<< Previous | Displaying results 6451-6500 of 6773 for "" | Next >>
September 19, 1941. On this date, German forces entered Kyiv in Soviet Ukraine.

July 10-August 15, 1941. On this date, people confined to the Kovno ghetto created a secret archive to record their experiences.

May 13, 1939. On this date, the German transatlantic liner St. Louis left Hamburg, Germany for Havana, Cuba.

August 15, 1941. On this date, Heinrich Himmler inspected Soviet prisoners of war at a Nazi camp in Minsk, Belarus.

December 7, 1941. On this date, Japan attacked the United States Pacific fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii.

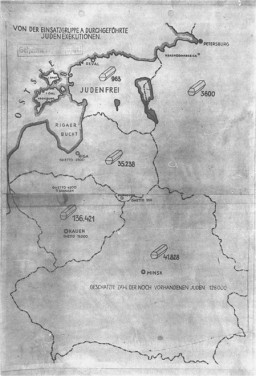
October 15, 1941. On this date, Walter Stahlecker submitted a report on the killing of Jewish civilians in the northwestern Soviet Union.
March 3-20, 1941. During these dates, German authorities announced, established, and sealed the Krakow ghetto.

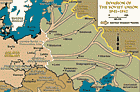
June 22, 1941. On this date, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in "Operation Barbarossa," its largest military operation during WWII.
August 24, 1941. On this date, Adolf Hitler ordered the cessation of centrally coordinated "euthanasia" killings due to public protests.

October 15, 1941. On this date, German authorities began the deportation of Jews from central Europe to ghettos in occupied eastern territory..
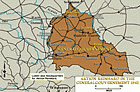
October 15, 1941. On this date, Heinrich Himmler tasks SS Gen. Odilo Globocnik with implementing "Operation Reinhard."
August 21, 1940. On this date, Samuel Soltz's visa was stamped by Chiune Sugihara, the Japanese consul to Lithuania.

November 25, 1940. On this date, Egon Weiss survived the explosion of the SS Patria, which was carrying 1,800 Jewish refugees.

February 9, 1939. On this date, the Wagner-Rogers bill was introduced, ultimately unsuccessfully, to permit the entry of 20,000 European refugee children into the United States.
August 15, 1941. On this date, German authorities sealed approximately 30,000 Jews in the Kovno ghetto in Lithuania.

August 20, 1941. On this date, German authorities opened the Drancy internment and transit camp in France.

October 29, 1941. On this date, German SS and police and Lithuanian police murdered 9,200 residents of the Kovno ghetto in Fort IX, Lithuania.

April 4, 1945. On this date, US troops liberated Ohrdruf, a subcamp of Buchenwald concentration camp.

June 6, 1944. On this date, US, British, and Canadian troops land on the beaches of Normandy, France.

April 11, 1945. On this date, Buchenwald prisoners stormed the watchtower and seized control of the camp. US forces liberated the camp the same day.

September 5, 1942. On this date, Germans issued this poster announcing the death penalty for anyone found aiding Jews who fled the Warsaw ghetto.

April 13, 1945. On this date, Otto Wolf, a teen diarist who chronicled his family's experience in hiding, wrote his last diary entry before his death.

April 17, 1945. On this date, Felicitas Wolf wrote her first entry in her brother Otto's diary after his disappearance.

January 20, 1942. On this date, Reinhard Heydrich presented plans for the "Final Solution to the Jewish Question" at the Wannsee Conference.

January 16, 1942. On this date, German authorities began the deportations of Jews and Roma from the Lodz ghetto to the Chelmno killing center.

November 20, 1945. On this date, the International Military Tribunal in Nuremberg, Germany, began the trials of 21 major Nazi leaders.

April 6, 1994. On the date, the Rwandan Genocide began when a plane carrying Rwandan President Juvenal Habyarimana was shot down.

October 23, 2000. On this date, the Rwandan "Media Trial" began, prosecuting members of media involved in the 1994 Rwanda genocide.
November 8, 1994. On this date, the United Nations established the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ITCR) in Arusha, Tanzania.

July 11, 1995. On this date, the Srebrenica massacre began. Bosnian Serb forces captured the town and killed approximately 8,000 Bosnian Muslims.

May 25, 1993. On this date, the United Nations Security Council created the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia (ITCY).
November 21, 1995. On this date, the three-year civil war in Bosnia-Herzegovina ended with a peace agreement negotiated in Dayton, Ohio.
April 22, 1993. On this date, dedication ceremonies for the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum take place.

December 15, 1961. On this date, Adolf Eichmann was found guilty of crimes against the Jewish people and sentenced to death.

June 25, 1948. On this date, the US Congress passed the Displaced Persons Act. This allowed approximately 400,000 displaced persons to immigrate to the US.

November 3, 1918. On this day, German sailors in Kiel revolt, and protests against World War I spread.

February 23, 1930. On this date, Nazi stormtrooper Horst Wessel dies after being shot and becomes a martyr in Nazi propaganda.

November 12, 1918. On this date, women gain the right to vote in Germany.

November 11, 1918. On this date, a negotiated ceasefire ends the fighting of World War I when it goes into effect at 11am.

May 12, 1925. On this date, German Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg is inaugurated, becoming the last president of the Weimar Republic.


November 22, 1930. On this date, Nazis attack a leftwing group at a dance hall in Berlin.
December 1935. The Lebensborn program is created at the direction of Heinrich Himmler in order to combat Germany’s falling birth rate.

June 1936. German physician Robert Ritter becomes head of a new eugenics research center focusing on racially classifying Roma and Sinti.

June 6, 1936. On this date, Minister of the Interior for the Reich and Prussia Wilhelm Frick issues a decree on “Combating the Gypsy Plague.”
July 16, 1936. On this date, German authorities order the roundup of Roma and Sinti in Berlin, confining them in a new camp in the Marzahn suburb.

December 08, 1938. On this date, Himmler orders that Nazi Germany’s policies regarding Roma and Sinti should be developed according to Nazi racial principles.

December 16, 1942. On this date, Heinrich Himmler issues an order that Roma and Sinti are to be deported to Auschwitz.
Listen to excerpts from oral testimonies to learn from survivors themselves about their individuals experiences, actions, and choices.
The International Military Tribunal (IMT) opened in Nuremberg within months of Germany’s surrender. Learn about the judges, defendants, charges, and legacies.

We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies, Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation, the Claims Conference, EVZ, and BMF for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of donor acknowledgement.