![A transport of Jewish prisoners marches through the snow from the Bauschovitz train station to Theresienstadt. [LCID: 69720]](https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/images/large/781755a6-1ba5-4d8e-8b2b-9f25bdf3687f.jpg)
Browse an alphabetical list of articles about the Holocaust and World War II. Learn more about topics such as the Nazi rise to power, how and why the Holocaust happened, life in Nazi camps and ghettos, and the postwar trials.
<< Previous | Displaying results 1051-1069 of 1225 for "Article" | Next >>
The July 20, 1944, plot was a failed attempt to assassinate Adolf Hitler. Learn more about the July 20 plot, including some of the motivations of the participants.

On July 1, 1941, a mob attacked Jews in the German-occupied city of Lwów, Poland. At least several hundred Jews were murdered and more were wounded. Learn about the Lwów pogrom.

Soon after Hitler came to power, debates began outside Germany about taking part in Olympics hosted by the Nazi regime. Learn more about calls to boycott the Games.

At the beginning of WWII, people with mental or physical disabilities were targeted for murder in what the Nazis called the T-4, or "euthanasia," program.

The 1936 Olympics in Berlin were more than just a worldwide sporting event. They also showcased the power of propaganda under Adolf Hitler’s Nazi dictatorship.

African American athletes, facing racism at home, also debated whether to join or boycott the 1936 Olympic games in Germany, then under a racist dictatorship. Learn more.

The 1936 Olympics were the first to employ the torch relay. Learn more about this new ritual, Nazi propaganda, and the Olympic Games in Berlin, Germany.

On November 9–10, 1938, the Nazi regime coordinated a wave of antisemitic violence in Nazi Germany. This became known as Kristallnacht or the "Night of Broken Glass."

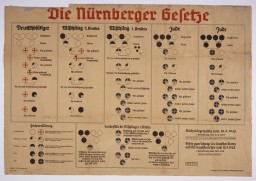
The Nazi regime’s Nuremberg Race Laws of September 1935 made Jews legally different from their non-Jewish neighbors. The laws were the foundation for future antisemitic measures .
The Weimar Republic existed in Germany from 1918-1933. Learn more about German police during that time.

In the spring of 1939, Gilbert and Eleanor Kraus rescued 50 Jewish children from Vienna, Austria, by bringing them to the United States. Learn about their mission.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of academics and teachers.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of business elites.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of civil servants.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of doctors and nurses.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of German clergy and church leaders.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of the German police.

To implement their policies, the Nazis had help from individuals across Europe, including professionals in many fields. Learn about the role of the military.

From April to July 1994, extremist leaders of Rwanda’s Hutu majority directed a genocide against the country’s Tutsi minority. Learn more

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.