a new identity in late 1943, Simone Weil falsified her student card from the year 1938-1939 to bear her assumed name, Simone Werlin. The card verified enrollment in the School of Social Work in Strasbourg. Using forged and falsified documents, Weil was able to move to Chateauroux, France, and establish an operation to rescue Jewish children as a member of the relief and rescue organization Oeuvre de Secours aux Enfants (Children's Aid Society; OSE).

-
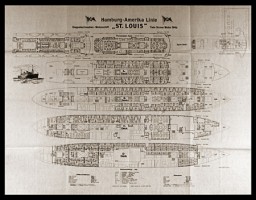
Plan of the "St. Louis"
DocumentPlan of the two-propeller passenger liner the "St. Louis," showing cabins and room numbers. In 1939, this German ocean liner carried almost 1,000 Jewish refugees seeking temporary refuge in Cuba. It was forced to return to Europe after Cuba and then the United States refused to allow the refugees entry.
-
Permit for stay in Japan
DocumentMost Polish Jewish refugees stayed in Japan much longer than their 10-day transit visas allowed. Many feared the day when Japanese authorities would no longer extend their stay with permits like the one shown here. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Permit for stay in Japan
DocumentJapanese authorities issued this "Permit for stay in Japan" to Ruth Segal (Rys Berkowicz). After several unsuccessful attempts to obtain visas for the United States, Ruth's father was able to secure a visa for her to go to New Zealand, in the British Commonwealth of Nations. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Postcard sent to Ruth Segal (back)
DocumentFamily and friends of Ruth Segal (Rys Berkowicz) sent this postcard to her in Kobe, Japan. They sent the postcard from Warsaw, in German-occupied Poland, on June 20, 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Swedish protective document
DocumentProtective document issued to a Jewish woman by the Swedish embassy in Budapest, Hungary, in 1944. Such documents protected the bearer from immediate deportation by the Germans to the Auschwitz killing center in occupied Poland. The "W" in the lower left corner indicates that Raoul Wallenberg initialed the document.

-
Second telegram from the Chief Rabbi of Vilna asking for aid
DocumentA second RCA Radiogram telegram from Rabbi Grodzenski, Chief Rabbi of Vilna, to the Central Relief Committee in New York. He requests aid for refugees who have gathered in Vilna. The telegram says that more than 1,600 yeshiva students and their families from over 10 cities throughout Poland have fled to Vilna, where they remain in terrible living conditions. November 5, 1939. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Certificate of Polish citizenship (inside)
DocumentMany refugees had difficulties replacing lost or invalidated personal identification documents. The certificate of Polish citizenship shown here was valid in place of a passport. A Polish Jewish refugee used this certificate to travel legally from Lithuania, through the Soviet Union, to Japan. It contains the Curacao notation needed to obtain Soviet and Japanese visas. The bearer of this certificate aimed to reach Palestine, but ended up spending most of the war in Calcutta, India, part of the British…

-
Page 2 of passport issued to Setty Sondheimer
DocumentSetty and Moritz Sondheimer and their two children fled Nazi Germany for Kovno, Lithuania, in 1934. There, Moritz opened a small factory manufacturing buttons and combs. This image shows page 2, containing an identification photograph, of a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer by the German Consulate in Kovno on January 29, 1938. With aid from Japanese diplomat Chiune Sugihara in obtaining Japanese transit visas, Setty and her family emigrated from Kovno in February 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition…

-
Page 5 of passport issued to Setty Sondheimer
DocumentPage 5 of a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer by the German Consulate in Kovno on January 29, 1938. This page contains three visas: (1) visa for Kovno valid from August 27, 1940, until December 31, 1940 (2) a second visa for Kovno valid until June 30, 1941, and (3) first visa for Yokohama, Japan, valid from June 7, 1941, until June 30, 1942. Unable to emigrate from Japan, Setty remained there until she was able to emigrate to the United States in 1947. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and…

-
Page 12 of passport issued to Setty Sondheimer
DocumentTransit visa in a passport issued to Setty Sondheimer, a German citizen. This visa, issued on August 6, 1940, enabled her to travel through Japan en route to Surinam, Curacao, or other Dutch colonies in the Americas. These plans were disrupted when travel across the Pacific Ocean was forbidden following U.S. entry into World War II. Setty remained in Japan until she was able to emigrate to the United States in 1947. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Suitcase label for Trans-Siberian Express
DocumentThe Soviet travel agency Intourist issued this type of luggage tag, showing a route map, to passengers on the Trans-Siberian Express. Some Jewish refugees traveled on the Trans-Siberian Express as they fled eastward. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Postcard of Moscow
DocumentA Jewish refugee purchased this postcard of the Lenin Library during a stopover in Moscow. Soviet Union, 1940-1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Trans-Siberian Railroad ticket
DocumentA train ticket for travel on the Trans-Siberian Railroad. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Intourist service voucher for the Trans-Siberian Railroad
DocumentVoucher for travel on the Trans-Siberian Railroad purchased at the "Intourist Travel Company of the USSR" in England for Joseph and Ruth Schaffer. Thousands of Jewish refugees fled Nazi Europe on the Trans-Siberian Railroad through the Soviet Union to Japan with the help of Japanese visas provided by Japanese diplomat Chiune Sugihara. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Receipt for items confiscated from Moshe Zupnik
DocumentSoviet authorities issued this receipt, in Russian, to Moshe Zupnik for the rubles they confiscated from him before he left the Soviet Union. Soviet authorities routinely confiscated most rubles and other valuables from Jewish refugees before they boarded steamers bound for Japan and left the Soviet Union. Vladivostok, Soviet Union, January 22, 1941. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Page 17 of passport issued to Setty Sondheimer
DocumentA page in a passport belonging to Setty Sondheimer containing stamps from Ecuador. These stamps are marked in red with the word "Anulado," the Spanish word for "canceled." The stamps were canceled when Setty's visa for Ecuador expired because she was unable to travel across the Pacific due to fighting in that theater. Setty remained in Japan for the duration of the war and emigrated to the United States in 1947. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Proclamation of restricted zone in Shanghai for refugees
DocumentProclamation issued on February 18, 1943, by the Imperial Japanese Army and Nazy authorities establishing, for reasons of "military necessity," a "designated area" for "stateless refugees" in the Hongkew area of the International Settlement. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Polish-language newspaper for refugees in Shanghai
DocumentPolish-language newspaper for refugees in Shanghai: Wiadomosci, "News for War Refugees in Shanghai." [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
American propaganda announcement
DocumentAnnouncement dropped by American planes on Shanghai near the end of the war. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Our Life newspaper: Allied victory
DocumentNewspaper Our Life, for September 7, 1945, showing the headline "Long Live Allied Victory". [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Yiddishe Shtime, December 1945
DocumentYiddishe Shtime fun Vaytn Mizrekh (Jewish Voice of the Far East), Shanghai, December 1945. Includes black border notice of 5,700,000 Jewish victims. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
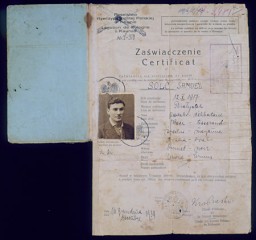
Polish citizenship certificate issued to Samuel Solc
DocumentPolish citizenship certificate issued to Samuel Solc on December 16, 1939, by the Britannic Majesty's Legation in Kovno, charged with representing Polish interests in Lithuania. Samuel decided to emigrate to Palestine in late 1939. His journey lasted over two years and took him through eight countries. Samuel arrived in Palestine on February 6, 1942, after stays in Lithuania; Kobe, Japan; Shanghai, China; and Bombay, India. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]
-
Polish citizenship certificate issued to Samuel Solc
DocumentThis page of a Polish citizenship certificate issued to Samuel Solc contains two visas. The first (left), stamped by the British Passport control in Shanghai, allowed Samuel to travel to Palestine via Burma, India, Egypt, and Rangoon. The second visa (right) bears the British Mandate "Government of Palestine" stamp, dated February 6, 1942, and allowed Samuel to remain in Palestine permanently. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
Lithuanian safe conduct pass (reverse)
DocumentA Lithuanian safe conduct pass bearing a stamp for transit through Japan (from Chiune Sugihara), two Soviet transit visas, a Lithuanian stamp, a U.S. non-immigrant visa, and a U.S. entry stamp from Seattle, Washington. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
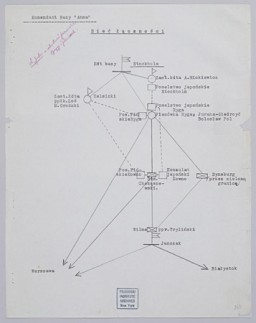
"Web of Communications" chart, July 1940
DocumentDiagram showing "the web of communications" between Japanese diplomats and members of the Polish resistance in the Baltic states and Scandinavia. The "Konsulat japonski Kowno" refers to Sugihara. Despite its ties with Nazi Germany, Japan pursued its own course in foreign policy. After the Germans occupied Poland and the Netherlands, Japan continued relations with both the Polish and Dutch governments-in-exile in London. July 1940.
-
Anti-Nazi Cartoon
DocumentThis cartoon, “The Modern Mercury” by Jerry Doyle, appeared in The Philadelphia Record, December 7, 1935. The faded large figure in the background bears the label “Olympics ideals of sportsmanship and international good will.” The image of Hitler in the foreground bears the words “1936 Olympics,” “Intolerance and discrimination,” and “Nazism.”

-

-

-

-
Document Belonging to Chief Prosecutor Benjamin Ferencz
DocumentOne page of a document belonging to Chief Prosecutor Benjamin Ferencz listing the defendants in the Einsatzgruppen Case along with their position and crimes, line of defense, counts against them, and sentence.

-
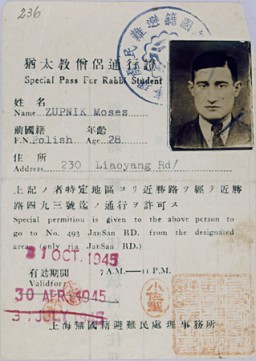
Pass issued to rabbinical student Moshe Zupnik
DocumentSpecial pass issued to rabbinical student Moshe Zupnik. Yeshiva students had to obtain special passes from Japanese authorities to leave the "designated area" in order to continue their studies at the Beth Aharon Synagogue, which was located outside the zone. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]
-
Pass for rabbinical student Chaim Gorfinkel
DocumentSpecial pass issued to rabbinical student Chaim Gorfinkel. Yeshiva students had to obtain special passes from Japanese authorities to leave the "designated area" in order to continue their studies at the Beth Aharon Synagogue, which was located outside the zone. [From the USHMM special exhibition Flight and Rescue.]

-
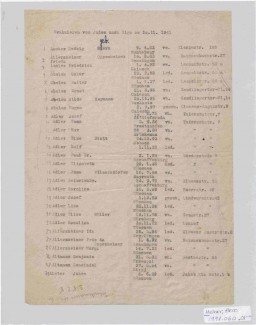
Listing of Jews for deportation to Riga, Latvia
DocumentThe SS compiled lists of Jews who were to be deported to ghettos, concentration camps, and killing centers. This document provides the names, birthdates, marital status, and addresses of Jews who were “evacuated” on November 20, 1941 from Germany to the Riga ghetto in German-occupied Latvia.
-
Census Card
DocumentOn December 17, 1941, the Romanian government issued a decree requiring a census of all those with "Jewish blood.” All persons having one or two Jewish parents or two Jewish grandparents were ordered to register at the Central Jewish Office. This is a census certificate issued by that office in 1942.

-
Census Card
DocumentOn December 17, 1941, the Romanian government issued a decree requiring a census of all those with “Jewish blood.” All persons having one or two Jewish parents or two Jewish grandparents were ordered to register at the Central Jewish Office. This is a census certificate issued by that office in 1942.

-
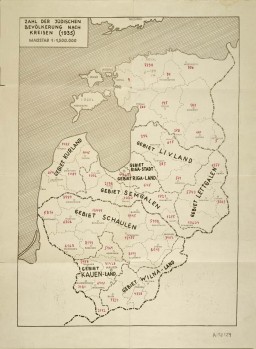
German Map of the Baltic Countries
DocumentThis German map indicates the number and distribution of Jews living in the Baltic countries as of 1935. It served as a reference for the SS mobile killing squad assigned to carry out the mass murder of the Jews there.